Table of Contents
Introduction
The body has a defensive response known as the immune system that comes to the rescue when traumatic events or injuries impact certain areas of the body. The immune system releases inflammatory cytokines to the affected area and begins the healing process to repair the damage while also getting rid of the foreign intruders in the body. Inflammation can be potentially beneficial and harmful to the body, depending on how severe the injury has potentially impacted the area. When inflammation begins to cause an impact on the surrounding muscles, ligaments, and joints, it can lead to chronic issues associated with pain. To that point, it causes the body to be dysfunctional while mimicking other symptoms. Today’s article examines how chronic inflammatory responses affect the joints, their associated symptoms, and how to manage chronic joint inflammation. We refer patients to certified providers specializing in anti-inflammatory treatments to help many individuals dealing with chronic inflammation of the joints. We also guide our patients by referring to our associated medical providers based on their examination when it’s appropriate. We find that education is the solution to asking our providers insightful questions. Dr. Alex Jimenez DC provides this information as an educational service only. Disclaimer
How Does Chronic Inflammatory Response Affect The Joints?
Have you been experiencing pain in some regions of your body? What about experiencing tenderness in your muscles? Do your joints ache when you are doing everyday activities? If you have been dealing with these issues, it might be due to chronic inflammatory responses affecting your musculoskeletal joints. As stated earlier, inflammation can be both beneficial and harmful to the body, depending on the severity of the impact the body has taken. In its beneficial form, the body activates the immune system and eliminates pathogens from bacteria, viruses, and other environmental triggers to promote healing and tissue repair. This potentially makes the affected area red and inflamed, thus repairing the damaged cells.
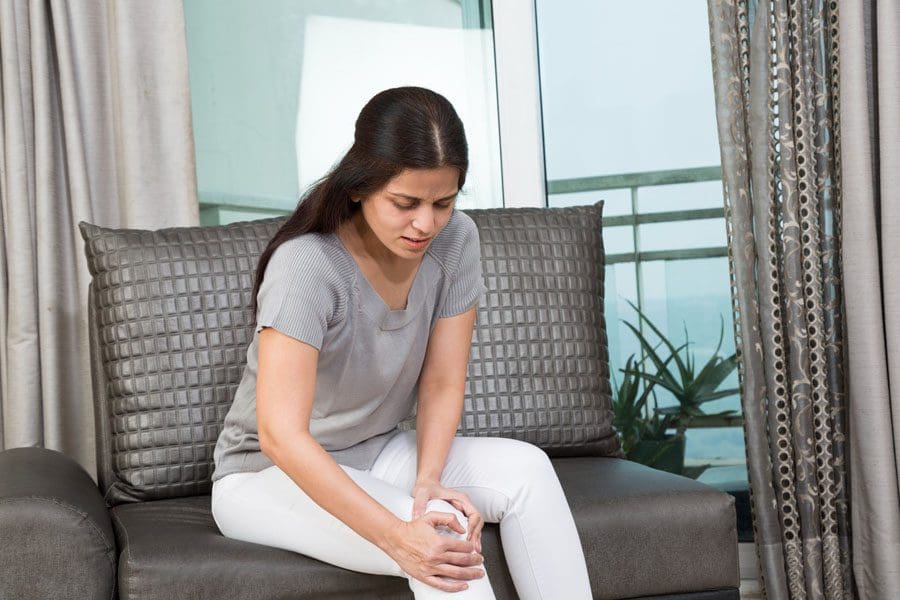
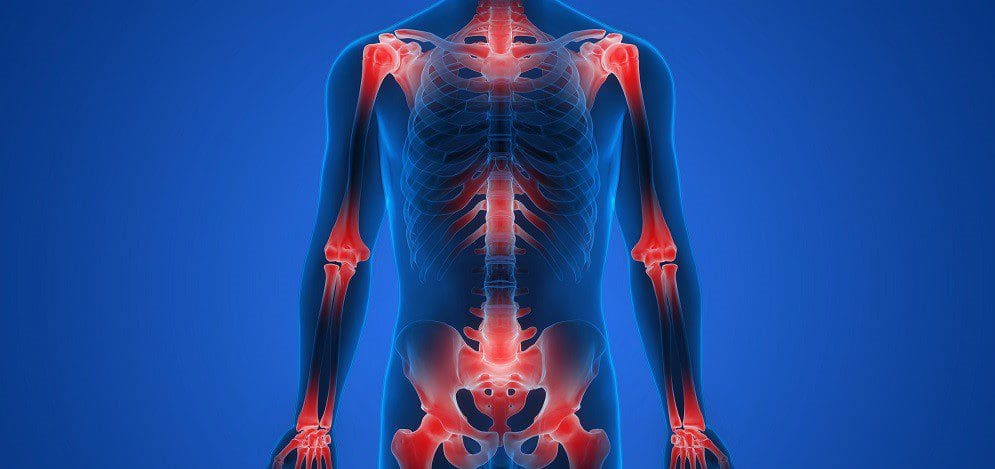
However, in its harmful form, studies reveal that chronic inflammatory responses can break down immune tolerance, causing significant alterations to all the tissues, organs, and joints. To that point, the residual effects of high inflammation can cause harm to the joints and cartilage, making them potentially involved with pain and possibly deformity over time. The joints help keep the body moving, surrounded by connective muscle tissue that helps stabilize the body; when chronic inflammatory responses start to affect the joints, they can become a mediator for pain and discomfort while triggering musculoskeletal disorders. Studies reveal that inflammation in the joints can cause damage to the cartilage and result in degenerative changes to the body. This includes functionality loss, joint instability, and other symptoms associated with chronic joint inflammation.
