Table of Contents
Introduction
The heart plays an important role in the body by pumping blood into the arteries, veins, and blood vessels to be transported through every muscle tissue and organ system so that they are doing their job correctly. From the central nervous system to the gut system all the way to the endocrine system, blood cells are being transported and moving throughout the body to make it functional. When unknown pathogens or stressors start to enter the body, it can cause a major disruption to the body through chronic illnesses and symptoms that can cause the body to be dysfunctional. In this 2 part series, we will be taking a look at diagnosis concepts for cardiovascular disease. In part 2, we will continue to discuss the diagnosis concepts for cardiovascular disease and be taking a look at the risk factors that cause cardiovascular disease. By referring patients to qualified and skilled providers who specialized in cardiovascular services. To that end, and when appropriate, we advise our patients to refer to our associated medical providers based on their examination. We find that education is the key to asking valuable questions to our providers. Dr. Alex Jimenez DC provides this information as an educational service only. Disclaimer
Can my insurance cover it? Yes, in case you are uncertain here is the link to all the insurance providers we cover. If you have any questions, please call Dr. Jimenez at 915-850-0900.
What Is The Cardiovascular System?
Since the heart plays an important part in the cardiovascular system by making sure that blood is pumping through the arteries and veins. Research shows that the cardiovascular system has an important function by getting oxygenated blood and nutrients throughout the entire body and removing waste out of the body as well. The body’s cellular structure actually depends on the cardiovascular system to keep things running smoothly. When disruptors like cardiovascular disease start affecting the heart, it can lead to many complications that can harm the body.
How To Prevent Heart Disease
Since heart disease is the number one cause of death in the US and studies have found that cardiovascular disease can cause mortality and morbidity in the body and can actually be one of the many factors for hypertension. The annual cost is 320 billion dollars for individuals that go through heart disease treatments in order to feel better. However, about 80 percent of heart disease ( heart attacks, angina, coronary heart disease, and congestive heart failure) can be prevented by non-surgical treatments like:
- Optimal nutrition
- Optimal exercise
- Optimal weight and body fat
- Mild alcohol intake
- Not smoking
HCTP Therapy

