Table of Contents
Introduction
Everyone wants to be healthier at some point in their lives. Some individuals train to be athletes and must follow procedures to maintain their health. In comparison, others want to get healthier by eating the right food, exercising for at least 30 minutes to an hour, meditating or doing yoga to relieve stress, and maintaining a healthy weight. However, many environmental factors do affect the human body. They can alter how a person looks, weight, levels of physical activity, and how different foods affect the body’s metabolism. When environmental factors start to take hold of a person’s health, it can trigger unwanted issues that affect not only the muscles in the body but the associated internal organs that help provide the functionality to the body. Today’s article focuses on the musculoskeletal system, how different issues affect the musculoskeletal system and associate with other problems in the body, and various treatments to improve musculoskeletal health. We refer patients to certified providers specializing in musculoskeletal therapies that help those with musculoskeletal disorders. We also guide our patients by referring to our associated medical providers based on their examination when it’s appropriate. We find that education is the solution to asking our providers insightful questions. Dr. Alex Jimenez DC provides this information as an educational service only. Disclaimer
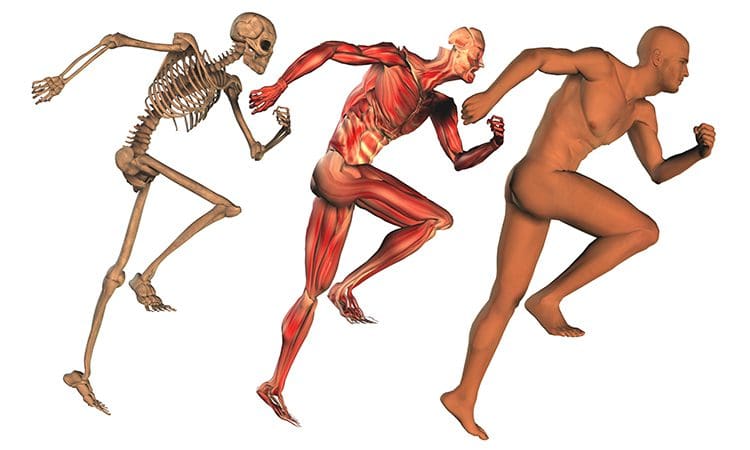
The Musculoskeletal System & Its Function
How does the musculoskeletal system play its role in the human body? The body is considered a complex being that consists of various organs, muscles, tissues, ligaments, and joints that help move a person from one place to another, resting while needed, and doing multiple activities in a casual relationship. Studies reveal that the musculoskeletal system is controlled by the central nervous system that interconnects the motor-sensory function for the body’s ability to move and rest.
The three main muscle groups that make up the musculoskeletal system are:
- Skeletal muscle- Muscle tendons that are connected to the bones
- Cardiac muscle- Muscles associated with the heart
- Smooth muscle- Muscles that line with blood vessels and specific organs (ex. intestines)
Each muscle group provides different functions that correlate to how the body moves. Skeletal muscles make the legs and arms move. Cardiac muscles help the heart pump blood to the various muscles, organs, and tissues. Smooth muscles help specific organs (intestines, stomach, and urinary tract) digest, collect nutrients, and eliminate toxins in the body.
