Introduction
Dr. Jimenez, D.C., presents how different infections are associated with Lyme disease in this 3-part series. Many environmental factors often play a role in our health and wellness and can lead to overlapping risk profiles that can cause pain-like issues in the body. In today’s presentation, we examine how Lyme disease affects the body and how it correlates with genes. Part 1 looks at the body’s genes and looks at the right questions to ask. Part 3 looks at the treatment protocols for Lyme Disease. We mention our patients to certified medical providers that provide available therapy treatments for individuals suffering from chronic infections associated with Lyme disease. We encourage each patient when it is appropriate by referring them to associated medical providers based on their diagnosis or needs. We understand and accept that education is a marvelous way when asking our providers’ crucial questions at the patient’s request and acknowledgment. Dr. Alex Jimenez, D.C., uses this information as an educational service. Disclaimer
The Factors Associated With Viruses
So first, about 8% of the human DNA is made up of endogenous retroviruses, typically called human endogenous retroviruses. This means that DNA fragments from viruses pass from generation to generation. This idea of human endogenous retroviruses will be important in this presentation when we talk about how they can amplify inflammation. So we mentioned earlier that we’re colonized with or infected by Epstein-Barr pretty early in age. So here we are by age 15, and virtually everybody carries the Epstein-Barr virus. And this paper is a translational mini-review series on B-cell subsets in disease. They talk quite a bit about the Epstein -Barr virus as it has been a leading candidate as a trigger for several autoimmune diseases since its initial description of raised Epstein-Barr virus antibodies in 1971.
It’s a plausible candidate since it’s ubiquitous and establishes a lifelong dormant infection with continuous viral production due to reactivation. And this idea of reactivation is going to be important as we move forward as it can modulate the human immune system. Another key issue we will need to hold onto as we move forward. To that point, they also talk about a Trojan horse. So the Epstein-Barr virus can infect a B-cell, and B-cells can migrate across a blood-brain barrier by their normal nature. Once this infected B-cell crosses a blood-brain barrier, it can release these Epstein-Barr encoding RNAs, which is an inflammatory process. Our body doesn’t like foreign RNA floating around. That is the initiation, perhaps, of some demyelinating activity. They go over four specific ways.
The first way is the molecular mimicry idea. So, molecular mimicry is the idea that you have an antibody that incidentally cross-reacts with your tissue. Then the second is these latent Epstein-Barr virus antigens could sustain the survival of autoreactive B-cells. And then Epstein-Barr infected can liberate these. Here are our human endogenous retroviruses in number three here. It activates these things leading to more inflammation and damage, which can correlate to muscle and joint pain. And then, finally, the Epstein-Barr itself continuously auto-activates or reactivates autoreactive B-cells. So making this the amplification feed-forward loop.
And by the way, Epstein-Barr has also been found in the inflamed gastrointestinal mucosa, including gastric and colonic, making it an interesting candidate for causative issues there as well. What about cytomegalovirus? Well, case reports of associated primary cytomegalovirus infection to the onset of autoimmune conditions. They’re certainly involved in allograft rejection and graft versus host disease. And they play a role in immunopathologies. And here is how that may occur. So, again, we see through various pathways and get the same molecular mimicry idea. We make an antibody against something that incidentally cross-reacts with our tissues. And, you know, why may that happen? One reason is that these bugs have co-evolved and may well have co-evolved camouflage, and that camouflage looks vaguely like us.
