Nerves control muscle fibers. Muscle twitching is an involuntary contraction of the muscle fibers. When individuals play sports/work out vigorously or for a long time, they may experience muscle twitching and can often see and/or feel the twitches happening. The most worked-out muscles are likely to twitch, which includes the biceps, thighs, and calves, but twitches can occur in any muscle. Chiropractic care, massage therapy, and functional medicine can help relax the muscles, improve circulation, restore function, and train individuals to prevent future episodes.
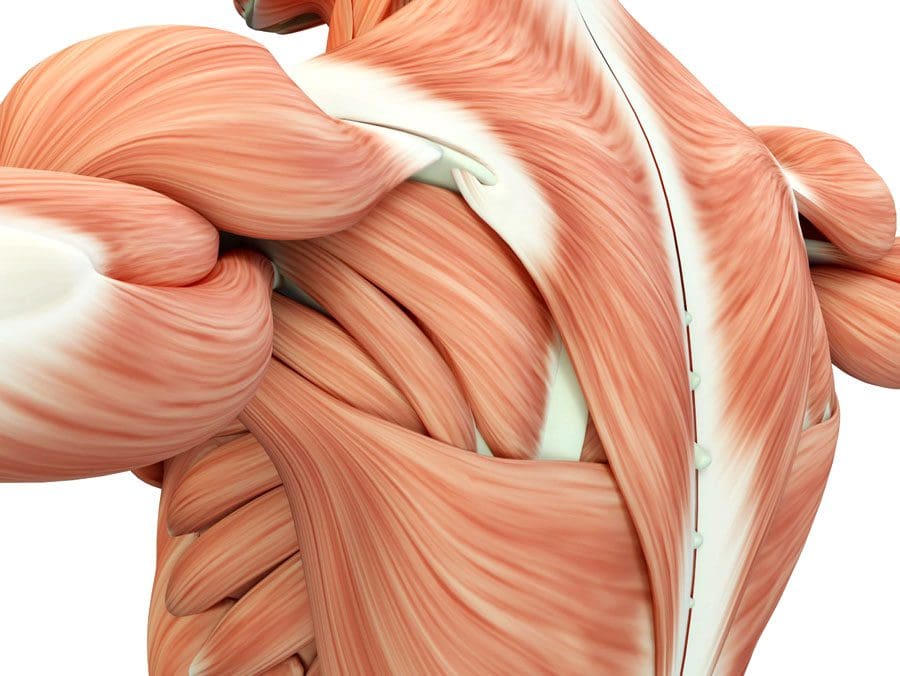
Table of Contents
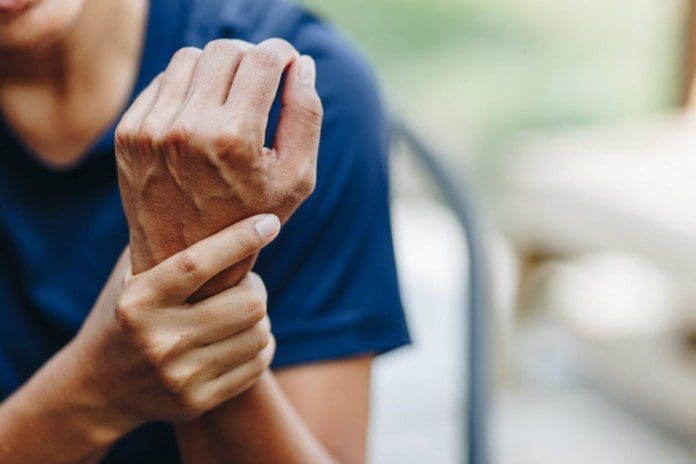
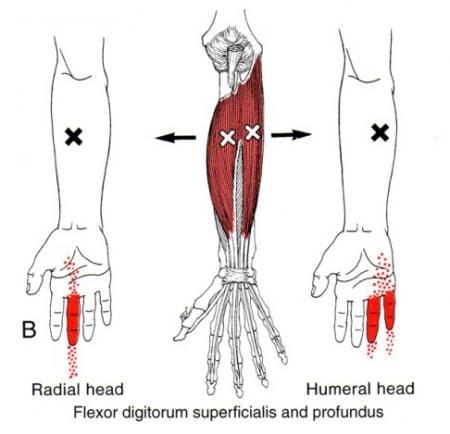
Muscle Twitching
A muscle twitch often occurs after intense physical activity or a hard workout because the muscle or muscles have been overworked, and there is hyper-excitability of the nerve/s that makes the muscle/s continue to contract.