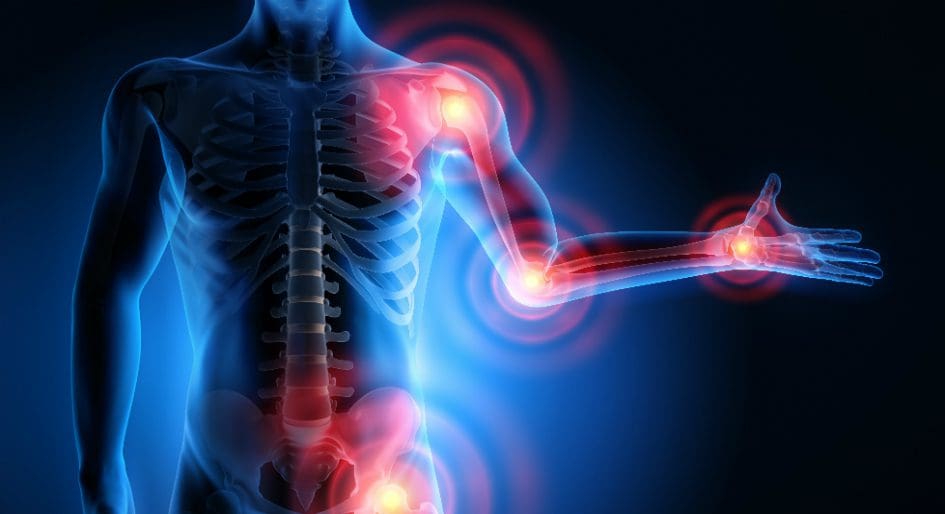
Issues That Affect The Musculoskeletal System
These factors are related to different issues that can not only disrupt the musculoskeletal system but can be an overlap of profiles affecting the cardiovascular system, spinal health, and gut system. The different factors that are associated with the musculoskeletal system are:
- Obesity
- Lack of physical activity
- Poor Posture
- Inflammation
- Unhealthy Diet
How would various factors implicate musculoskeletal issues while triggering different bodily problems? Well, let’s use obesity as an example. Obesity is associated with issues like back and joint pain as studies reveal that these musculoskeletal issues make up pain and disability as a dominant source. A poor diet of processed foods high in fats and sugars can be associated with the risk of developing obesity.
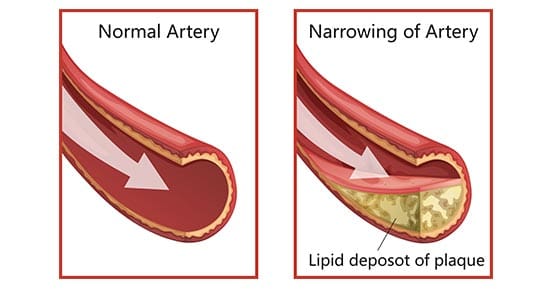
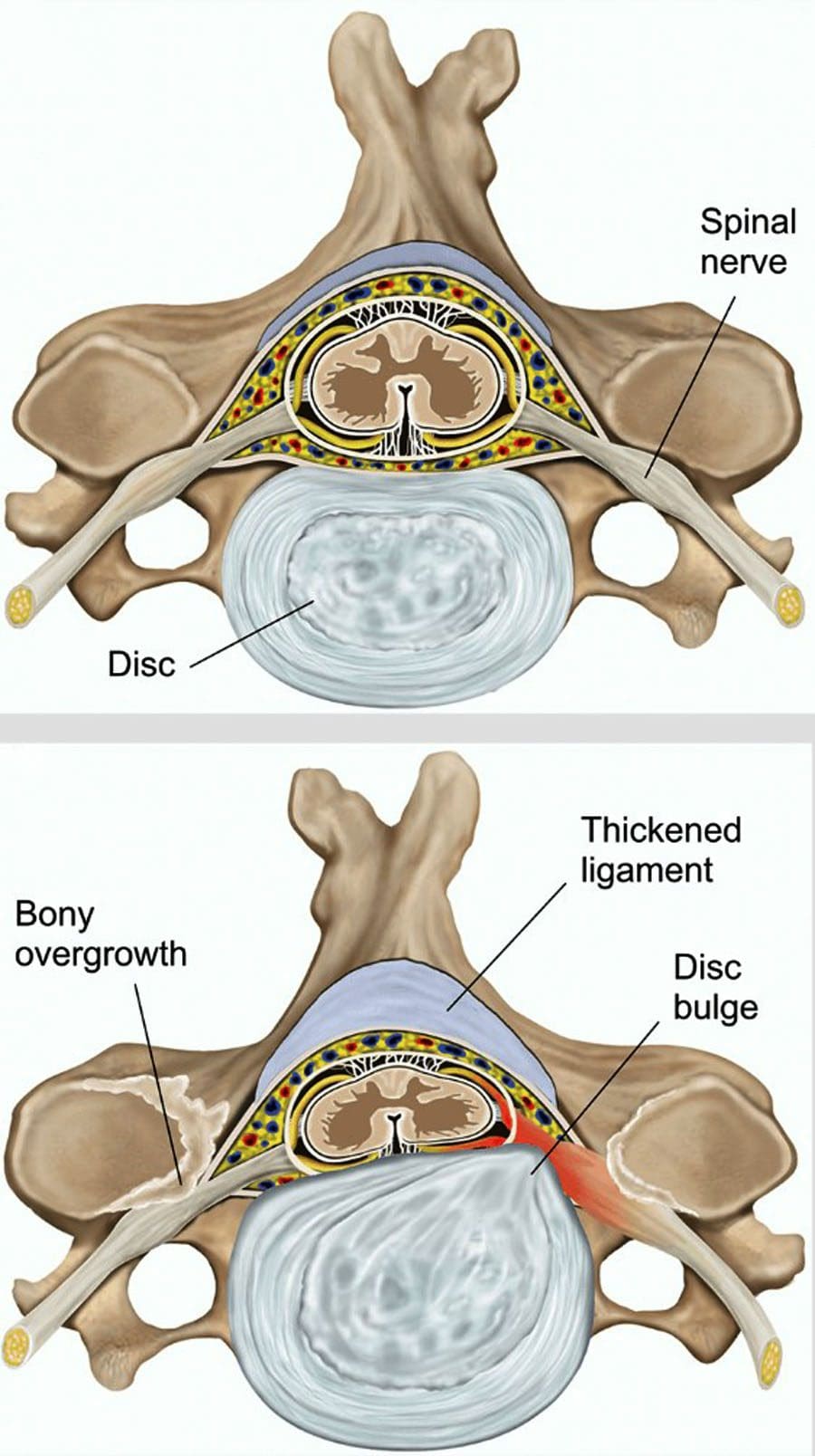
