Table of Contents
Introduction
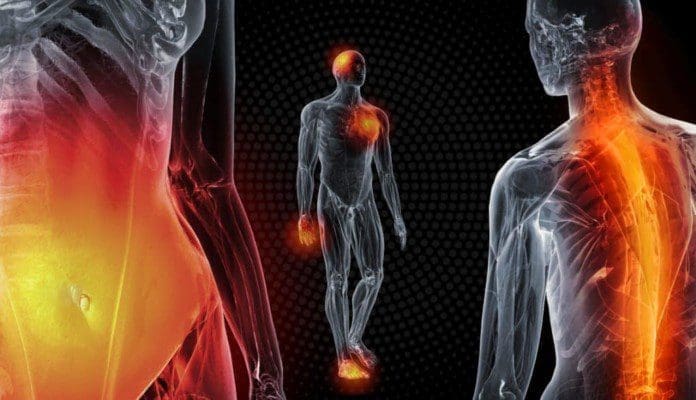
Around the world, many individuals will have some reaction to the foods they consume. This type of reaction can lead to a series of unwanted symptoms that affect not only the vital organs of the body but also the musculoskeletal system. This allergic reaction can cause inflammatory effects that lead to joint pain and swelling while affecting a person’s quality of life. Inflammation is the body’s natural defense response from the immune system to repair the body inside and out. When food allergies start to affect the entire body, it can cause the individual to be in constant pain, and many individuals will go to treatments to reduce the symptoms caused by food allergic reactions; however, the residual effects of the allergic reaction can still interfere with the body and affect the musculoskeletal system. Today’s article focuses on food allergies, how they are associated with inflammation in the musculoskeletal system, and how MET therapy can help relieve inflammation