The Symptoms Associated With Chronic Joint Inflammation
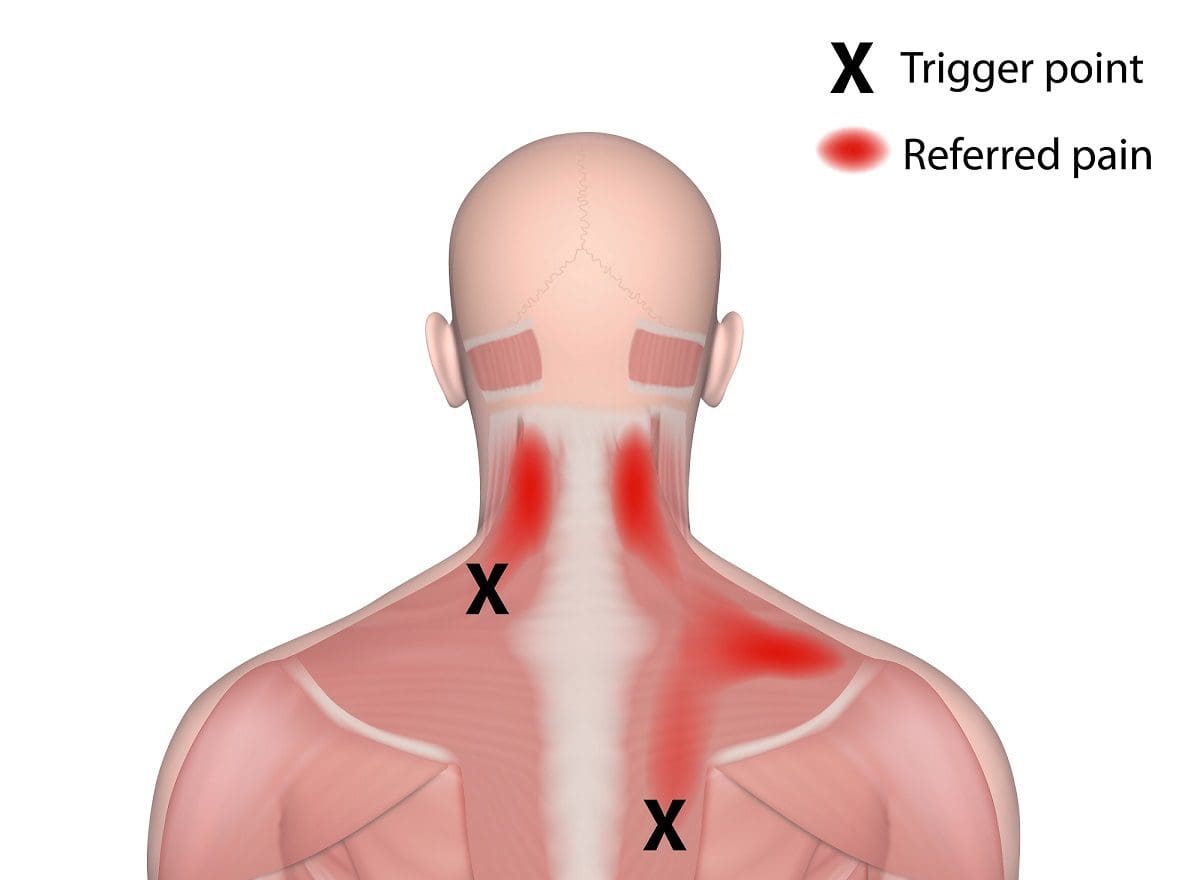
When it comes to chronic joint inflammation, it can mimic other chronic conditions that present joint instability while overlapping different chronic disorders. This makes diagnosing difficult, especially if the person is dealing with inflammation on one side of their body, but it affects another part. This is known as referred pain, and studies reveal that most inflammatory forms that affect the joints are sometimes arthritic and have systemic symptoms that may occur in different body areas. Some of the symptoms associated with chronic joint inflammation can include:
- Swelling
- Stiffness
- Grinding sounds
- Difficult mobility
- Numbness
- Joint deformity
The Difference Between Healthy Joints & Inflamed Joints-Video

Have you been dealing with joint pain throughout your life? Do you feel muscle stiffness in certain areas when you move around? Or do you feel muscle tenderness in certain areas? Many of these symptoms are associated with joint inflammation, potentially overlapping with musculoskeletal pain. The video above explains the difference between healthy joints and inflamed joints. Healthy joints are utilized when the surrounding muscles are strong and functional while no pain is inflicted on the body. Inflamed joints may be caused by numerous factors like lifestyle habits, physical inactivity, or previous conditions associated with inflamed joint pain. Studies reveal that inflammatory cytokines may potentially amplify musculoskeletal discomfort that affects the musculoskeletal tissues that surround the joints. To that point, inflammation of the musculoskeletal system may overlap with joint pain, thus directly impacting a person’s quality of life. Fortunately, there are ways to manage chronic joint inflammation and restore a person’s health and wellness.