HCTP therapy is a form of regenerative medicine that helps speed up the body’s natural healing process. HCTP or human cellular tissue products is the correct term for stem cells* that international and nationally affiliated clinics and distribution organizations use to help repair damaged cells, tissues, and organs. HCTP therapy as a regenerative treatment can provide the help and needs to repair diseased cells that have been affected by chronic illnesses back to their original state in the body.
Diagnosing Cardiovascular Disease
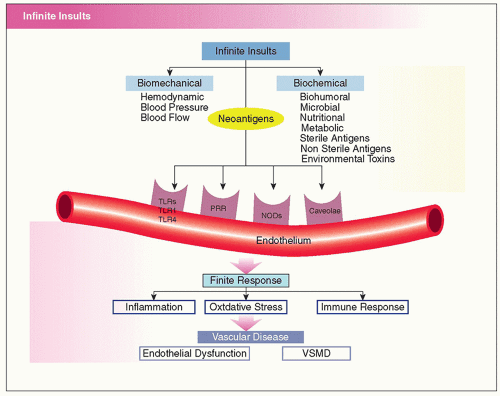
Since cardiovascular disease is a collection of disorders that can affect the heart, it is important that individuals go to their primary healthcare providers to get their heart diagnosed to make sure that cardiovascular disease doesn’t progress further. Studies have found that diagnosing cardiovascular disease or any diseases that affect the body, assesses the prognosis of the disease by facilitating the specific markers of proteins and nucleic acids to implicate the regulation of the body’s metabolism, controlling blood circulation, and inflammation. The blood vessel has only 3 finite responses to an infinite number of insults:
- Inflammation
- Oxidative stress
- Immune vascular dysfunction and imbalance
Blood Vessels Are Innocent Bystanders
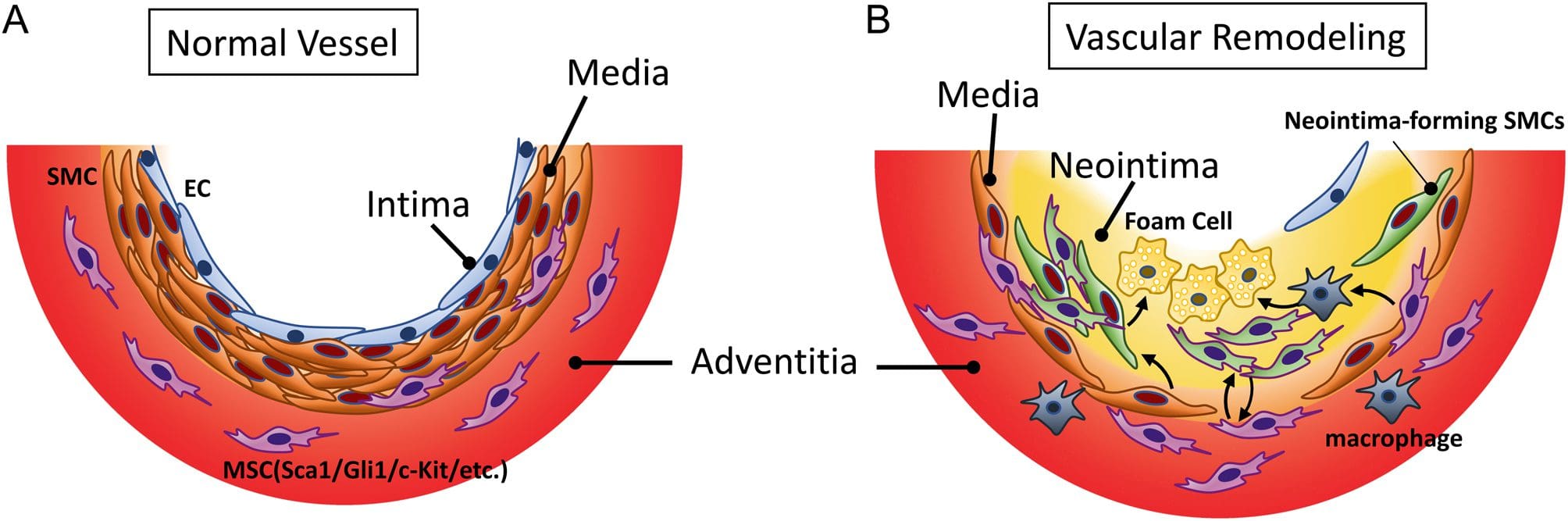
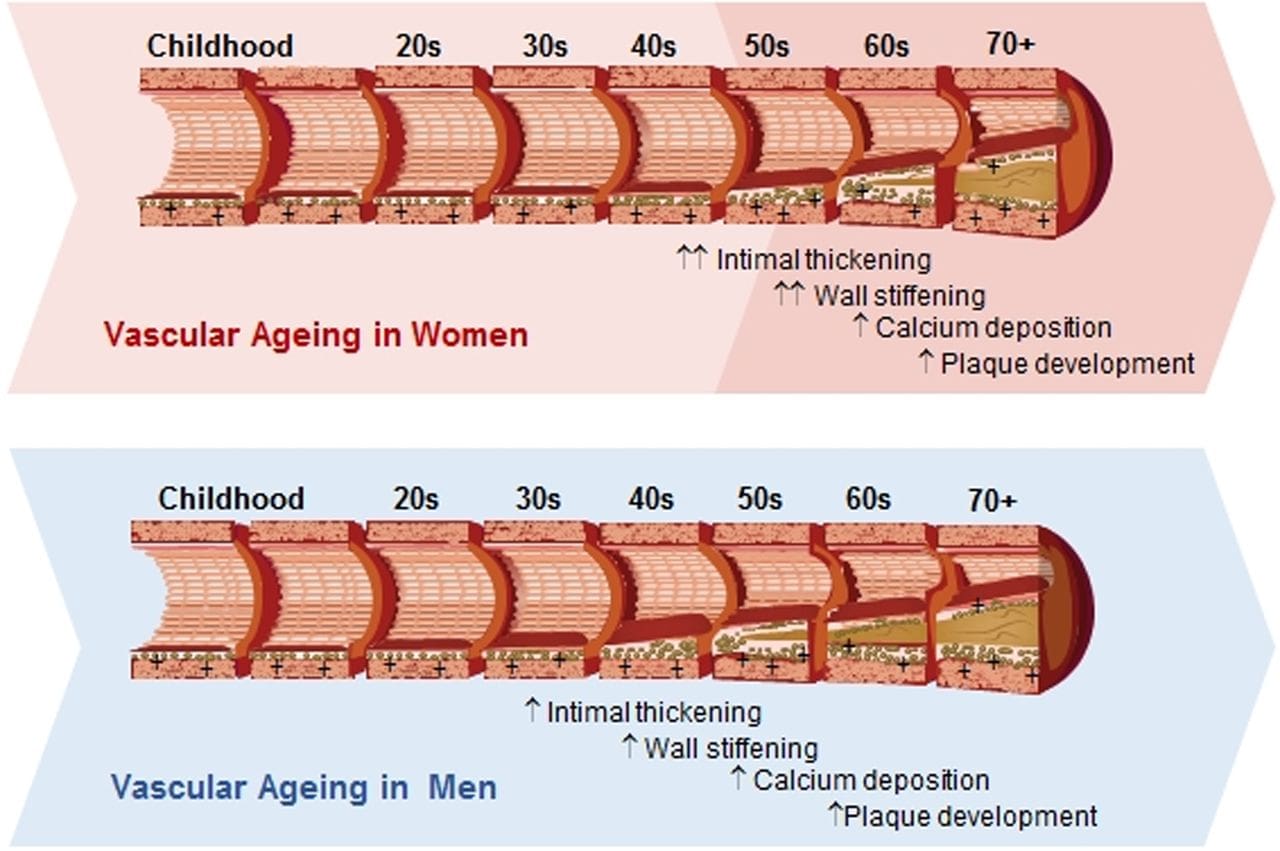