- A muscle twitch that can be seen is called fasciculation.
- A muscle twitch that cannot be seen is called fibrillation.
- If there is pain or the twitching is prolonged, it is a muscle spasm.
Causes
The most common causes include the following:
- Intense exercise and rigorous physical activity build up lactic acid in the muscles.
- Dehydration is a very common factor for shaky muscles.
- Vitamin D and calcium deficiencies could cause muscle spasms in the hand, calves, and eyelids.
- Using caffeinated products to increase physical performance.
- Not enough or a lack of healthy sleep.
- Anxiety or stress.
- Certain medications like estrogen and corticosteroids.
- Nicotine and tobacco use.
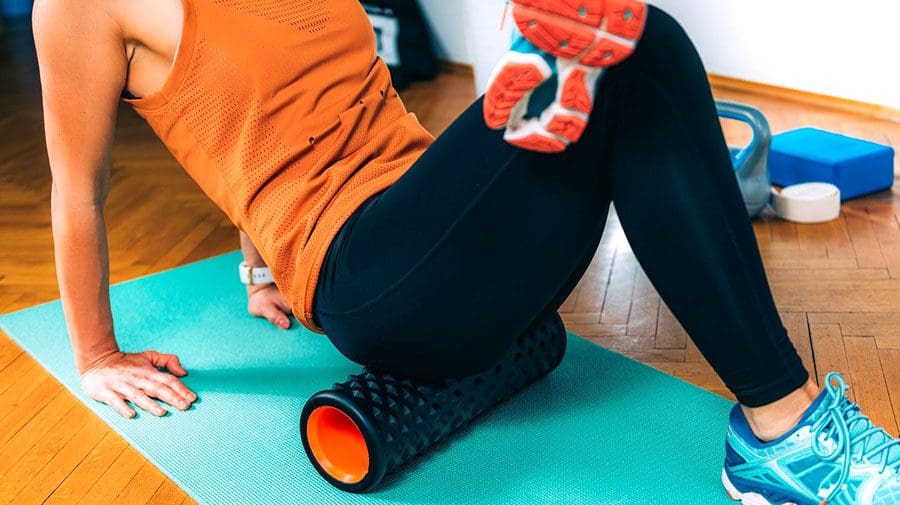
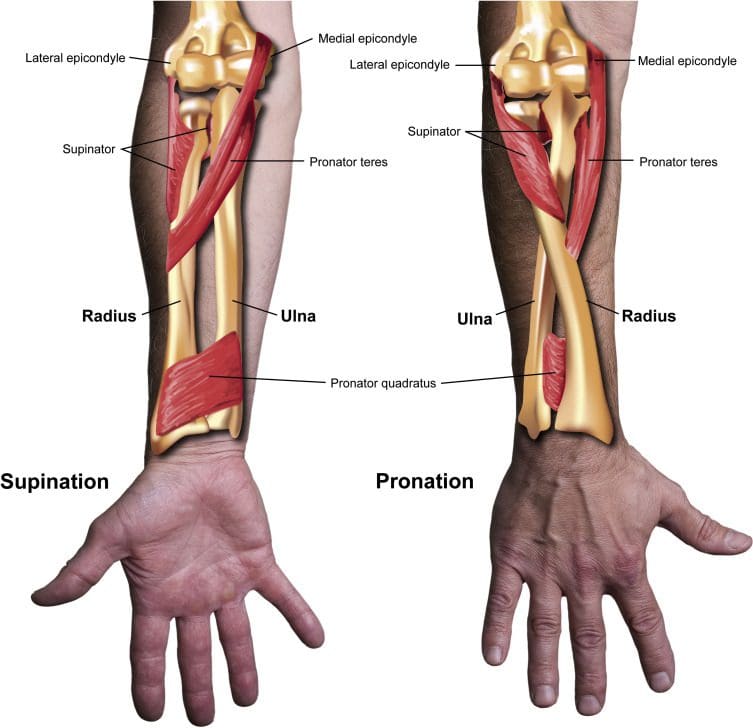
Physical Activity/Exercise
- Intense exercise and physical activity can cause muscle fatigue.
- Muscle fatigue triggers twitching and cramping in overworked muscle fibers.
- Electrolytes play a role in muscle contraction.
- Electrolyte loss and imbalances within muscle fibers through sweating can lead to twitching.
Dehydration
- Muscle mass comprises 75% water.
- Water carries nutrients and minerals to muscles to support function.
- Not being properly hydrated can cause twitching and cramping.
Vitamin D Deficiency
- Nerves need vitamin D to relay messages to and from the brain to the body’s muscles.
- A vitamin D deficiency can cause muscle weakness and twitching.
Magnesium Deficiency
- Magnesium deficiency is known as hypomagnesemia.
- Magnesium plays a role in maintaining nerve and muscle health.
- Magnesium helps transport calcium across cell membranes to support nerve and muscle function.
- A magnesium deficiency can cause twitching anywhere in the body, including the face.
Causes of magnesium deficiency include:
- Poor diet
- Diarrhea
- Drinking too much alcohol
- Not addressing magnesium deficiency can increase the risk of cardiovascular disease.
Caffeine
- Caffeine is a stimulant.
- Drinking too much coffee, tea, or energy drinks can cause fasciculation.
Not Enough Sleep
- Brain chemicals or neurotransmitters transmit information from the brain to the nerves that control muscle contraction.
- Sleep deprivation can affect how neurotransmitter receptors work.
- This means excess neurotransmitters can build up in the brain.
- Lack of sleep can affect neurotransmitter function.
- A common site of fasciculation tiredness occurs in the eyelids.
Anxiety and Stress
- Experiencing psychological stress or high anxiety levels can cause excess muscle tension.
- This can lead to muscle twitching.
- Muscle fasciculation caused by stress can occur anywhere in the body.
Certain Medications
- Certain medications can lead to involuntary muscle twitching.
- The reaction can be a side effect due to interactions with other medications.
- Individuals should discuss side effects and medication interactions with their doctor when taking a new medication.
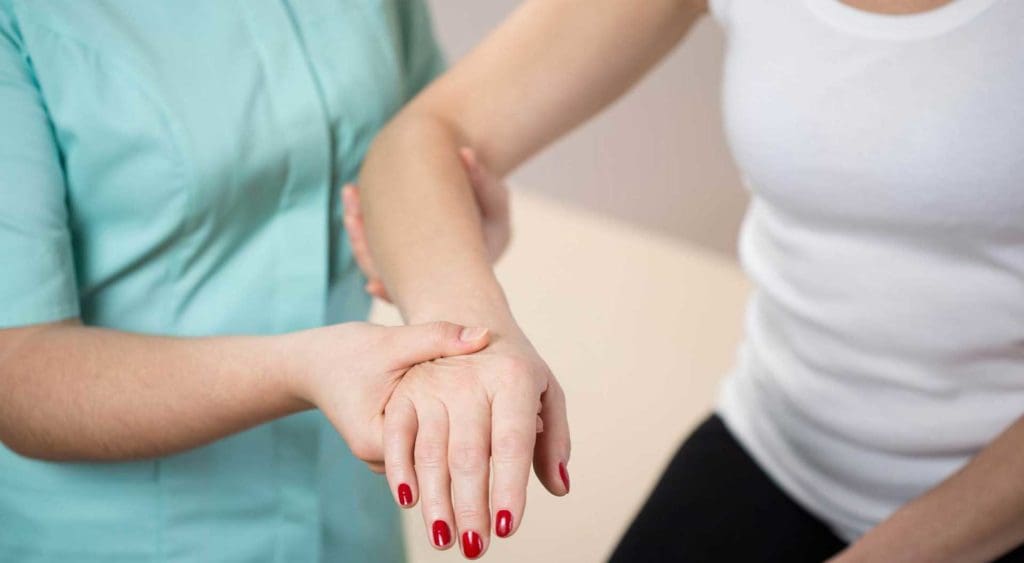
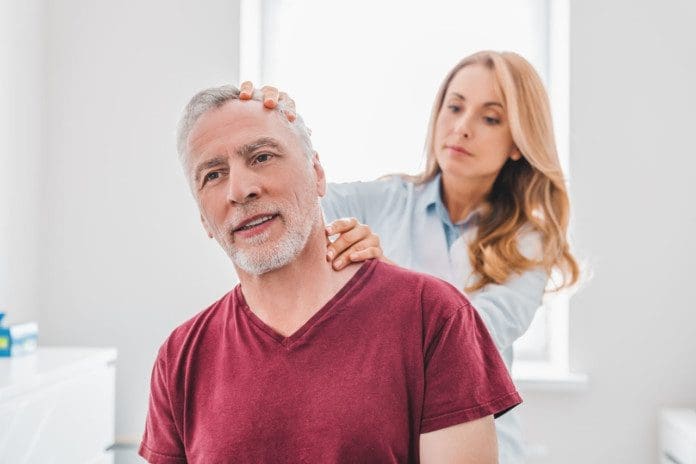
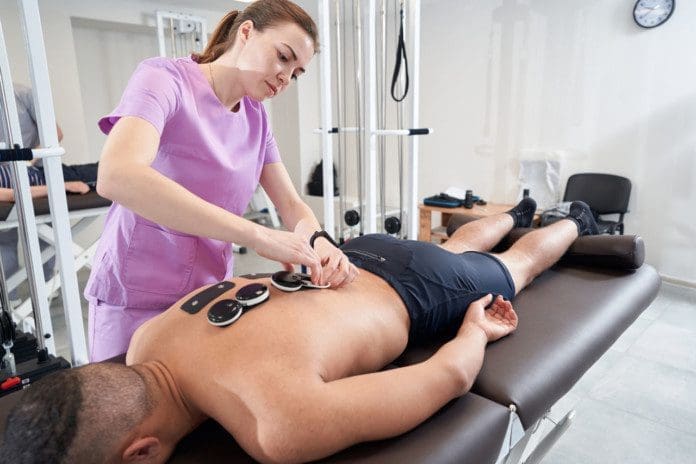
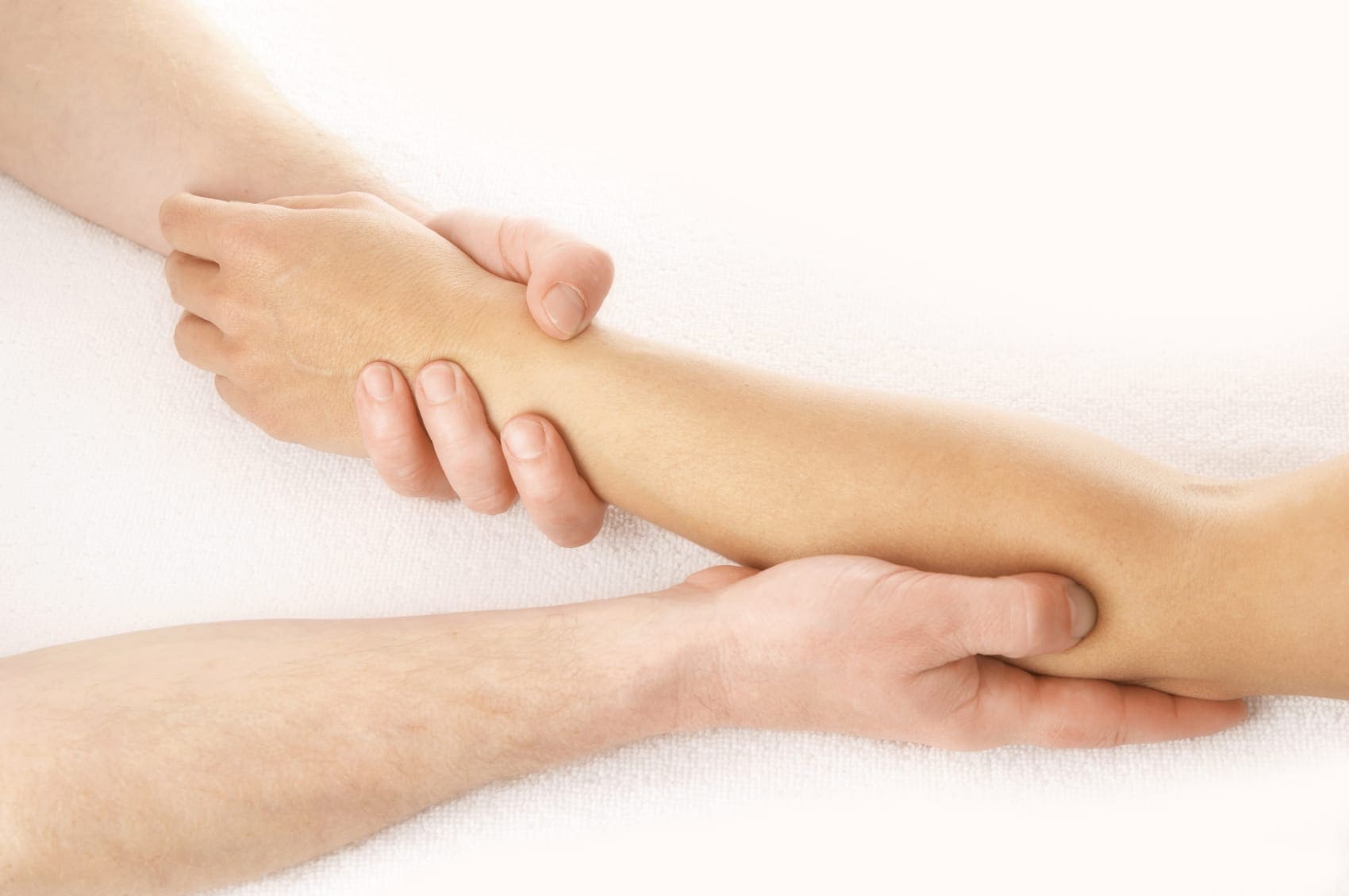
Chiropractic Care
Chiropractors are experts on the musculoskeletal system and have many techniques to treat muscle fasciculation and spasms. It often depends on the cause/s, and specific treatment varies on a case-by-case basis. Common chiropractic treatments include:
- Massage therapy
- Heat and ice therapy
- Manual manipulation
- Joint adjustments
- Ultrasound
- Stretches to keep the muscles flexible
- Exercises to strengthen the muscles
- Nutritional recommendations
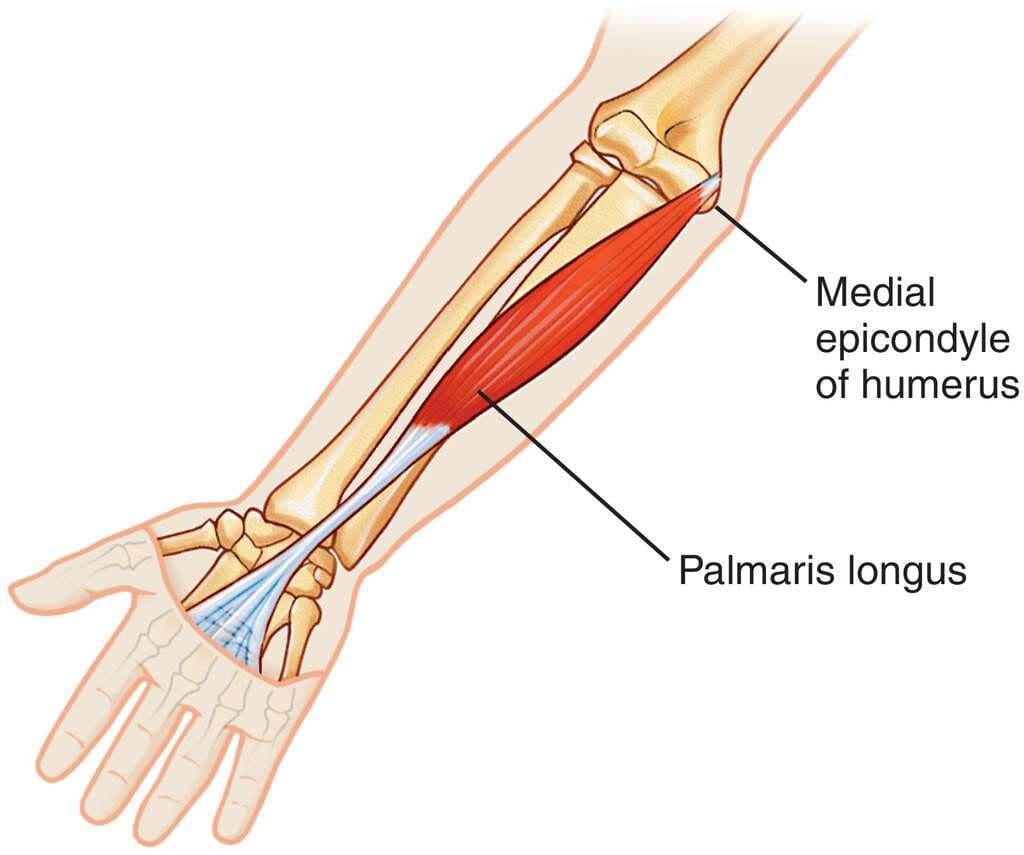
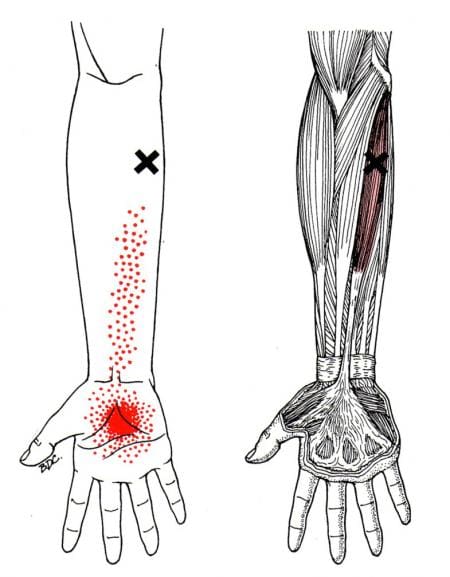
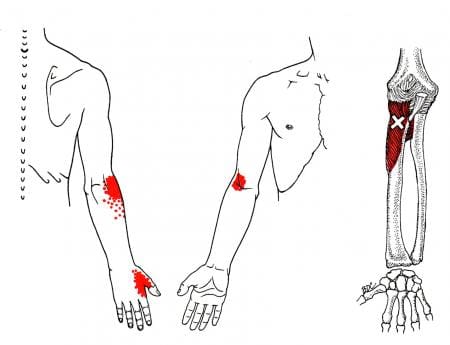
Fasciculation
References
Bergeron, Michael F.. Muscle Cramps during Exercise-Is It Fatigue or Electrolyte Deficit?. Current Sports Medicine Reports July 2008 – Volume 7 – Issue 4 – p S50-S55 doi: 10.1249/JSR.0b013e31817f476a
Gragossian A, Bashir K, Friede R. Hypomagnesemia. [Updated 2022 May 15]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (F.L.): StatPearls Publishing; 2022 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK500003/
Küçükali, Cem Ismail, et al. “Peripheral nerve hyperexcitability syndromes.” Reviews in the neurosciences vol. 26,2 (2015): 239-51. doi:10.1515/revneuro-2014-0066
Maughan, Ronald J, and Susan M Shirreffs. “Muscle Cramping During Exercise: Causes, Solutions, and Questions Remaining.” Sports medicine (Auckland, N.Z.) vol. 49, Suppl 2 (2019): 115-124. doi:10.1007/s40279-019-01162-1
Miller, Kevin C et al. “Exercise-associated muscle cramps: causes, treatment, and prevention.” Sports health vol. 2,4 (2010): 279-83. doi:10.1177/1941738109357299
Riebl, Shaun K, and Brenda M Davy. “The Hydration Equation: Update on Water Balance and Cognitive Performance.” ACSM’s health & fitness journal vol. 17,6 (2013): 21-28. doi:10.1249/FIT.0b013e3182a9570f















 Headache Chiropractor
Headache Chiropractor