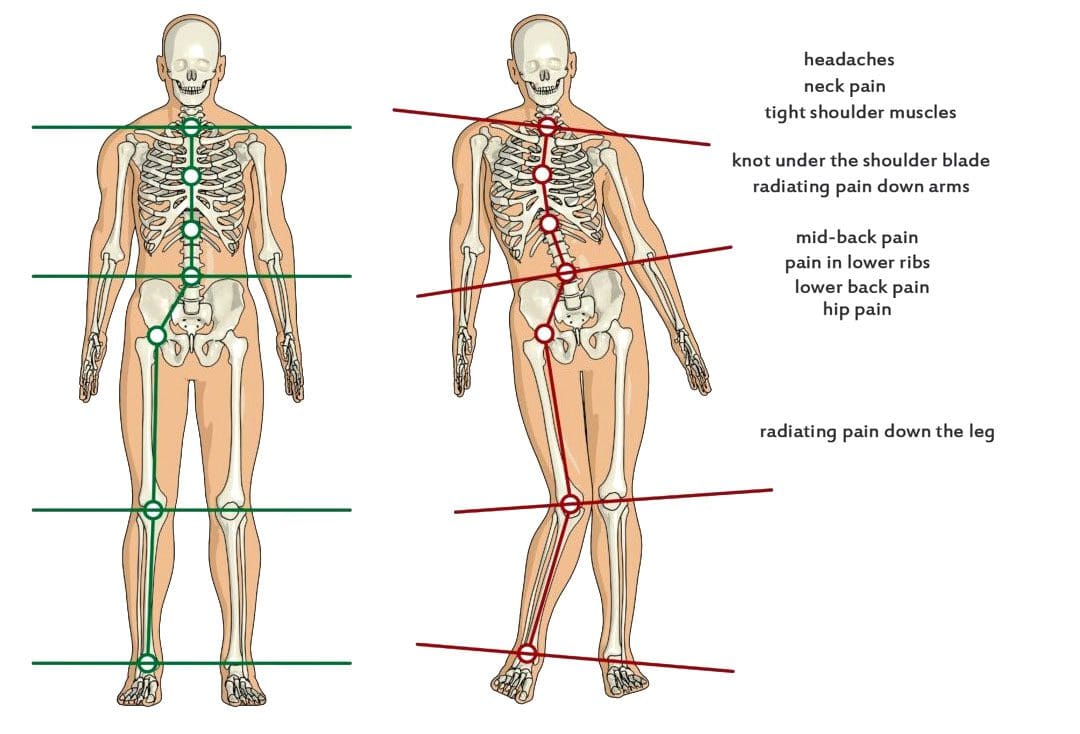
Sitting at a desk or standing at a workstation in the same position for hours at a time every day or night can strain the body’s neuromusculoskeletal system. This causes hunching of the shoulders which leads to body tension, headaches, and neck, shoulder, back, leg, and foot pain. Taking regular breaks to move and stretch out provides various benefits that include pain symptom relief, increased circulation, improved posture, increased energy, muscle relaxation, and improve overall health. Here we look at stretches for sitting and standing jobs.

Table of Contents
Stretches For Sitting and Standing Jobs
Sitting or standing for too long can affect an individual’s health. The body is made to move and not remain in one position for long periods. Standing and sitting for a prolonged period of time increases the risk for chronic conditions, sleep disorders, digestion issues, weight gain, obesity, heart disease, cancer, and diabetes. To help break the cycle of staying in one position, experts recommend taking movement breaks for one to three minutes every 30 to 45 minutes, or at least once an hour.
Individuals are encouraged to find ways to set up a job/work system where they are not limited to just sitting or standing but have a balance where they can move around, do some desk work, move some more, and so on where the body is regularly engaging all the muscles and not only using a few that often leads to overworked muscles and overcompensating postures that lead to injuries. This can be using a standing desk, taking quick short walks, or doing some stretches. Movement loosens up the body and helps maintain mental focus.
Flexibility Breaks
The following stretches for sitting and standing jobs are recommended to be done as often as possible to develop healthy habits.
- Set an alarm for every 45 to 55 minutes and perform the stretches.
- Hold each stretch for at least 15-30 seconds.
- Avoid exercises or stretches that cause discomfort or pain.
Chest Stretch
Many individuals begin to hunch forward. Therefore, it is essential to stretch the pectoral/chest muscles and shoulders. Individuals with shoulder problems or injuries should avoid this stretch.
- Stand with the feet shoulder-width apart.
- The stretch can be performed seated in a chair.
- Move the arms behind the body and, if possible, interlock the fingers together.
- Straighten the arms and gently lift the hands up until you feel a stretch in the chest.
- Hold for 10 to 30 seconds.
- Repeat 5-10 times.
- Individuals can also use a resistance band and hold it overhead.
- Individuals can put their forearms on either side of a doorway, and gently press forward until the stretch is felt in the chest.
Upper Back Stretch
The upper back stretch will help get circulation moving in all the muscles between the shoulder blades as well as the traps and the shoulders.
- Begin in a seated or standing position.
- Stretch the arms straight out.
- Place one hand on top of the other.
- Reach away with your arms.
- Relax and gently bend the head down.
- Imagine the arms curving up and over an imaginary sphere.
- Hold the stretch for 10 to 30 seconds.
Neck Stretch
Tension in the neck can lead to headaches and upper back pain. Forward head posture is common when working at a desk/workstation, which places extra weight and stress on the neck muscles. The head can weigh up to 11 pounds. Staying aware of posture and regular stretching can provide relief.
- Start in a sitting position, with the back straight and the shoulders back.
- Reach down and grab the side of the chair with your hand.
- Gently pull on the chair, while tilting the head in the opposite direction, feeling the stretch down the side of the neck and shoulder.
- Hold for 10 to 30 seconds and repeat on the other side.
- Repeat five to 10 times on each side.
Inner Thigh Stretch
Stretching the inner thigh is important for the hips and groin. This stretch helps open the hips and gets rid of tightness and tension in the lower body.
- In a seated position, widen the legs, toes outward, and lean forward with the elbows on the thighs.
- Keep the back straight and the abs contracted.
- Gently press forward while using the elbows to push the thighs out until a stretch is felt in the inner thighs.
- Hold for 10 to 30 seconds.
- Repeat as many times as necessary to get a thorough stretch.
Regular stretching will help to improve the range of motion and help the muscles move more efficiently. Stretching may also help individuals reach or maintain a healthy weight for improved posture.
Benefits of Stretching
References
Cooley D, Pedersen S. A pilot study of increasing non-purposeful movement breaks at work as a means of reducing prolonged sitting. J Environ Public Health. 2013;2013:128376. doi:10.1155/2013/128376
Daneshmandi H, Choobineh A, Ghaem H, Karimi M. Adverse effects of prolonged sitting behavior on the general health of office workers. J Lifestyle Med. 2017;7(2):69-75. doi:10.15280/jlm.2017.7.2.69
Fathollahnejad, Kiana, et al. “The effect of manual therapy and stabilizing exercises on the forward head and rounded shoulder postures: a six-week intervention with a one-month follow-up study.” BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders vol. 20,1 86. 18 Feb. 2019, doi:10.1186/s12891-019-2438-y
Feldman, Anatol G. “The Relationship Between Postural and Movement Stability.” Advances in experimental medicine and biology vol. 957 (2016): 105-120. doi:10.1007/978-3-319-47313-0_6
Korakakis, Vasileios, et al. “Physiotherapist perceptions of optimal sitting and standing posture.” Musculoskeletal Science & Practice vol. 39 (2019): 24-31. doi:10.1016/j.msksp.2018.11.004
Lurati AR. Health issues and injury risks associated with prolonged sitting and sedentary lifestyles. Workplace Health Saf. 2018;66(6):285-290. doi:10.1177/2165079917737558
Nakphet N, Chaikumarn M, Janwantanakul P. Effect of different types of rest-break interventions on neck and shoulder muscle activity, perceived discomfort and productivity in symptomatic VDU operators: A randomized controlled trial. Int J Occup Saf Ergon. 2014;20(2):339-53. doi:10.1080/10803548.2014.11077048
Sanders, Martha J, and Claudia Michalak Turcotte. “Posture makes perfect.” Today’s FDA: official monthly journal of the Florida Dental Association vol. 25,2 (2013): 62-5.
Shaghayegh Fard, B et al. “Evaluation of forward head posture in sitting and standing positions.” The European spine journal: official publication of the European Spine Society, the European Spinal Deformity Society, and the European Section of the Cervical Spine Research Society vol. 25,11 (2016): 3577-3582. doi:10.1007/s00586-015-4254-x