Table of Contents
Introduction
When it comes to the human body in motion, the arms can carry, lift, and move items from one place to another without pain. The arms have different muscles that work together to protect the arm and shoulder joints while providing mobility and movement. One of the muscles that help the arms carry items is the brachialis muscles, which work together with the bicep and tricep muscles. As part of the forearm, it can succumb to various injuries affecting the muscle, tendons, and ligaments. When this happens, referred pain can affect the arm and develop trigger points to overlap chronic conditions that can potentially cause more pain. Today’s article looks at the brachialis muscle’s function, how trigger points affect the muscle, and various ways to manage brachialis trigger points. We refer patients to certified providers who specialize in arm pain treatments to aid individuals suffering from trigger points associated with the brachialis muscles along the upper arms. We also guide and inform our patients by referring them to our associated medical providers based on their examination when appropriate. We established that education is a great solution to asking our providers profound questions the patient requests. Dr. Jimenez DC takes note of this information as an educational service only. Disclaimer
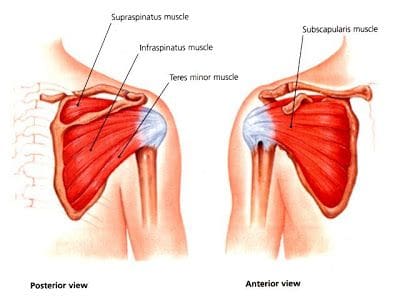
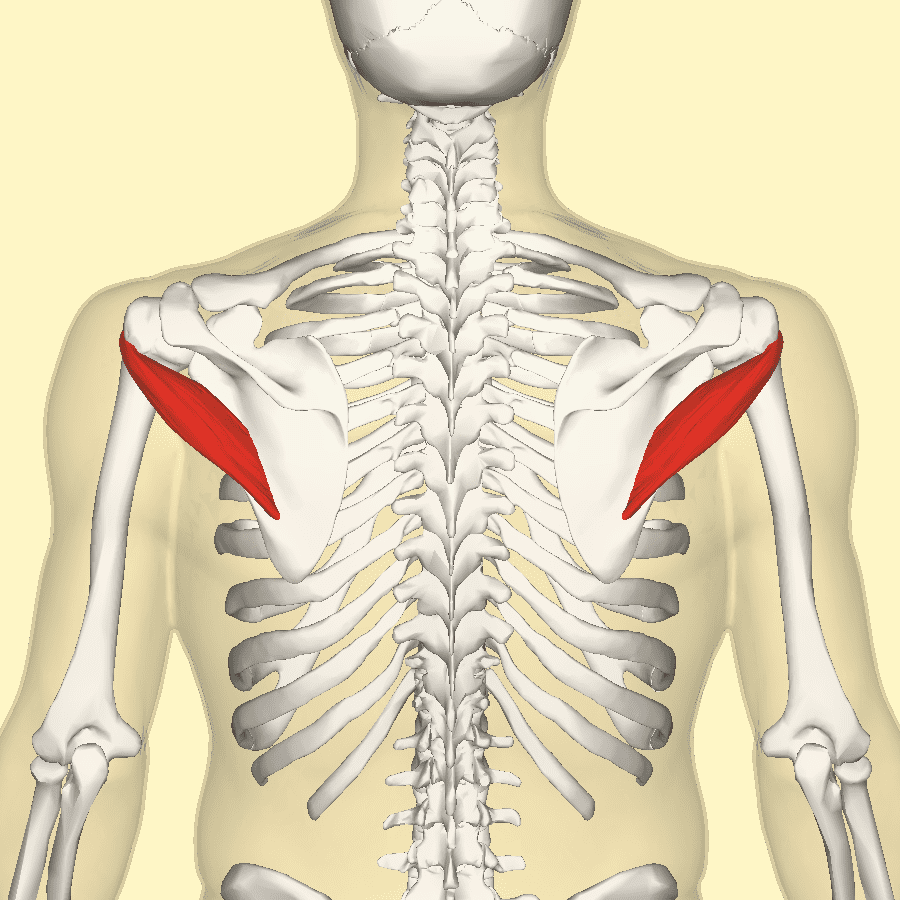
What Is The Brachialis Muscle Function?