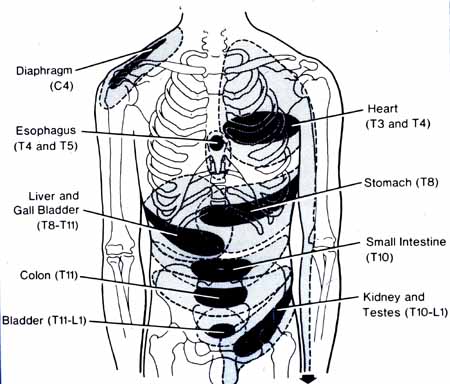
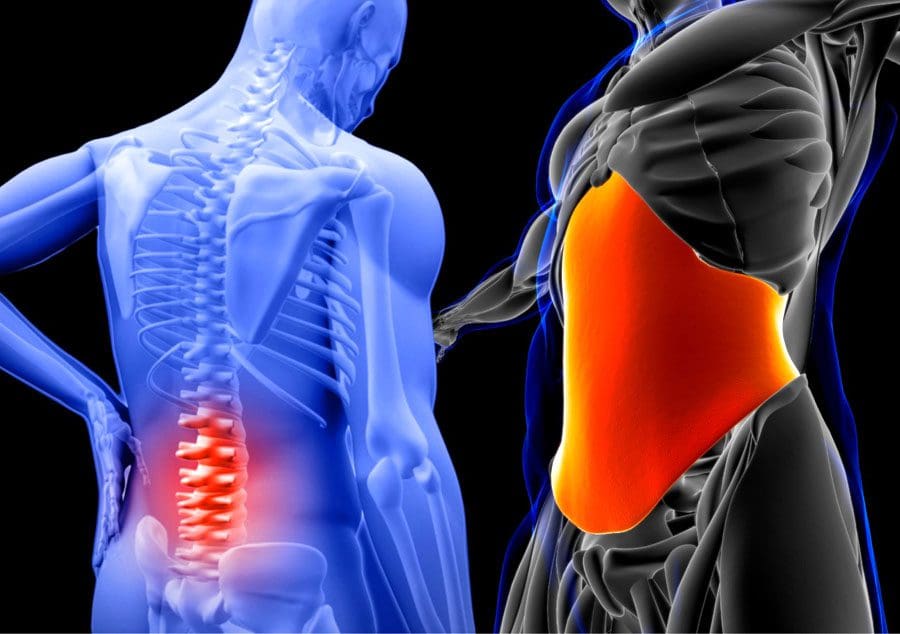
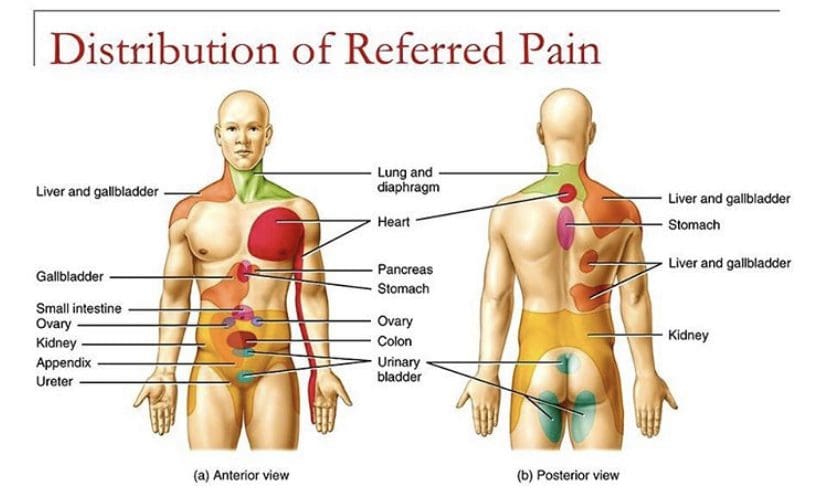
Not only that, but obesity could potentially be involved in the thoracic spine and upper back pain due to the result of physical inactivity and poor dieting. The weight on the body can strain the muscles and ligaments in the back, causing the spinal vertebrae to become misaligned and pressure the nerves exiting the spinal cord. The misalignment of the vertebrae is called a subluxation. When a person is suffering from upper back pain, it can overlap with chest pain, which can be a concerning issue to vital organs like the heart, which potentially involved in the risk of cardiovascular disease. It is related to subluxation that may affect the heart contraction rate, rhythm, and power through the sympathetic efferent pathways originating from the thoracic region.
An Overview Of The Musculoskeletal System-Video