Symptoms Associated With Autoimmune Disorders
So these antibodies cross-react. We also see various ways that environmental factors can cause inflammation in the body, which can be amplified. We have a TH4 amplification pathway. We have a Lox Cox amplification pathway and a myeloid IL-6 TNF alpha pathway, all amplifying inflammation. Then we see vascular damage through a variety of mechanisms. And this vascular damage, of course, increases downstream oxidative stress and inflammation. And then finally, through various pathways, CMV appears capable of suppressing the immune system. As we find in many of these bugs, these are not unique necessarily to CMV but probably carry across many other viruses and bacteria. So here’s a list of a few autoimmune conditions that are associated with viruses and a few viruses that are associated with autoimmune disorders. These include:
- Type 1 diabetes
- Influenza A viruses
- Sjögren’s syndrome
- Celiac disease
- Multiple sclerosis
- Other viruses (Measles, mumps, & rubella)
- Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE)
So now we are going to look at one of the autoimmune conditions that are associated with viruses. So systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is associated with EBV infection and is correlated with many risk factors. This is a systematic review and meta-analysis. And in summary, they mentioned that their study supports the hypothesis that prior EBV infection is essential for developing SLE. So, we see more and more of these situations. We’ve connected Klebsiella overgrowth in the gut and ankylosing spondylitis. Now we’re seeing this with Epstein-Barr and SLE and many more. So then, let’s skip to bacteria for a minute. Why does it take so long to cure tuberculosis? If you have strep, it is cured for ten days, right? Why does treating tuberculosis takes six months or maybe even a year and a half? Well, there’s a glossary from this paper, and it talks about antibiotic indifference.
Antibiotic indifference is a catchall term for bacteria that aren’t bothered by antibiotics. One sub-mechanism of this is biofilm formation. Bugs can join a preexisting biofilm, or they can create their biofilm. There’s this idea of dormancy, which is a non-replicating state. And, of course, most antibiotics require an interruption in protein synthesis or something like that to disrupt reproduction. So dormancy renders the bug temporary, which causes antibiotic indifference. And then latency is an asymptomatic infection related to quorum sensing and so on. Persist forms is another broad term, which means this subset of this population can persist in the immune system or the antibiotic treatment. And then phenotypic antibiotic resistance is a general term for this phenomenon. And here’s the interesting part, this phenomenon is common to all bacteria.
And when we say all, we mean probiotic bacteria and pathogenic bacteria. So remember that, in AFMCP, you learned that this 50-micron biofilm layer is on the colon, which is part of the barrier function. So probiotics do these things too. So it’s common to all bacteria. And these bacteria-resistant populations may be enriched under various conditions, which are operant in vivo, such as intracellular growth, DNA damage exposure to other antimicrobials, and biofilm production. And then, there’s this whole array of how these bugs can manipulate the local microenvironment to manipulate the immune system. And this idea of micro RNA. So we all have heard of messenger RNA, but this is different than micro RNAs are regulatory molecules. And in this paper, they talk about how they interact with the vitamin D-dependent antimicrobial pathway. And in this paper, we talk about micro RNAs and how leprosy regulates micro RNA profiles locally, interfering with the immune response. And here again, decreased expression of these micro RNAs. And what we find is that T-cells are centrally important in the process of clearing these infections. So the vast majority of people exposed and colonized or infected with the micro bacterium are protected from developing tuberculosis by this T-cell response. And micro RNAs regulate T-cells.
Delay Responses
A strong delayed-type hypersensitivity response is associated with the clearance of the illness. Whereas a cytotoxic T-cell response or a strong humoral antibody response is more associated with prolonged infection or progression to tertiary disease, we found this research study that explains the whole of its delayed-type hypersensitivity reactions was only discussed in blood transfusion reactions. But here we’re learning that they may be the central issue curative for, especially these chronic infections. And remember, we mentioned earlier that micro RNAs might regulate vitamin D, but vitamin D also regulates micro RNAs. And as a small reminder here, vitamin D interacts with both macrophage and dendritic cells and alters the T-cell balance, the T-reg TH1217 and so on, and even the B-cell production of immunoglobulin. These micro RNAs are important at every step of the innate and adaptive immune response. And we can see that they intervene on a multitude of levels. So, at one point in the future, these may be targets of therapy or understanding of what’s happening in the immune response.
So, again, the delayed-type hypersensitivity reaction, the last one we talked about, was leprosy, but this is syphilis. A weak, delayed-type hypersensitivity reaction is associated with progression. A strong delayed-type hypersensitivity reaction is related to a cure. And it appears to be the delayed-type hypersensitivity reaction is the most important piece. Whether or not you have a high or a low antibody production is a little immaterial. And it may have more to do with preventing infection than the clearance and treatment of the disease. So back in 1968, we discovered that this particular spirochete that causes syphilis could be resistant to appropriate antibiotic therapy. So these are 45 volunteers who had had syphilis for a long time. They were treated a long time ago, and 11 of them had lymph nodes sampled, and they were found to harbor syphilis bugs.