associated with food allergies. We utilize and provide valuable information about our patients to certified medical providers who use soft tissue stretching methods like MET to reduce inflammation associated with food allergies affecting the musculoskeletal system. We encourage patients by referring them to our associated medical providers based on their findings. We support that education is a marvelous way to ask our providers the most interesting questions at the patient’s acknowledgment. Dr. Alex Jimenez, D.C., incorporates this information as an educational service. Disclaimer
What Are Food Allergies?
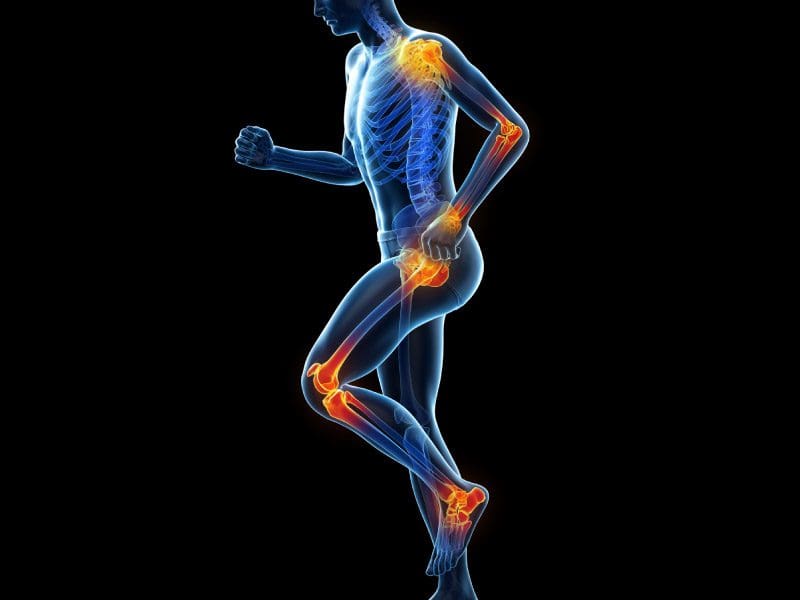
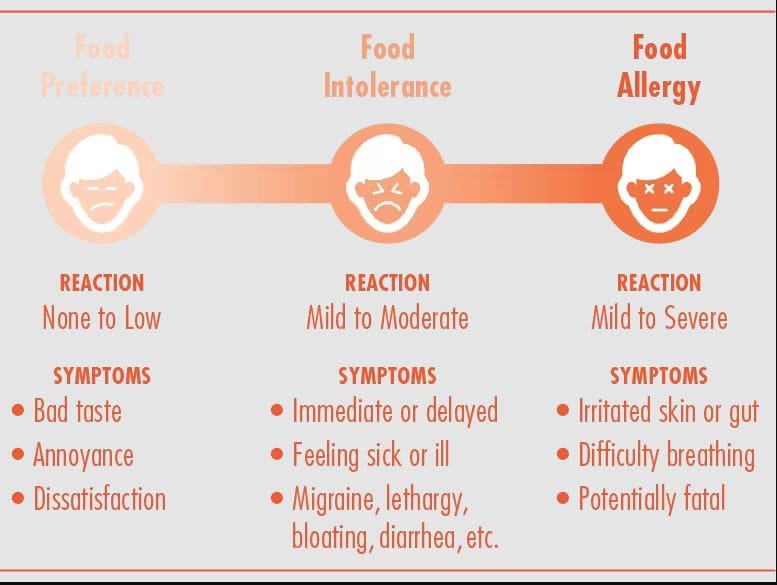
Have you been dealing with muscle swelling in different locations of your body? Do you see redness or feel a burning sensation in your muscles? Or do your muscles and joints feel achy throughout the day? Many of these pain-like symptoms are associated with inflammatory effects caused by food allergies. Research studies have revealed that food allergies