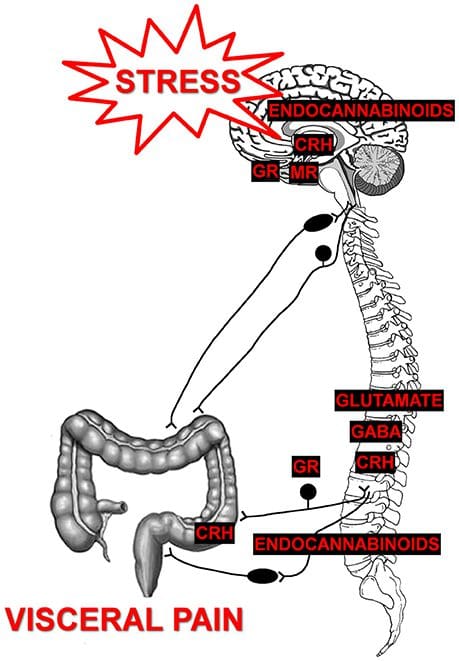
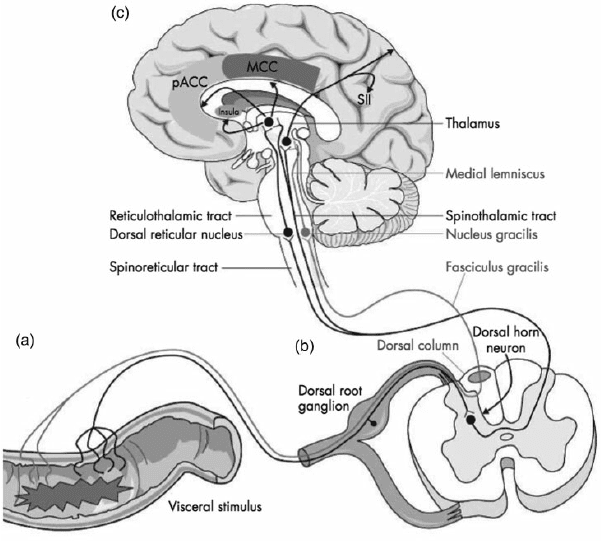
Are you experiencing pain in your upper back or chest? How about cardiac issues associated with shouldering and arming pain? Many of these issues are related to factors that affect the musculoskeletal system that might potentially be involved with chronic issues. The video above summarizes the musculoskeletal system’s role in the body. When environmental factors become a risk of developing musculoskeletal disorders that can potentially be involved in different bodily problems, studies reveal that musculoskeletal disorders associated with abnormal functions may cause a significant impact on regular performances. An example would be a person dealing with bad hip pain and cannot do any exercises triggering heart issues. This is defined as somato-visceral pain where the affected muscle is associated with an internal organ being a pain mediator.
Treatments For Improving Musculoskeletal System
In most treatments, many individuals utilize the following to improve not only the musculoskeletal system but other issues that affect the body:
- Exercise
- Healthy Diet
- Stress Management Treatments
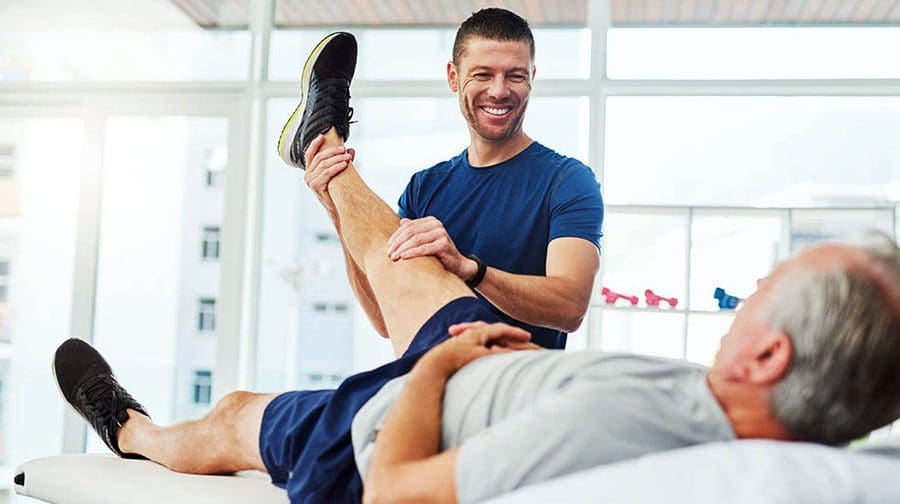
- Chiropractic Therapy
No matter what affliction or health problem a person is dealing with, having the best treatment solution possible is a start on a person’s health and wellness journey. The first step is to have a precise diagnosis to the doctor while giving as much information as possible is critical. Providing them with a complete health history is an essential first step. After a manual examination of the issues causing them pain, the primary physician could refer the individual for chiropractic care to relieve issues affecting their musculoskeletal system.
Many people usually only associate chiropractic care with back problems. Still, the reality is that chiropractic therapy can be helpful for the musculoskeletal system and various issues related to the muscles and organs. A chiropractor can provide therapeutic stretches and recommend exercises to individuals to help them avoid the same problems later on. Many chiropractors offer recommendations and nutrition that individuals can utilize to help improve their condition. For the musculoskeletal system, a healthy diet may help achieve and maintain a healthy body weight while reducing the risk of chronic disease. Eating the right amount of healthy greens, fruits, beneficial carbs, and healthy fats can help reduce the risk of developing chronic issues in the body like cardiovascular diseases. However, if primary cardiac problems affect the body, it is best to seek medical attention as soon as possible.
Conclusion
The body is considered a complex being that consists of various organs, muscles, tissues, ligaments, and joints that provide various activities to the host. The musculoskeletal system has three muscle groups: skeletal, cardiac, and smooth muscles provide different functions that correlate to how the body moves. When various factors begin to cause issues to the musculoskeletal system, they can potentially be involved with pain issues that affect more than the body. Treatments like chiropractic care, a healthy diet, exercise, and stress management may be the stepping stones to alleviating various issues that are affecting the musculoskeletal system and a great start in achieving health and wellness.
References
Kennel, Peter J, et al. “Skeletal Muscle Changes in Chronic Cardiac Disease and Failure.” Comprehensive Physiology, U.S. National Library of Medicine, 20 Sept. 2015, www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6752037/.
Malik, Khalid M, et al. “Musculoskeletal Disorders a Universal Source of Pain and Disability Misunderstood and Mismanaged: A Critical Analysis Based on the U.S. Model of Care.” Anesthesiology and Pain Medicine, Kowsar, 15 Dec. 2018, www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6348332/.
Murphy, Andrew C, et al. “Structure, Function, and Control of the Human Musculoskeletal Network.” PLoS Biology, Public Library of Science, 18 Jan. 2018, www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5773011/.
Stochkendahl, Mette J, et al. “Diagnosis and Treatment of Musculoskeletal Chest Pain: Design of a Multi-Purpose Trial.” BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders, BioMed Central, 31 Mar. 2008, www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2315652/.