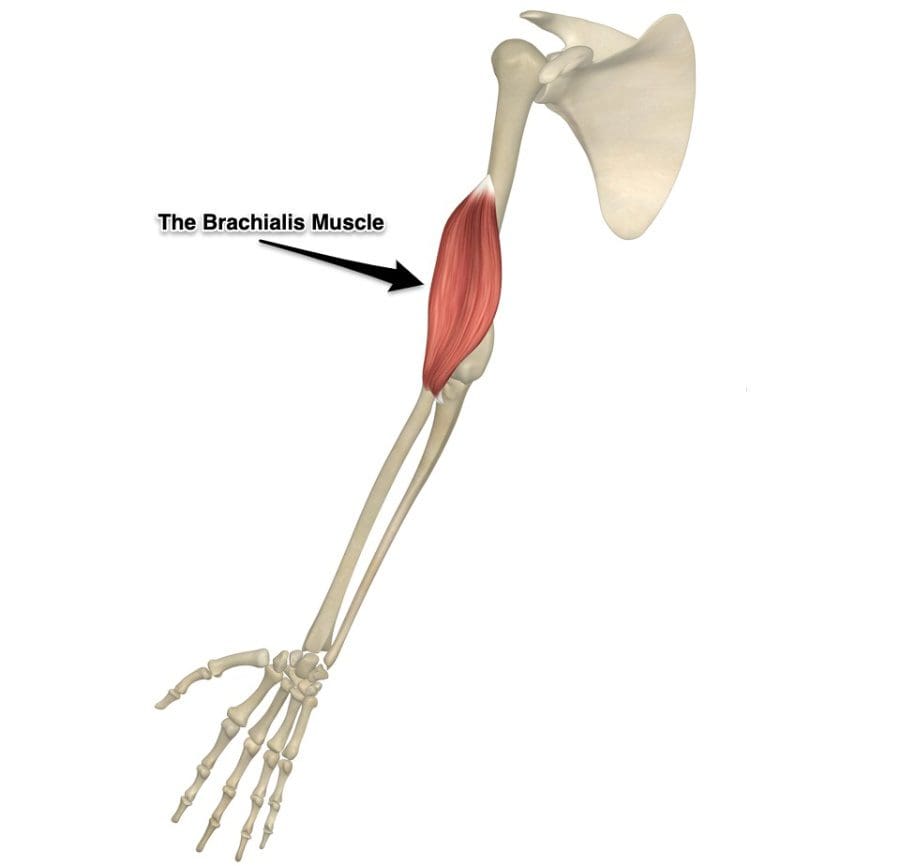
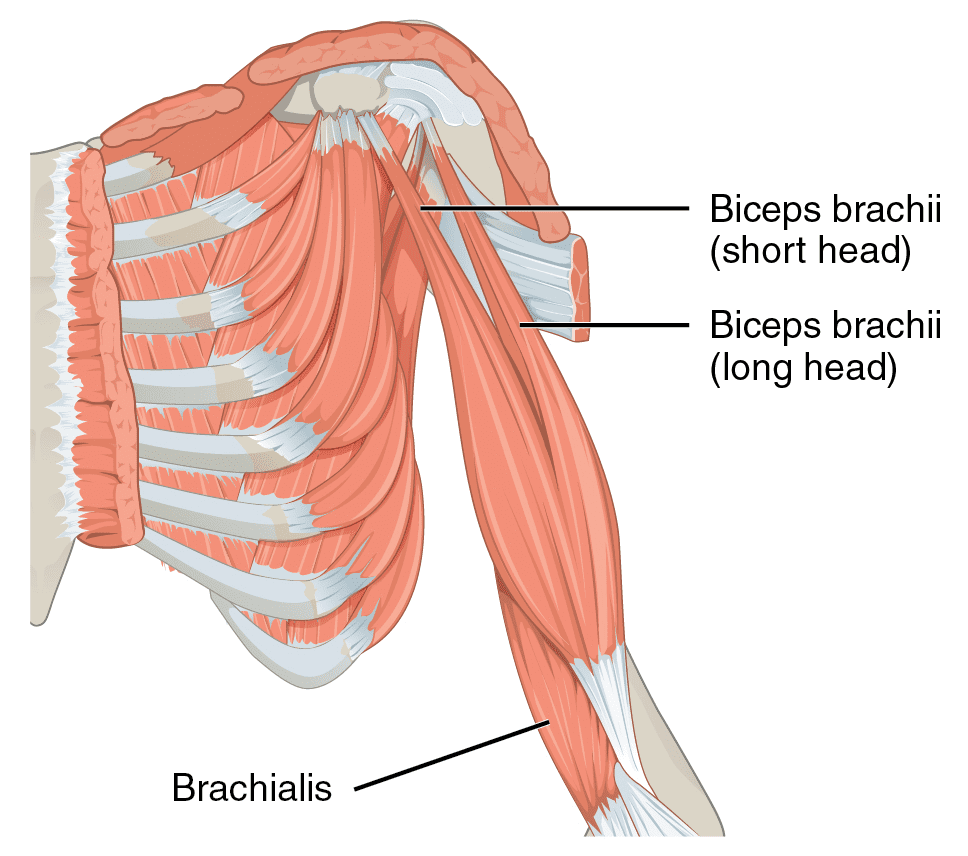
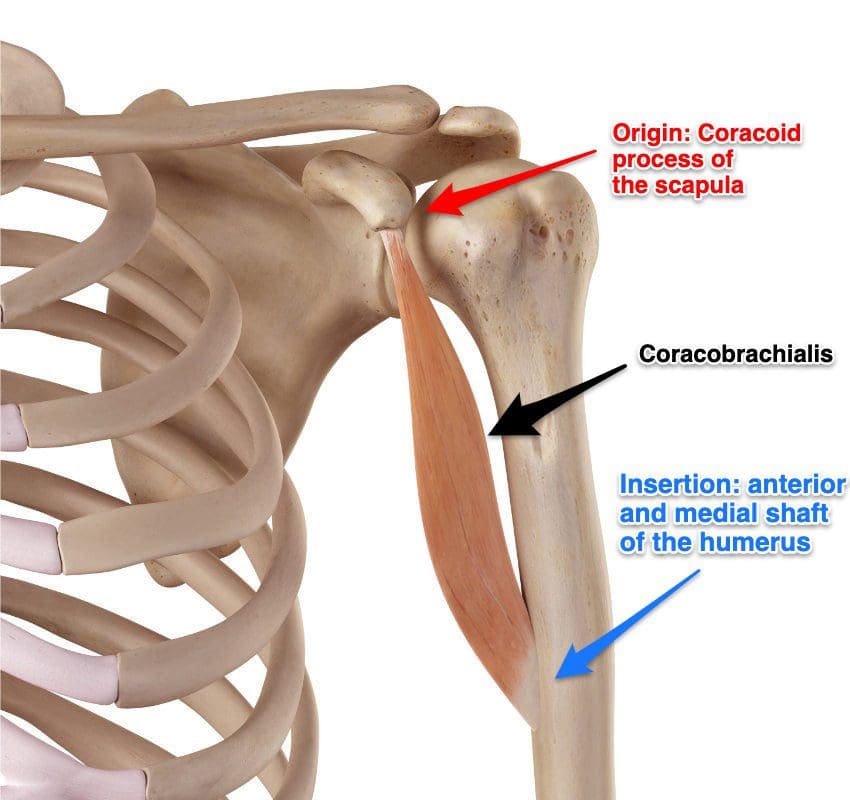
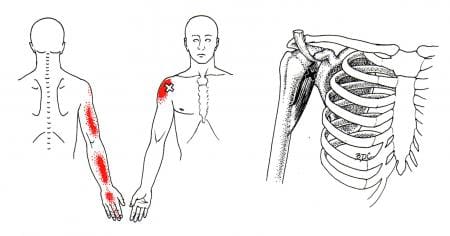
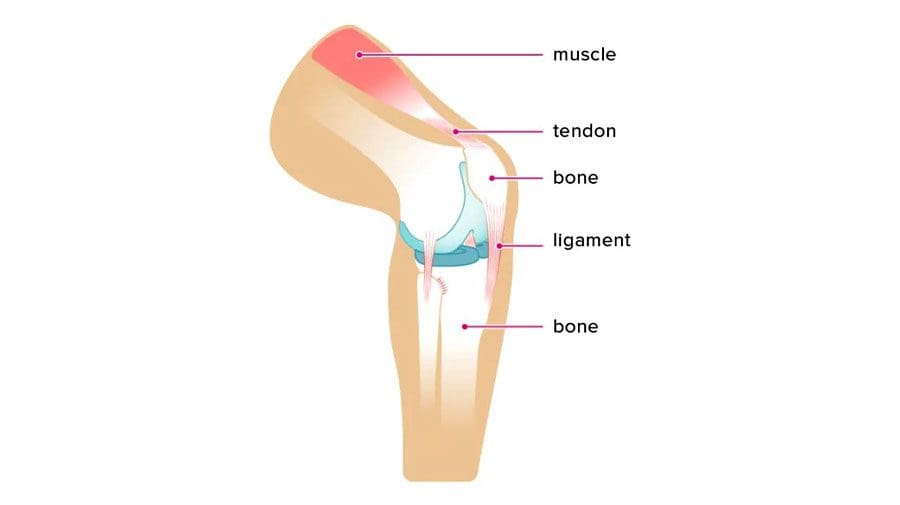
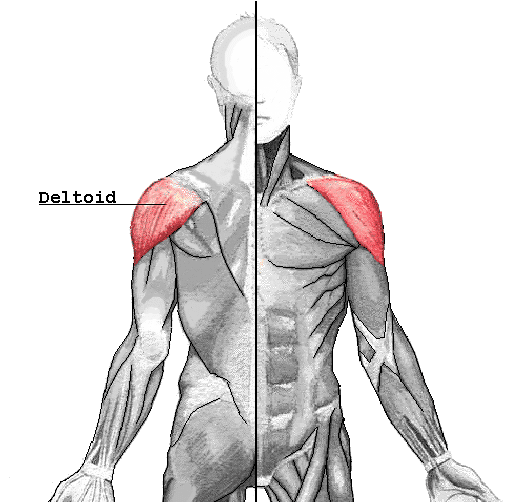
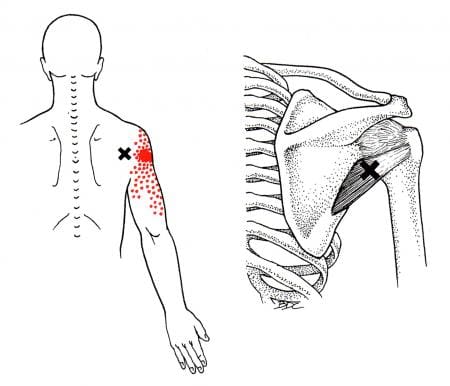
Have you been experiencing muscle strain in your forearms? What about stiffness in your wrist? Or do your arm muscles begin to spasm out of nowhere? Many people who have experienced these pain symptoms might be caused by trigger points associated with the brachialis muscle. The brachialis is an important muscle that flexes the forearm at the