are often defined as an immune reaction to food proteins that many individuals worldwide and, when indigested, are responsible for various symptoms that involve the skin, gastrointestinal tract, and respiratory tract. Many individuals would often confuse a food allergy with food intolerance since the musculoskeletal and gastrointestinal systems are caused by inflammation. Research studies have found that food intolerances are non-immunological responses that cause numerous symptoms and hypersensitivity to the body. Many factors correlate to food intolerances, and food allergies can affect the musculoskeletal system with pain-like symptoms like inflammation.
Food Allergies Associated With Inflammation In The Musculoskeletal System
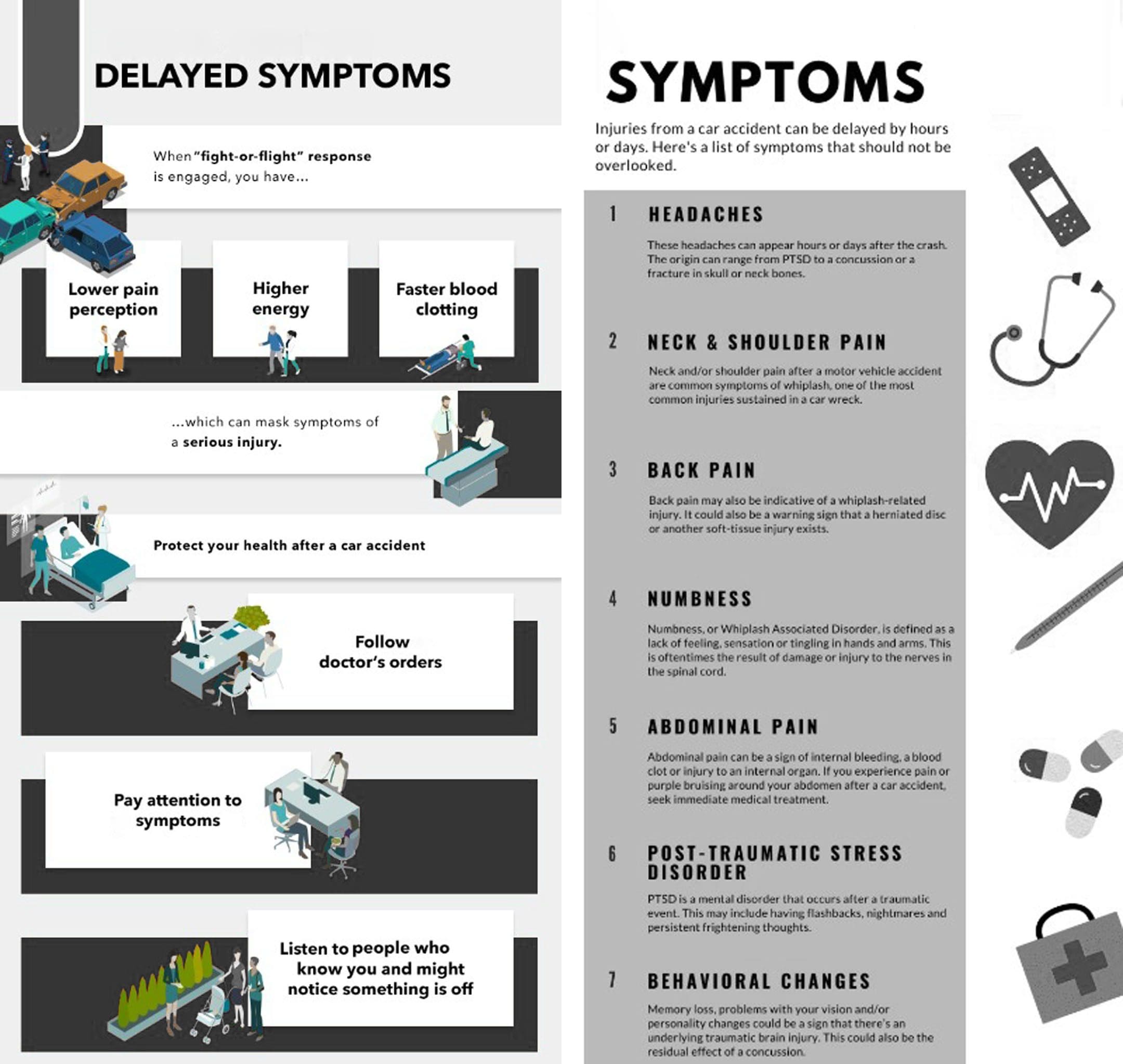
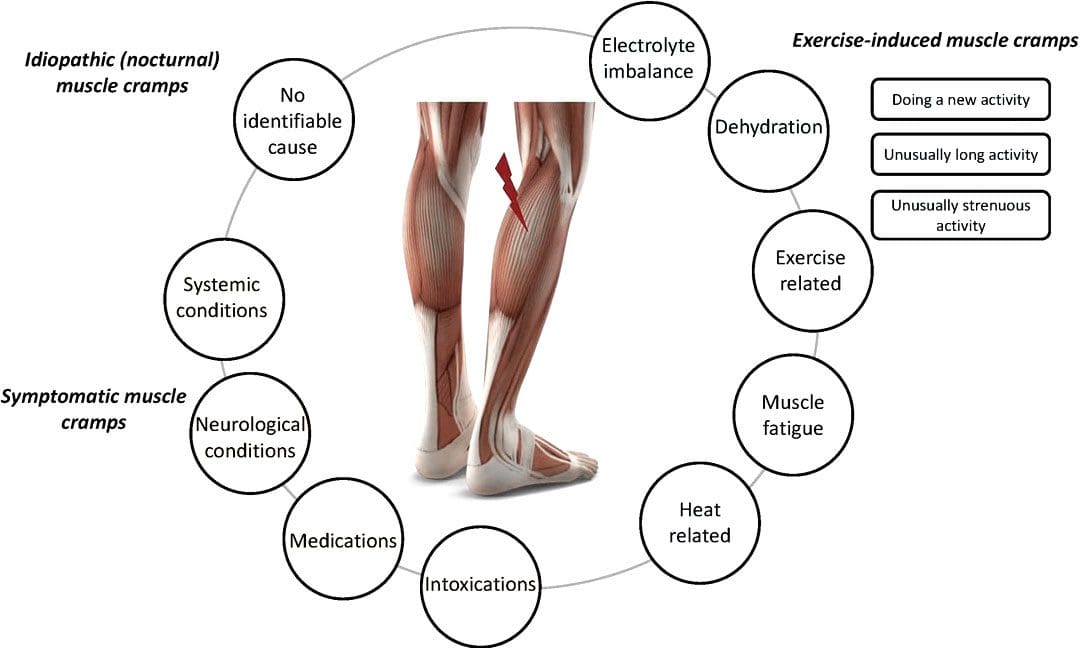
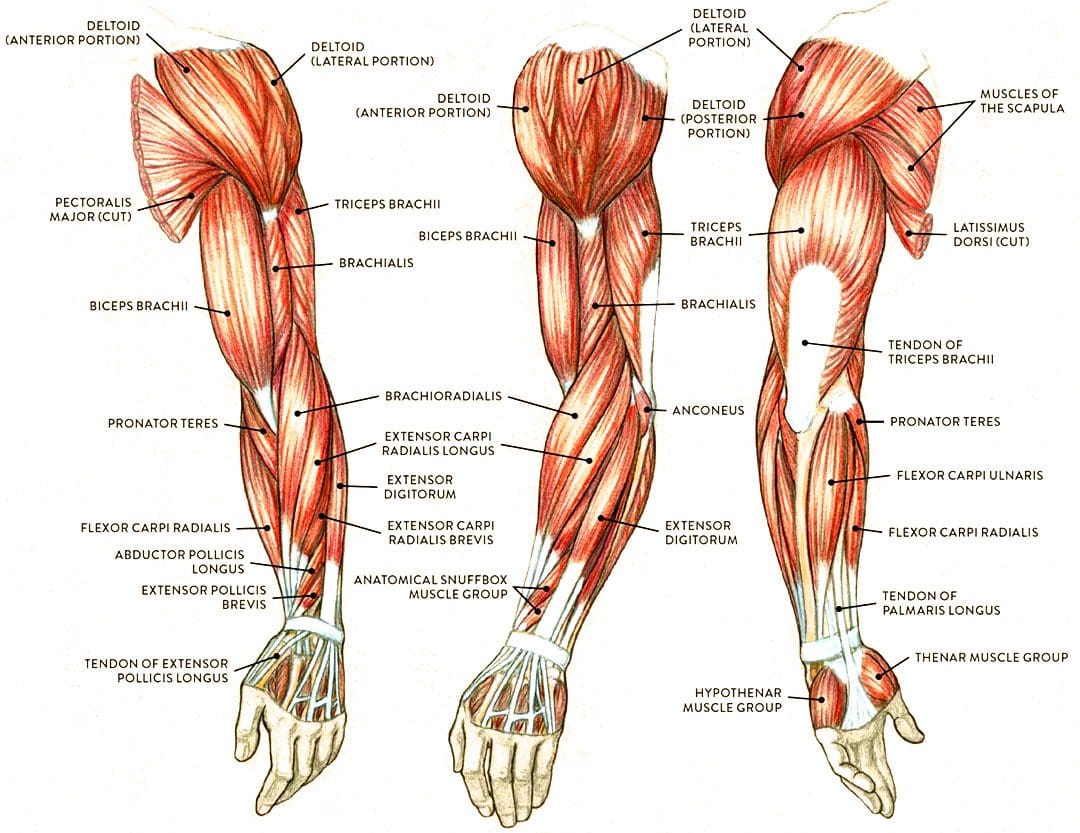
When food allergies or food intolerances occur in the body, it can cause the individuals to have unwanted pain-like symptoms to cause inflammation to appear in the body. When it comes to inflammation in the body, it is produced by the immune system. It helps repair old cells and attack foreign invaders affecting the musculoskeletal system. In “Clinical Applications of Neuromuscular Techniques,” Dr. Leon Chaitow, N.D., D.O., and Dr. Judith Walker DeLany, L.M.T. stated that specific individualized pathophysiological responses exist to many foods and liquids that are being taken accounted for a significant amount of overlapping symptoms being produce. The book also states that it includes pain and discomfort to the musculoskeletal system. To that point, to figure out these presenting symptoms, whatever allergic pathogen is being derived from the food itself could be the result. Additional studies mentioned that food allergies and tolerances are sometimes not established when inflammation from the GI tract and causing pain-like symptoms associated with the musculoskeletal system. Fortunately, there are various treatments to reduce the effects of food allergies and intolerances while restoring the musculoskeletal system.