The blood vessel in the cardiovascular system responds acutely as a defense mechanism to internal and external insults that are “correct and normal” but these chronic insults result in a chronic exaggerated and dysregulated cardiovascular dysfunction with preclinical then clinical cardiovascular disease due to maladaptation. Research shows that many cardiovascular diseases can cause an overproduction of the blood vessel causing many chronic symptoms like vascular malformation, inflammation, or plaque build-up in the blood vessels. Since the cardiovascular system is the innocent bystander and the blood vessels are taking a beating from chronic disorders, the subsequent environmental-gene expression patterns can produce downstream mediators that damage the arteries. However, proper assessment, comprehension, prevention, and treatment of the top five and other 395 chronic heart disease risk factors and the downstream mediators, will reduce chronic heart disease.
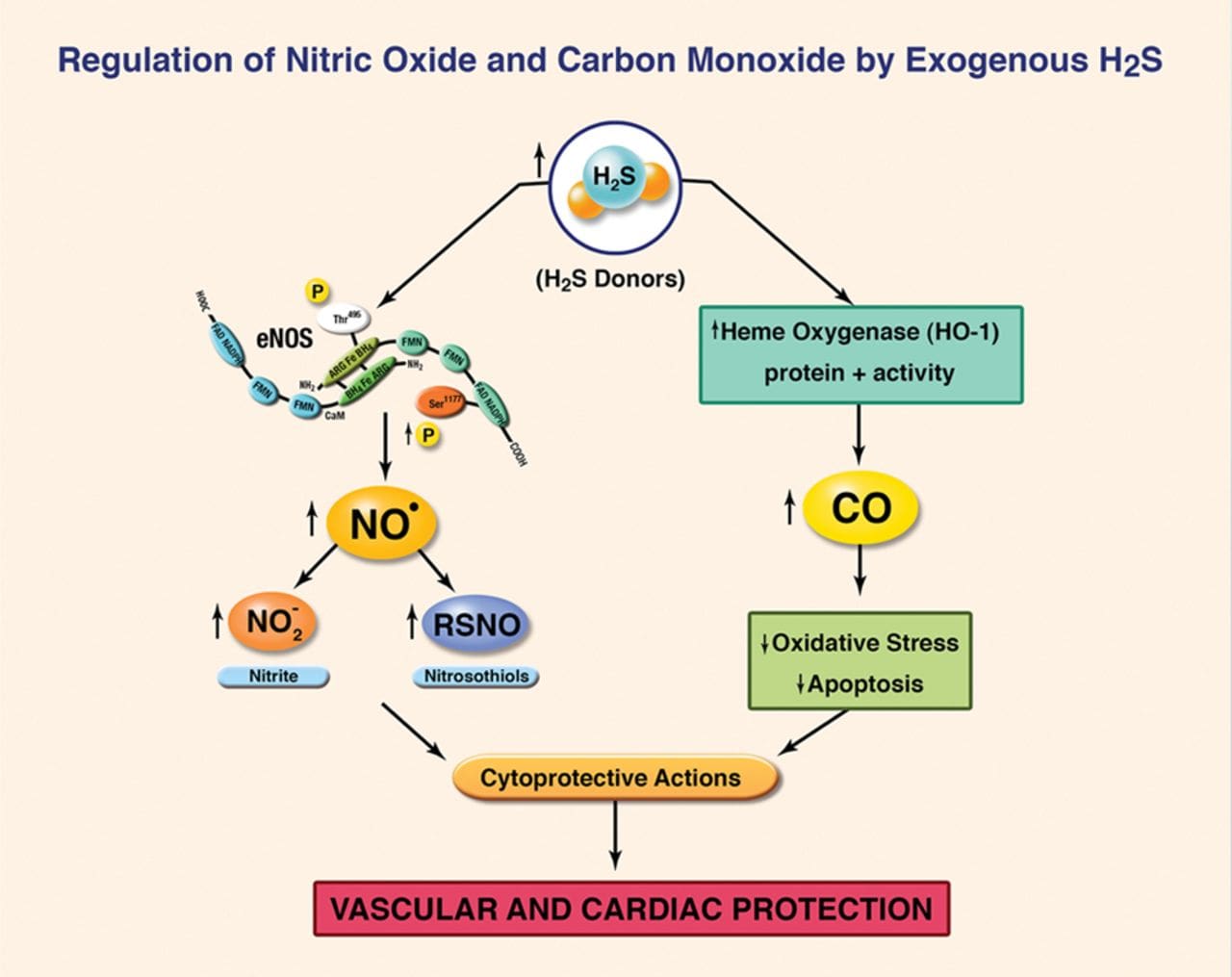
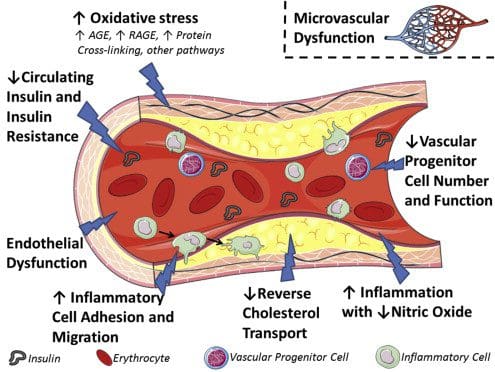
Endothelial Dysfunction & Membrane Dysfunction
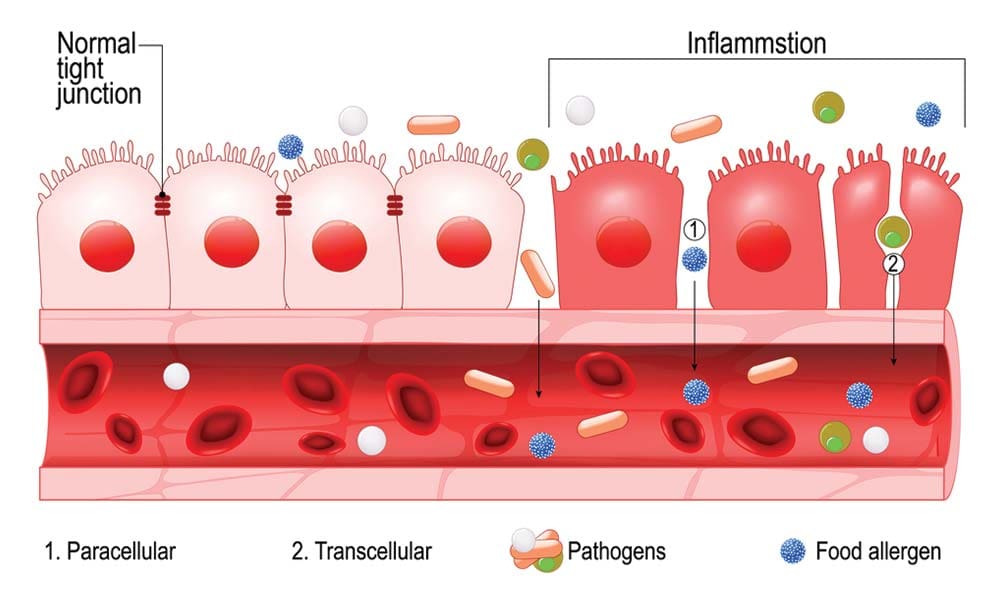
The endothelium is recognized as a smart barrier and key regulator for blood flow in micro-and macrovascular circulation in the heart. When there is endothelial dysfunction, studies have found that endothelial dysfunction can predispose the