And then, in five more of these subjects, after being treated for a second time, five more had lymph nodes sampled, and in three of them, the majority had continued treponemes found. So, they looked at a bunch of infected rabbits and let the infection bloom and blossom for 14 to 22 months. And then, four of these 23 rabbits still harbored these infections after treatment. And the question becomes, why would that be? Well, it’s this infectious disease conundrum again. All right, here are some spirochetes, and you know, it’s not just about Borrelia burdorferi anymore.
Lyme Disease
Here are six species of Borrelia that are associated with the symptoms of Lyme disease. Here are three species of BLI that are associated with tick-borne relapsing fever. Borrelia miyamotoi is related to, but distinct from, relapsing fever. And then there are a few stragglers that are symptomatic, but it needs to be more well-characterized. And then there are co-infections. These hitchhikers are diseases of their own but are often carried by the same tick. So there are a couple of species of Babesiosis, four species of Bartonella, Human Granulocytic Anaplasmosis, and Human Monocytic Ehrlichiosis. And then, a couple of species of Rickettsia are all associated with a tick-borne illness. And then some imitators aren’t necessarily tick-borne like Powassan virus or West Nile virus, which mosquitoes can carry, but tick-borne encephalitis virus.
And then Coxsackie and cytomegalovirus, EBV, a bunch of herpes viruses, and so on. And then also this bacteria streptococcal a, which is associated with this pandas syndrome. And then this really strange, alpha-gal syndrome. So alpha-gal is a carbohydrate, and certain ticks, particularly lone star ticks, but probably others, can inject this alpha-gal into a bite, resulting in a red meat allergy. So there are all kinds of things you must consider when considering tick-borne disease.
This is not a new disease. The ice mummy found in 1991 in Eastern Alps appears to have had Lyme disease. So what’s going on? Why do we see so much more Lyme diseases? And we don’t think anybody knows, but we wonder if it has something to do with the hundreds of billions of tons of pollutants we put into our environment. Or is it the time society we live in? So the CDC gets about 30,000 case reports of Lyme disease, and new reports pop up yearly. They estimate that it’s underreported by almost ten times. So there are about 300,000 new cases of Lyme disease every year.
To put that into perspective, that’s about the same as the number of new invasive breast cancer cases. It’s a little more than prostate, rheumatoid arthritis, or colon cancer. It’s more than Parkinson’s Type one diabetes, HIV, multiple sclerosis, or West Nile virus. And yet there’s a real discrepancy in research spending; according to NIH statistics, malaria gets about $118,000 per case in the United States. West Nile virus gets about $13,000 per case. The new issue in the United States, Lyme disease, is 82 bucks. So why do we have some gaps in our knowledge? Here’s a map of case reports. So these are actual case reports, so remember they’re maybe underreported by as much as ten times. So you could multiply any of these numbers by ten and look particularly at Florida over here; Florida has 2,327 cases between 1990 and 2018.
Guidelines For Lyme Disease
So these are the guidelines of the Infectious Disease Society of America for tick-borne illness. And these guidelines tell us that it is perfectly fine to diagnose Lyme disease by history, erythema migraines, and rash. Still, you need testing to diagnose extracutaneous manifestations if they don’t have that rash. So we talked about the evidence before. Let’s take a look at the evidence behind these recommendations. On 20% is level one, which levels one is, you know, randomized controlled trials. 25% is level two, well-designed clinical trials without randomization. And then level three is opinion. So 55% of these recommendations are opinions.