The Benefits Of A Healthy Diet & Chiropractic Care-Video

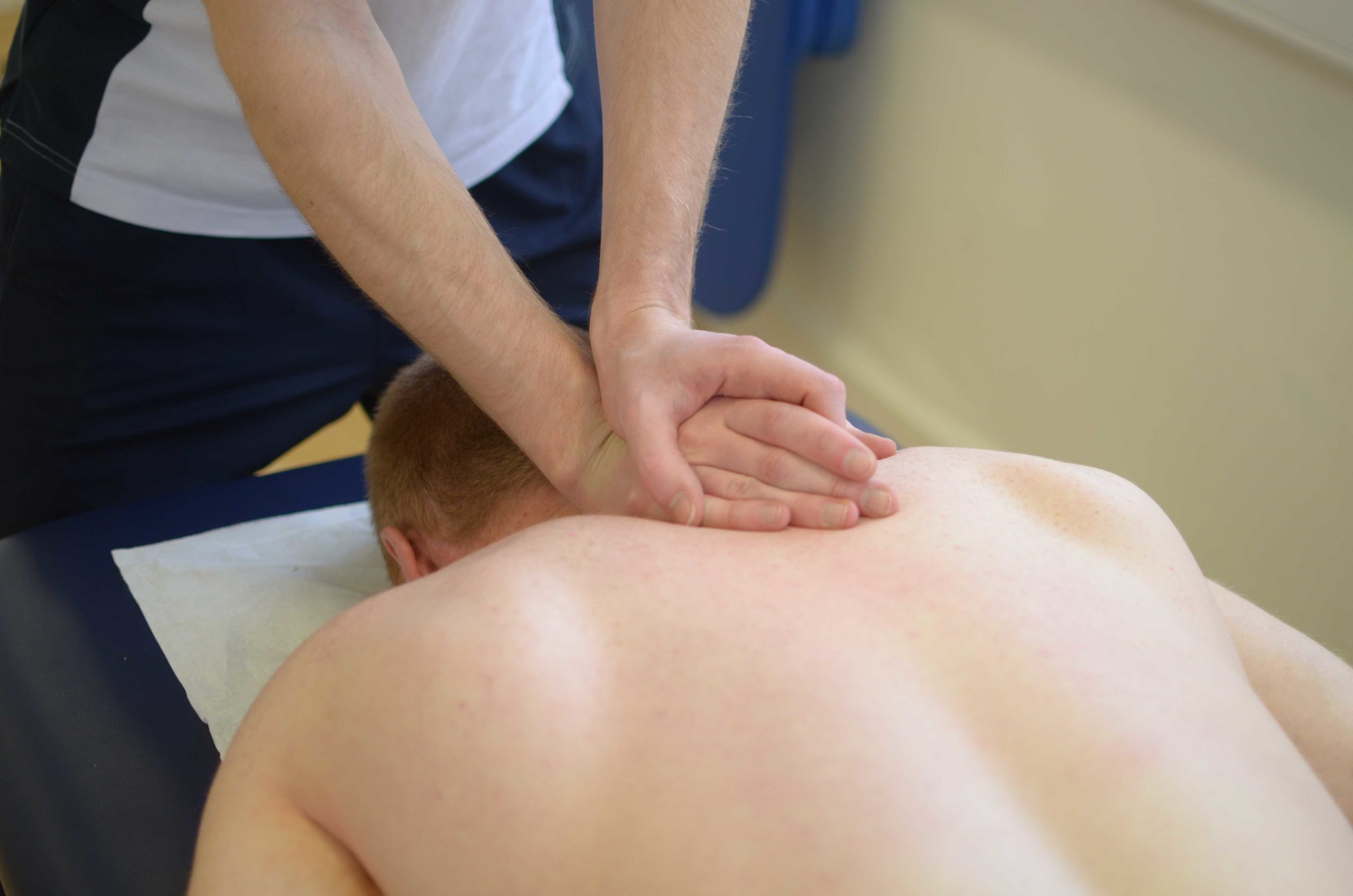
Have you been dealing with gut inflammation that is affecting your musculoskeletal system? Are you experiencing aches and pains throughout your entire body? Or do you have joint issues that are causing you limited mobility? Many of these issues are associated with food intolerances and allergies that can cause inflammation of the musculoskeletal system leaving the individual in pain. Fortunately, there are many ways to reduce the effects of inflammation associated with food allergies. The video above explains how eating the right foods while being considerate of food allergies can be combined with treatment like chiropractic care, which can help reduce inflammation while realigning the body through manual manipulation. Chiropractors also use soft tissue techniques like MET to help regain joint mobility and reduce the effects of inflammation-causing muscle and joint stiffness.
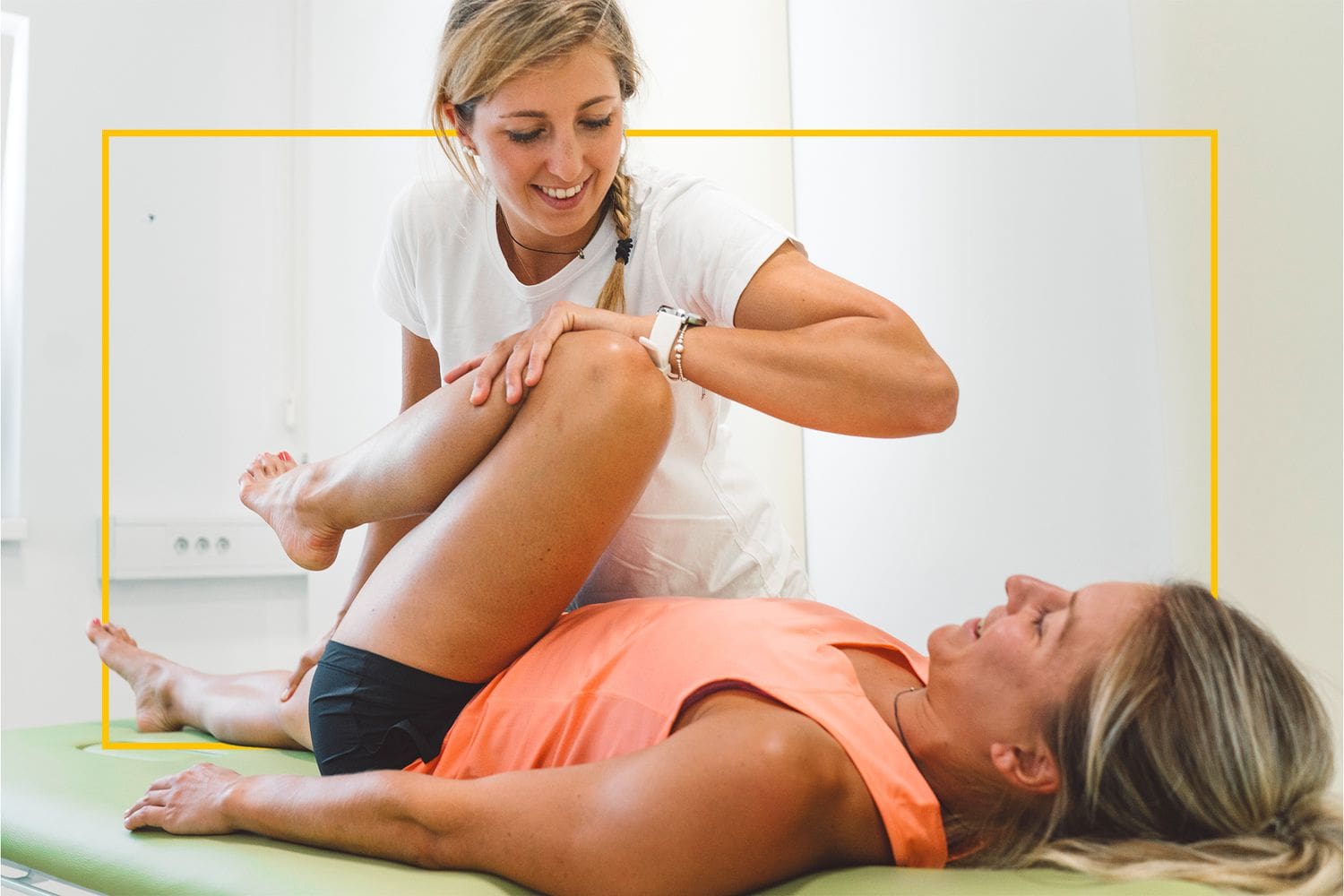
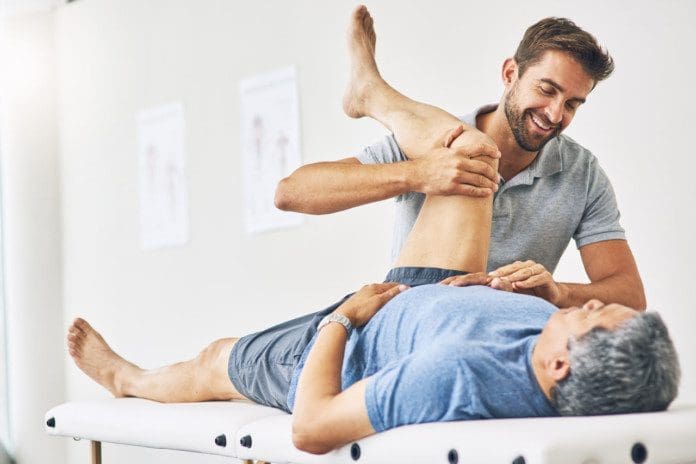
MET Therapy Relieving Inflammation Associated With Food Allergies
Therapies like soft tissue massages, massage therapy, physical therapy, or chiropractic care all work together with having a nutritional diet plan to prevent flare-ups from food allergies and intolerances. Research studies have found that MET helps stretch the affected muscles induced by inflammation associated with food allergies. This technique allows the body to naturally heal itself and prevent inflammation from exceeding more into the body. Combined with anti-inflammatory foods, many individuals know what food they can and can not consume. Additionally, it allows them to be more mindful of their bodies and sends them on the right track of their health and wellness journey.
Conclusion
Overall, many individuals often confuse food allergies and food intolerances, which can cause the musculoskeletal system to be dealing with symptoms of inflammation and pain. Since inflammation is the body’s natural defense system, it is important to be mindful of what is consumed to prevent overlapping risk profiles from causing muscle and joint pain. Luckily, numerous treatments are available to reduce the effects of chronic inflammation associated with food allergies and help the body naturally heal itself. Combining treatments like MET and a healthy nutritional diet can help the body reduce the effects of inflammation from affecting the musculoskeletal system while also allowing the individual to make smart choices in their health and wellness journey.
References
Chaitow, Leon, and Judith Walker DeLany. Clinical Applications of Neuromuscular Techniques. Churchill Livingstone, 2003.
Lopez, Claudia M, et al. “Food Allergies – Statpearls – NCBI Bookshelf.” In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL), StatPearls Publishing, 31 Jan. 2023, https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK482187/.
Ohtsuka, Yoshikazu. “Food Intolerance and Mucosal Inflammation.” Pediatrics International : Official Journal of the Japan Pediatric Society, U.S. National Library of Medicine, 2015, https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25442377/.
Sbardella, Silvia, et al. “Muscle Energy Technique in the Rehabilitative Treatment for Acute and Chronic Non-Specific Neck Pain: A Systematic Review.” Healthcare (Basel, Switzerland), U.S. National Library of Medicine, 17 June 2021, https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8234422/.
Tuck, Caroline J, et al. “Food Intolerances.” Nutrients, U.S. National Library of Medicine, 22 July 2019, https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6682924/.