elbow. This muscle works with the biceps as it can carry heavy items, like the deltoid, and is the opposite of the tricep muscles. However, it can become overused and succumb to injuries that can invoke pain in the arm muscles, thus leading to the development of trigger points along the brachialis muscle.
How Does Trigger Points Affect The Brachialis Muscle?
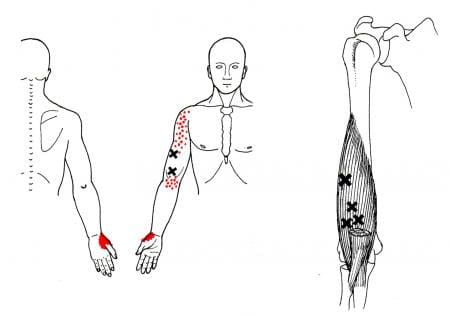
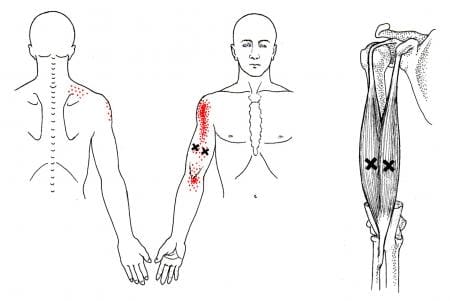
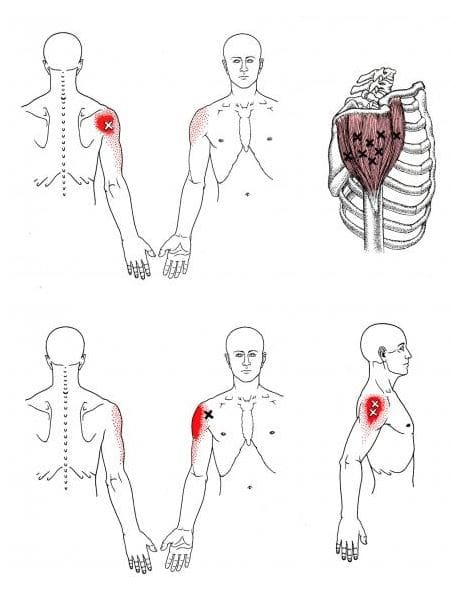
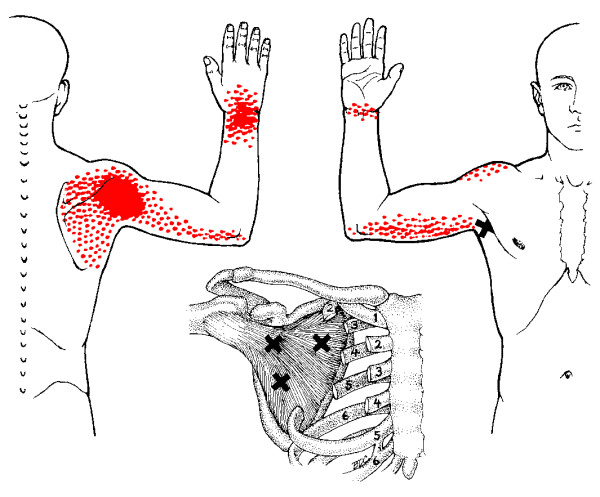
When the brachialis muscle becomes injured, many people will experience pain when flexing their elbows inward or