Can electrolyte chewing gum help physically active individuals, fitness enthusiasts, and athletes experiencing extreme heat and dehydration?

Table of Contents
Electrolyte Chewing Gum
Electrolyte powder mix and drinks have been marketed as efficient and time-saving for fast-paced lives. Now, electrolytes are in chewing gum form. These gums work by activating salivary glands and making the mouth water. Manufacturers claim the gum’s sour taste makes the mouth water, quenches thirst, and replenishes some electrolytes. Some brands don’t list the percentages or amounts of ingredients, making determining each gum’s electrolyte content difficult. However, electrolyte chewing gum is designed to eliminate feelings of thirst and is not meant to hydrate the body. This can be dangerous because it gives the individual a false sense of hydration. When the thirst mechanism is impaired, an individual may not drink enough fluids, leading to dehydration. The Food and Drug Administration has not studied the effectiveness of electrolyte gum.
Signs The Body Is Not Getting Enough Electrolytes
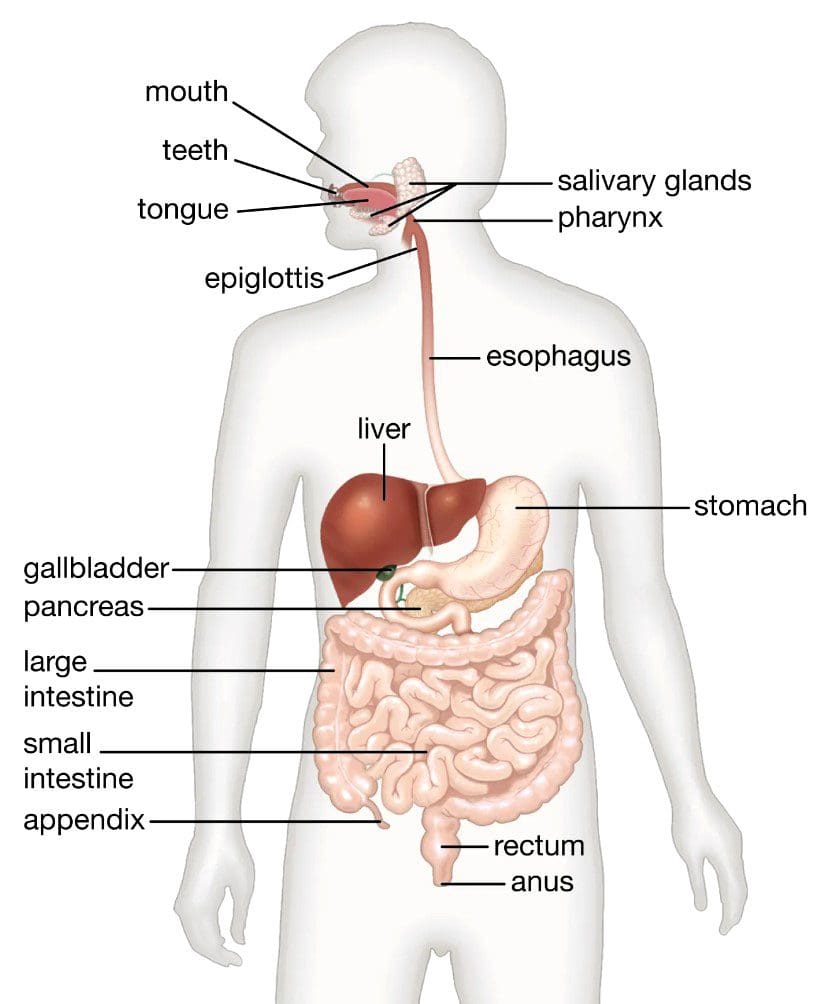
Electrolyte deficiency can result from insufficient fluids or excessive sweating (National Library of Medicine, 2024). Signs that the body is not getting enough electrolytes can vary because the body needs each electrolyte for specific functions. The symptoms can range from neurological symptoms such as headaches and seizures in the case of low sodium to muscle cramps and weakness when there are low potassium levels. (National Library of Medicine, 2023) (National Library of Medicine, 2023) However, individuals can still have electrolyte imbalances even if they do not have symptoms. This is why proper hydration and intake of electrolytes through water and food are important.
Ingredients
The ingredients listed on electrolyte chewing gum include:
- Sugar
- Gum base
- Corn syrup
- Citric acid
- Glycerin
- Natural flavors
- Soy lecithin
- Artificial sweeteners
- Artificial color
- Electrolytes in sodium citrate and potassium citrate
However, gum brands fail to include the percentages of the ingredients, making it hard to figure out the actual electrolyte content. The amount can determine their effectiveness. Given their size, estimates point to very little electrolyte content, possibly around 10 milligrams of sodium per piece, which is insufficient to hydrate the body.
Rehydrating the Body
Food and fluids are reliable sources of electrolytes that the body can absorb. Sources include:
- Fruits like bananas and oranges contain potassium and magnesium.
- Vegetables also contain potassium and magnesium.
- Dairy for calcium.
Electrolyte supplements are generally unnecessary if you eat a balanced diet. However, these products could be useful during exercise, especially for their sodium content (National Library of Medicine, 2024). When exposed to the heat, consider a rehydration solution like sports drinks or making your own. The presence of sugar increases the absorption of sodium by the intestine. Sugar in electrolyte solutions does not add calories; it helps the intestine absorb the sodium faster and holds water in the bloodstream, helping maintain blood pressure. While chewing a piece of electrolyte gum might make it easy to get balanced electrolytes, it is not enough to replenish the body. Individuals who need more electrolytes should talk to their healthcare provider about the best way to meet their body’s needs. They may recommend drinks or powders specially formulated to provide an electrolyte boost.
Injury Medical Chiropractic and Functional Medicine Clinic works with primary healthcare providers and specialists to develop highly effective treatment plans through an integrated approach for each patient and restore health and function to the body through nutrition and wellness, functional medicine, acupuncture, Electroacupuncture, and integrated medicine protocols. If the individual needs other treatment, they will be referred to a clinic or physician best suited for them. Dr. Jimenez has teamed up with top surgeons, clinical specialists, medical researchers, nutritionists, and health coaches to provide the most effective clinical treatments.
Balancing Body and Metabolism
References
National Library of Medicine, MedlinePlus. (2024). Fluid and electrolyte balance. Retrieved from medlineplus.gov/fluidandelectrolytebalance.html
National Library of Medicine, MedlinePlus. (2023). Low blood sodium. Retrieved from medlineplus.gov/ency/article/000394.htm
National Library of Medicine MedlinePlus. (2023). Low blood potassium. Retrieved from medlineplus.gov/ency/article/000479.htm