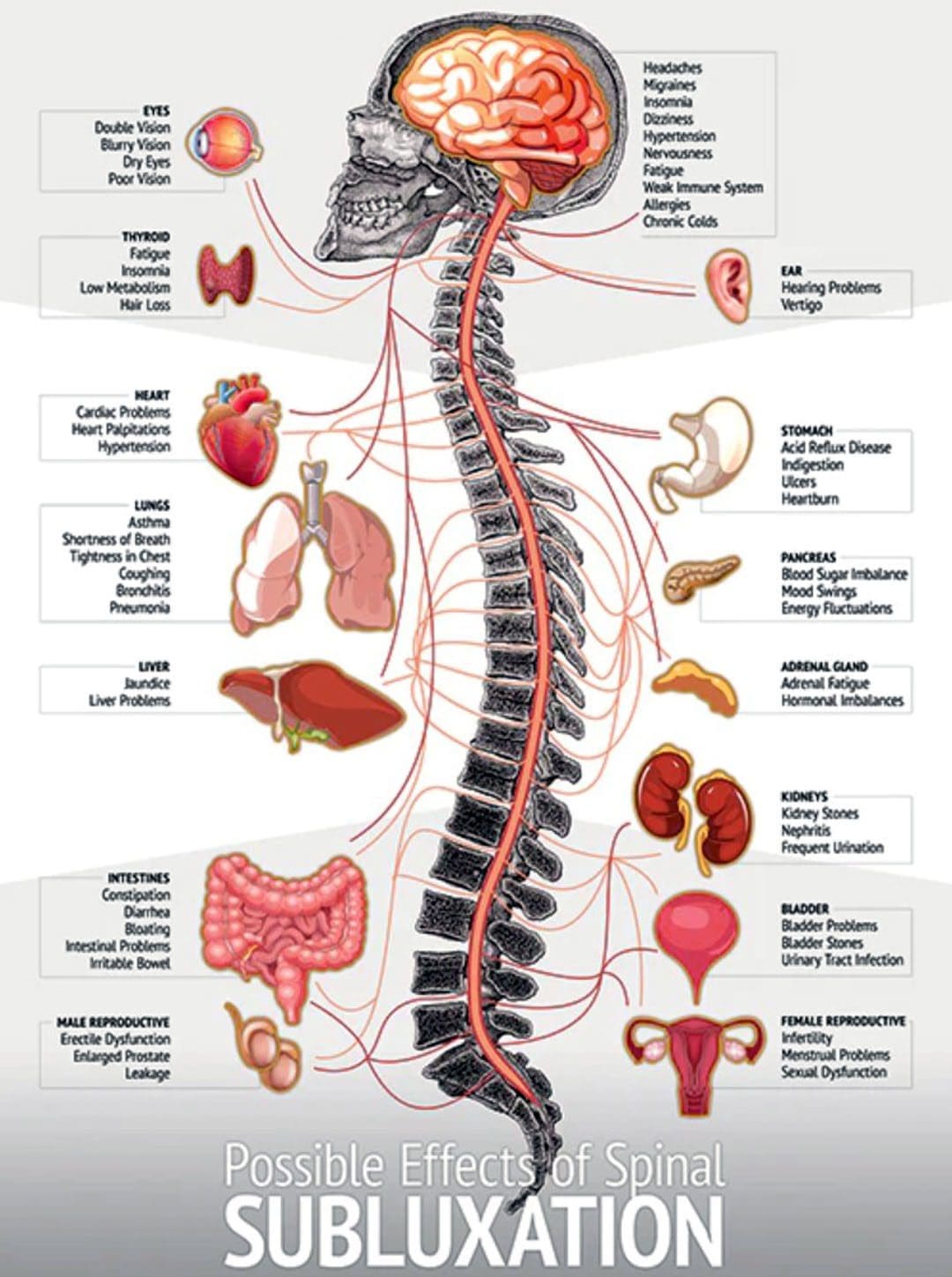
 Why The Spine Goes Out of Alignment
Why The Spine Goes Out of Alignment