outward. According to Dr. Travell, M.D., these pain symptoms may be due to referred pain and tenderness from brachialis trigger points or radial nerve entrapment. During heaving lifting, the forearm flexion stress overload activates trigger points along the brachialis. Studies reveal that excessive sudden physical stress or repetitive activities may result from a muscle sprain or tear in the brachialis muscle. To that point, these symptoms associated with trigger points can cause overlapping risk profiles that can mask the condition. Some of the conditions that can overlap and activate trigger points include:
- Carrying heavy groceries
- Holding power tools
- Tennis elbow
- Playing a string instrument
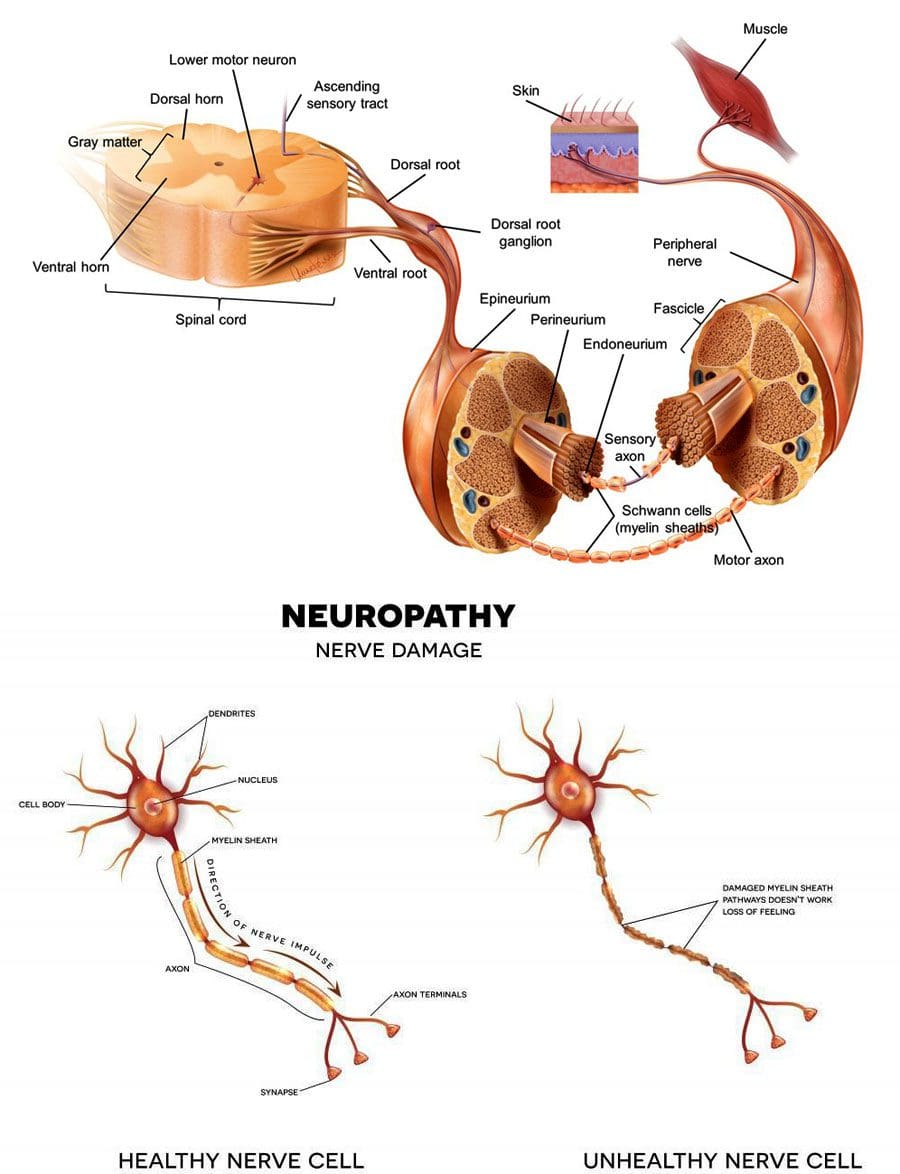
Studies also reveal that active trigger points along the affected muscle can increase weight coefficients and alter motor control without co-contraction patterns. This is due to trigger points becoming tricky to diagnose and mimic other conditions affecting the arms’ muscle group. Many people with pain-like symptoms associated with trigger points often complain about numbness or deep pain in their arms and hands. To that point, trigger points can also be involved with nerve entrapment in the brachialis muscles.