blood vessels to vascular lesions, inflammation, and other disorders that can affect the heart. Membrane dysfunction is when the body barriers and membranes protect cells and provide the initial interaction of the external infinite insults with the internal signaling mechanisms. Research studies have shown that mitochondrial disorders are considered the most frequent genetic diseases and can have a high incidence of cardiac involvement with metabolic disturbances. This will increase membrane permeability and dysfunction results in both abnormal intracellular and extracellular signaling mechanisms. This includes the endothelium, enterocyte, brain dysfunction, and all other cell membranes that can affect the cardiovascular system if they are dysfunctional.
Continuum Of Risk
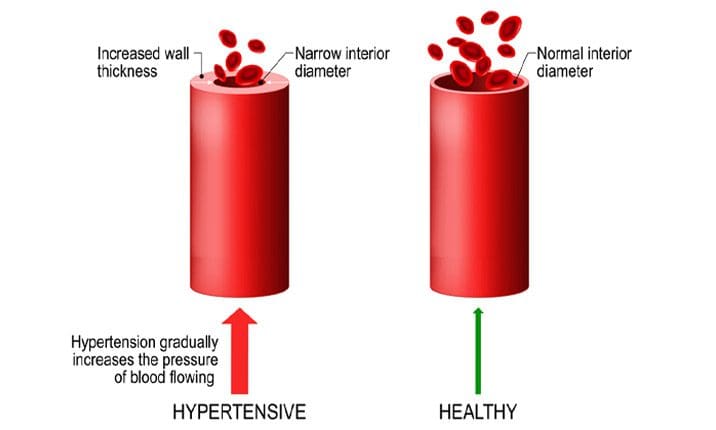
There is a progressive continuum of risk within the chronic heart disease risk factors and mediators that affect the blood vessels in the heart can be leading initially to functional abnormalities (endothelial dysfunction) then to structural abnormalities ( VSMH, arterial stiffness, LVH, carotid IMT), and eventually to preclinical and clinical cardiovascular disease. The vascular system provides transport and integrative biological activity with cell dominance to deliver micronutrients, oxygen and engage in metabolism, communication, and excretion.
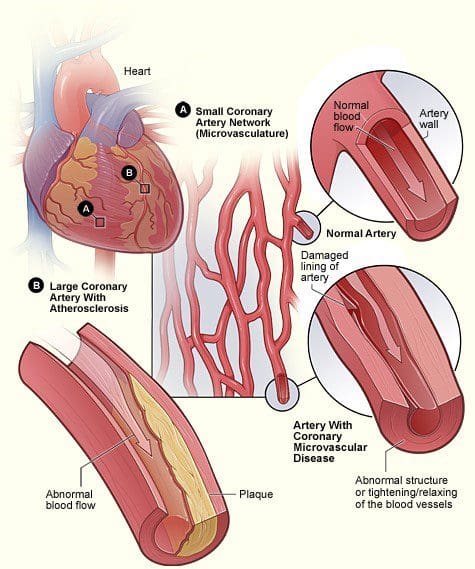
Risk Factors For Vascular Disease
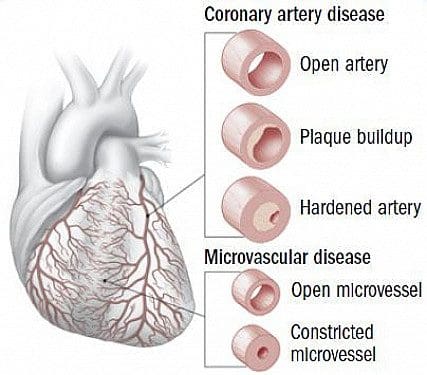
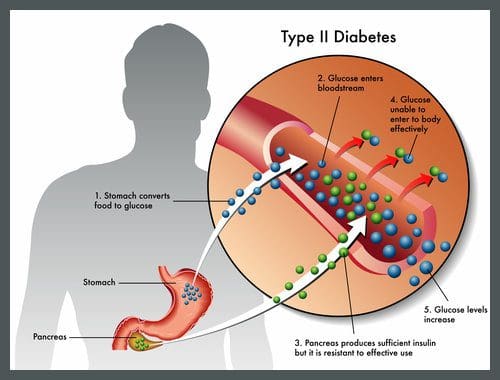
It is important to measure sensitive indicators of endothelial dysfunction and vascular disease to determine if the risk factors and insults induce vascular responses with functional and/or structural abnormalities. Studies have shown that vascular disease is a circulatory problem that causes reduced blood flow through the arteries that can cause either thigh or calf pain during walking or exertion. Standard chronic heart disease risk factors that do not adequately identify at-risk individuals and early detection with aggressive treatment will reduce cardiovascular disease, chronic heart disease, and chronic heart failure. Other research studies have shown that vascular disease has been associated with multiple risk factors which include smoking, diabetes, prior coronary artery disease, and even a sedentary lifestyle. These risk factors if not treated or changed can cause vascular disease to progress further to chronic illnesses.
Conclusion
By figuring out the diagnosis of cardiovascular diseases and figuring out what it can cause to the body, is essential to know that changing a certain lifestyle is essential for optimal wellness. The cardiovascular system’s job is to make sure that blood is flowing throughout the body and transporting oxygen-riched blood, nutrients, and hormones to each of the organs. When there are disruptors that can affect the cardiovascular system and the body, it can cause many risk factors to pop up if it is not treated. By catching the risk factors early and changing a person’s lifestyle habits with functional medicine, the individual can being their wellness journey risk-free.
References
Barthelmes, Jens, et al. “Endothelial Dysfunction in Cardiovascular Disease and Flammer Syndrome-Similarities and Differences.” The EPMA Journal, Springer International Publishing, 6 June 2017, https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5545991/.
Bisaccia, Giandomenico, et al. “Mitochondrial Dysfunction and Heart Disease: Critical Appraisal of an Overlooked Association.” International Journal of Molecular Sciences, MDPI, 9 Jan. 2021, https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7827742/.
Gul, Fahad, and Sean F Janzer. “Peripheral Vascular Disease.” StatPearls [Internet]., U.S. National Library of Medicine, 29 Apr. 2021, https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK557482/.
Medical Professionals, Cleveland Clinic. “Cardiovascular System: Overview, Anatomy and Function.” Cleveland Clinic, 13 Sept. 2021, https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/body/21833-cardiovascular-system.
National Center for Biotechnology Information (US). “The Heart and Blood Vessels.” Genes and Disease [Internet]., U.S. National Library of Medicine, 1 Jan. 1998, https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK22227/.
Stewart, Jack, et al. “Primary Prevention of Cardiovascular Disease: A Review of Contemporary Guidance and Literature.” JRSM Cardiovascular Disease, SAGE Publications, 1 Jan. 2017, https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5331469/.
Thiriet, Marc. “Cardiovascular Disease: An Introduction.” Vasculopathies: Behavioral, Chemical, Environmental, and Genetic Factors, U.S. National Library of Medicine, 19 Feb. 2019, https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7123129/.
Zemaitis, Michael R. “Peripheral Arterial Disease.” StatPearls [Internet]., U.S. National Library of Medicine, 9 Jan. 2022, https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK430745/.