Managing Chronic Joint Inflammation
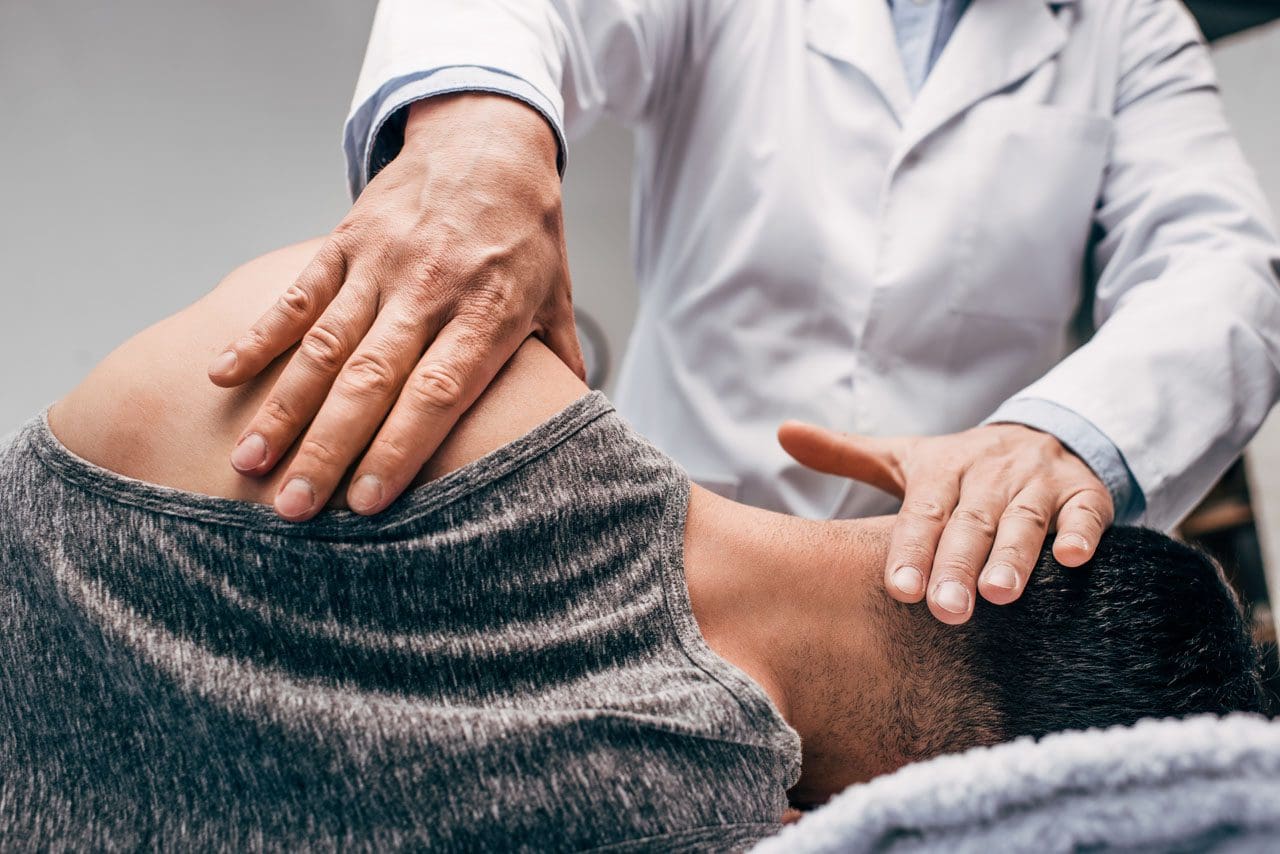
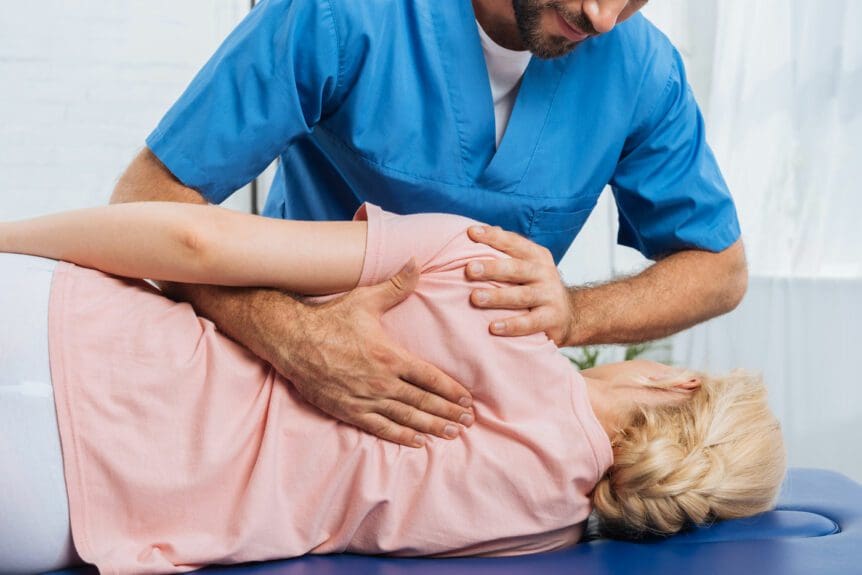
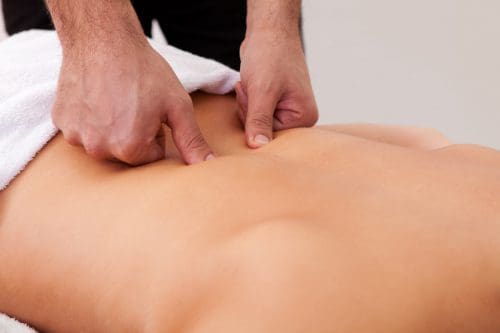
Since inflammation is beneficial and harmful to the body, there are different ways to manage chronic inflammatory markers triggering joint pain. Many individuals who want to lower inflammation in their joints will begin to incorporate natural ways to lessen the pain. Eating foods high in fiber may potentially help lower inflammatory markers, including physical activities to improve musculoskeletal and joint stability and utilizing chiropractic care. Studies reveal that chronic joint inflammation associated with pain does affect a person’s ability to sleep and emotional health. To that point, incorporating treatments to manage inflammatory effects may potentially improve a person’s self-efficacy. Now how does chiropractic care help manage chronic joint inflammation? Chiropractic care includes inflammation reduction techniques that help loosen the stiff muscles that surround the inflamed joints. Joint inflammation may also be due to subluxation (spinal misalignment) associated with environmental factors. Utilizing chiropractic care not only alleviates the symptoms caused by joint inflammation but may potentially alleviate the cause of inflammation. Once a person has completed their chiropractic care treatment, they can return to normal activities without the risk of re-injury and re-inflammation.
Conclusion
Inflammation in the body can be beneficial and harmful depending on the impacted area. The body unleashes inflammatory cytokines when a traumatic event or injury has occurred in certain body areas. This is due to the immune system naturally responding to the damaged cells, thus causing the