The Brachialis Trigger Points Release-Video

Have you been experiencing stiffness in your hands and arms? What about muscle spasms near your elbow? Or does constant pain affect your forearm muscles when you bend your arm? Many of these symptoms are associated with trigger points affecting the brachialis muscle that is causing pain in the forearms. Trigger points or myofascial pain syndrome can affect a person’s well-being by impairing their mobility in the affected areas, causing pain, and even reducing their overall sense of life. Trigger points affecting the brachialis muscles can mimic chronic conditions like nerve entrapment that can affect the motor function of the forearm. Luckily, trigger points are treatable, and there are ways to reduce the pain-like symptoms from the affected brachialis muscles. The video above shows how to treat trigger points along the forearm. Incorporating non-invasive treatments to reduce future trigger points to form can reduce the pain symptoms and release the trapped nerves that are causing motor function problems in the arms.
Ways To Manage Brachialis Trigger Points
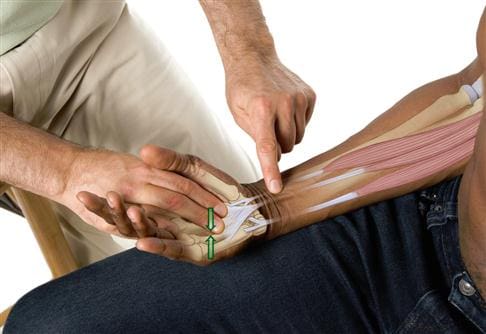
As stated earlier, trigger points are tricky to diagnose since they can mimic other chronic conditions along the affected muscles. When the affected muscle succumbs to injuries and is not treated, it can develop tiny knots along the taut muscle band fibers known as trigger points over time. To that point, it can cause referred pain-like symptoms along the muscle group. Luckily, treatments can help reduce pain-like symptoms and prevent trigger points from forming along the muscle fibers. Studies reveal that trigger point injections are one of the various treatments that can help reduce pain in the brachialis muscle. With gentle stretching and physical therapy, allow mobility back to the arm. One way to manage brachialis trigger points that many people can use is to place a pillow at the angle of the elbow to prevent the arms from tightening or use a hot pack to relax the forearm muscles to relieve muscle strain and aches. Another way is not to overuse their forearms when playing an instrument or carrying items on their forearms. This can prevent trigger points from forming in the future and reduce pain-like symptoms from affecting the forearms.
Conclusion
The brachialis is the main muscle that is important to the forearms. This large muscle works with the bicep and tricep muscles to help the host carry heavy objects while bending at the elbows. However, like all the muscles in the body, the brachialis muscles can succumb to injuries and develop trigger points along the brachialis muscle fiber bands. Trigger points along the brachialis muscle are associated with pain-like symptoms that can mimic conditions like tennis elbow or nerve entrapment in the forearms. Fortunately, various treatments are utilized by doctors to help many patients dealing with trigger points along the brachialis muscle and can help reduce pain in the forearms. This allows mobility back to the arms and prevents future trigger points from forming.
References
Geri, Tommaso, et al. “Myofascial Trigger Points Alter the Modular Control during the Execution of a Reaching Task: A Pilot Study.” Scientific Reports, Nature Publishing Group UK, 5 Nov. 2019, https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6831581/.
Plantz, Mark A, and Bruno Bordoni. “Anatomy, Shoulder and Upper Limb, Brachialis Muscle.” In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL), StatPearls Publishing, 22 Feb. 2022, https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK551630/.
Sharma, