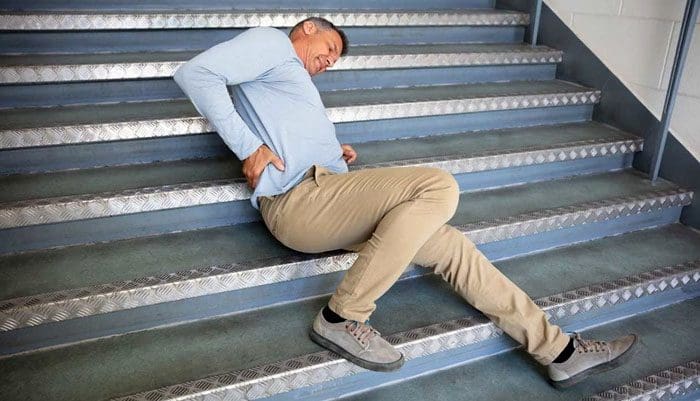
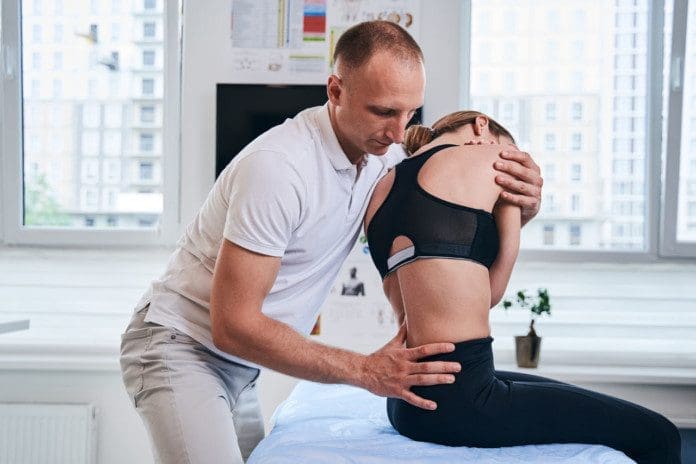
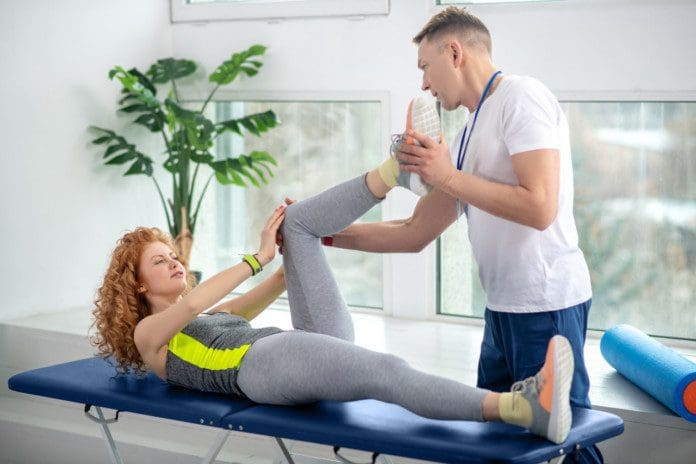
The body is a connected whole and more than just separate parts and regions. When back pain presents, it might not be the back muscles or spine but could be tense, tight hips, and hamstrings causing low back pain. How it happens, how to stretch and loosen up, and target these areas could help alleviate the pain.
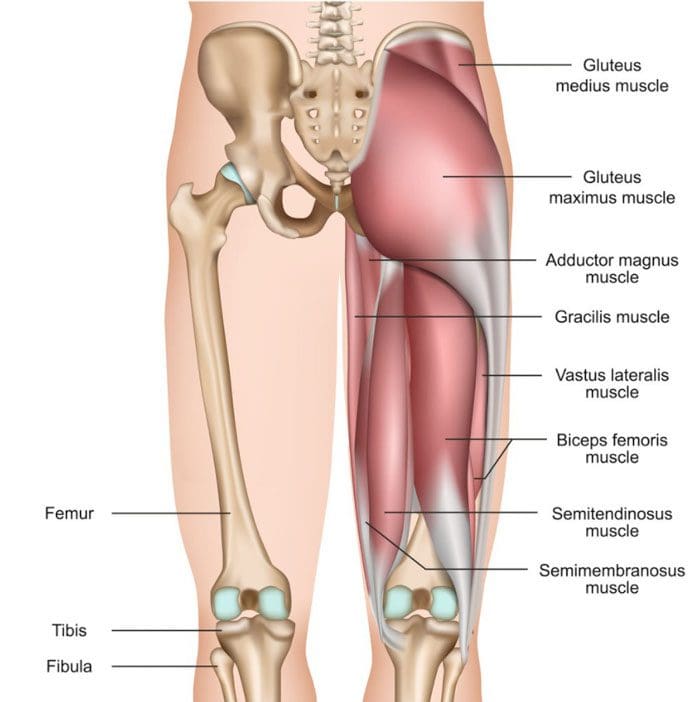
Table of Contents
The Hips and Hamstrings
When the hip flexors and hamstrings become tense, the tightness can alter the pelvic alignment. This affects spinal alignment leading to discomfort and low back pain. The hip flexors are a group of muscles around the front of the hips, and they activate when moving the leg and knee upward. The hamstrings are the muscles in the back of the thighs that allow for flexion of the knees and hip extension. Muscle tightness in the hips and/or hip joint stiffness can also contribute to low back pain. Not being able to rotate, flex, or extend the hip forward or backward can affect:
- Walking
- Running
- Swinging
- Twisting movements
- This increases mechanical strain on the lower back.
Hamstring tightness can be a side effect of:
- Low back pain
- Pelvic positioning
- Muscle guarding
- Weakness
- All can contribute to the hamstrings feeling tight.
Tense Hips and Hamstrings
The factors creating this tightness can come from:
- A sedentary lifestyle
- Little to no physical activity
- Sitting too long with no stretching or movement.
- Injury
- Intense workout
Losing the ability to function through the entire length of motion can also indicate muscle weakness and a lack of joint movement where the joint around the muscle becomes stiff. This can be caused by:
- A lack of movement
- Arthritis
- Age-related changes
Stretching and Treatment
Stretching exercises can be the first line of treatment. It is recommended to start with gentle stretches targeting these areas. What works best for the individual is the stretch they are comfortable repeating enough to make a difference. Warming up the muscles first will generate the best results. An easy place to begin is a gentle forward fold stretch.
- Stand up straight, or sit with the legs extended out in front.
- Then, reach with the fingers toward the toes. Don’t worry if you can’t reach them.
- Don’t bounce.
- Hold the position for a few seconds.
- Repeat five to 10 times.
For the hip flexors, stretches include:
If the stretching does not bring relief, it is recommended to progress to a personalized treatment and stretching program with a chiropractor or physical therapist. Chiropractic and physical therapy can relieve the problems without medication, injections, or surgery and provide lifelong techniques for maintaining optimal flexibility, mobility, and strength. The hands-on treatment loosens and relieves the tense tightness, reinforcing the flexibility and range of motion. Treatment includes:
- Joint mobilization to the hips and spine.
- Soft tissue mobilization.
- A personalized strengthening program with stretches and exercises that target the specific muscles.
- Health coaching.
- Anti-inflammatory diet recommendations.
Body Composition
Monounsaturated Fats
Monounsaturated fat is considered healthy fat. This type of fat makes up a significant component of the Mediterranean diet. Studies have shown monounsaturated fats like extra-virgin olive oil can help prevent adverse events related to cardiovascular disease. A meta-analysis evaluating diets high in monounsaturated fats indicated a significant reduction in:
- Triglycerides
- Bodyweight
- Systolic blood pressure in individuals with type II diabetes.
- A significant increase in HDL or good cholesterol.
Another study showed the protective effects of monounsaturated fatty acids reduced the risk factors associated with metabolic syndrome and cardiovascular disease. Monounsaturated fats can have a positive impact on overall health. Monounsaturated fat sources include:
- Olive, peanut, and canola oil
- Avocados
- Almonds
- Pecans
- Hazelnuts
- Sesame and pumpkin seeds
References
Estruch, Ramón et al. “Retraction and Republication: Primary Prevention of Cardiovascular Disease with a Mediterranean Diet. N Engl J Med 2013;368:1279-90.” The New England journal of medicine vol. 378,25 (2018): 2441-2442. doi:10.1056/NEJMc1806491
Gillingham, Leah G et al. “Dietary monounsaturated fatty acids are protective against metabolic syndrome and cardiovascular disease risk factors.” Lipids vol. 46,3 (2011): 209-28. doi:10.1007/s11745-010-3524-y
American College of Physicians. (February 2017) “American College of Physicians issues guideline for treating non-radicular low back pain” www.acponline.org/acp-newsroom/american-college-of-physicians-issues-guideline-for-treating-nonradicular-low-back-pain
MedlinePlus. (2019) Hip flexor strain – aftercare medlineplus.gov/ency/patientinstructions/000682.htm
NCBI. (2021) Hamstring Injury www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK558936/