area to be red, hot, and swollen to promote healing. To that point, inflammation can impact the surrounding muscles, ligaments, and joints, which can lead to chronic issues associated with pain. Chronic joint inflammation is residual high inflammatory effects that cause harm to the cartilage and joint structures, thus making them potentially involved with pain and possible deformity. Fortunately, treatments like high fiber and anti-inflammatory foods, getting enough exercise, and chiropractic care may help manage chronic joint inflammation and its associated pain symptoms. This way, many individuals can resume their normal activities.
References
Furman, David, et al. “Chronic Inflammation in the Etiology of Disease across the Life Span.” Nature Medicine, U.S. National Library of Medicine, Dec. 2019, https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7147972/.
Kim, Yeesuk, et al. “Diagnosis and Treatment of Inflammatory Joint Disease.” Hip & Pelvis, Korean Hip Society, Dec. 2017, https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5729162/.
Lee, Yvonne C. “Effect and Treatment of Chronic Pain in Inflammatory Arthritis.” Current Rheumatology Reports, U.S. National Library of Medicine, Jan. 2013, https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3552517/.
Poudel, Pooja, et al. “Inflammatory Arthritis – Statpearls – NCBI Bookshelf.” In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL), StatPearls Publishing, 21 Apr. 2022, https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK507704/.
Puntillo, Filomena, et al. “Pathophysiology of Musculoskeletal Pain: A Narrative Review.” Therapeutic Advances in Musculoskeletal Disease, SAGE Publications, 26 Feb. 2021, https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7934019/.