So here’s the bug umbrella. It has about 132 active genes. Its closest competitor is syphilis, with about 22 active genes and functional genes. It has a linear chromosome most bacteria, not all, but most have a circular chromosome. And it has 21 plasmas, which are this non-primary chromosomal DNA fragments. And its closest competitor is chlamydia, with only seven. So it’s a very complex disease. And this bug engages in stealth pathology. And stealth pathology has four basic strategies: immune suppression, genetic phase, antigen variation, physical seclusion, and secreted factors. So let’s jump into immune suppression. It’s aided and embedded by the tick because it has analgesics, anticoagulants, and immune suppressive factors in its saliva. And then, Borrelia burgdoferi can cause immunosuppression by complement inhibition and induction of inhibitory cytokines such as IL-10.
Inflammation & Lyme Disease
And then, you know, we normally think of IL-10 as anti-inflammatory. Well, true, but an anti-inflammatory response responds immunosuppressive, which can induce monocyte and lymphocyte tolerization and antibody sequestration in immune complexes. What about genetic and phase shifting and all that good stuff? Well, it can engage in gene shifting similar to ribosomes into mutation and recombination, similar to the way HIV does variable antigen expression in a way identical to ni serious species auto resuscitation of dormant organisms are this auto resuscitation or quorum sensing ideas similar to mycobacterium and then fibronectin binding like staph and strep.
It also responds to calprotectin. Now, this is the same calprotectin we frequently measure as a marker of inflammation in the stool, right? So, calprotectin can induce a dormant cyst-like state in spirochetes, allowing it to persistent tissues without replicating. And this provides a means of it avoiding antibiotic therapy. Although gene antibiotic resistance was previously considered uncommon, newer studies suggest it does happen. So the regular old acquired genetic raising of mics, if you will, is now seen in Brellia. What about physical seclusion Well, the lime spirochete uses physical seclusion at intracellular sites. It combines with synovial, endothelial, and fibroblast tissue or can become intracellular in these tissues. Fibroblast tissue, macrophagic cup for cells and neurons. So it can find its way inside these cells. And in fact, it has been grown for long periods in fibroblasts in this case, but in other tissues as well.
And it can also cloak itself by binding to a variety of proteins. Here’s a cartoon of fibronectin, which can bind to proteoglycans, collagen, plasminogen, integrin, and so on. And this functionally hides it from the immune system. And then these secreted factors, well, the first secreted factors, are how they get into cells that we discussed earlier. So, adherent and point. Adherent allows the bacteria to adhere to a cell, and the end enables it to make a pore and gain entry to the cell. And then the quorum sensing, we also talked about auto resuscitation. And this suggests that Lyme spirochetes engage in auto resuscitation, like other dormant organisms such as tuberculosis. So a summary, it can inhibit the active immune sub-response by both the innate and the adaptive, and it can evade the immune system by the various mechanisms we discussed.
Conclusion
So persister mechanisms; this is a study on antibiotic use and how it induces persister forms. And we see on the top half here that when exposed to doxycycline, it upregulates and downregulates these genes and amoxicillin. Different sets of genes are changed. And so this tells us that it has several tricks up its sleeve to evade treatment, not just antibiotics, but our immune system as well. We’ve alluded to these different forms. We’ve used the term cyst a few times. It’s a spirochete. Spirochete requires a cell wall, but it can lose its cell wall when it loses. And cell wall becomes what’s known as an L-form or cell wall deficient form. And there may be hundreds of these that can form a cyst. I like to think of the cell wall’s inadequate structure like a grape and the cyst more like a raisin.
The raisin is a long-term storage form, right And then they can all join and form biofilms. And this shapeshifting is weird, but it’s pretty common. Here’s an example that we’re all familiar with. This yucky creepy crawly thing turns into a beautiful butterfly. So here’s some spirochetes in here are some colonies, some biofilms. So the columns vertically are two days, three days, and seven days or up to 21 days. And then the different colors going are other stains. And we see a progressively complex biofilm forming, but aside, biofilms of themselves are not; pathogenic biofilms are just a way in which bacteria colonize. The biofilm composition makes it either protective or pathogenic from a functional medicine point of view; we would like to move biofilms in the direction of probiotics and protection using diet and lifestyle modification and supplements, and so on.
Disclaimer
















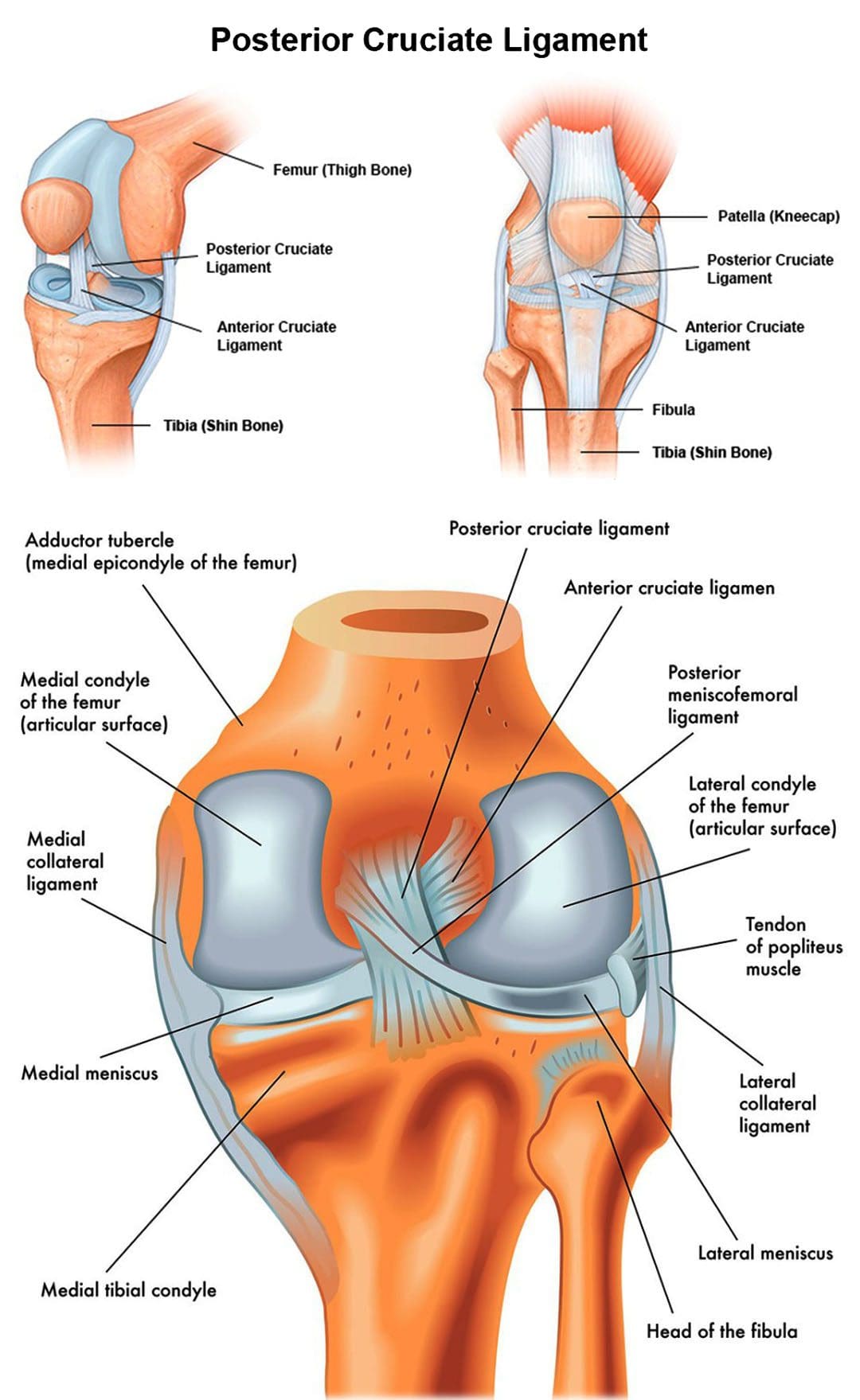 Posterior Cruciate Ligament
Posterior Cruciate Ligament






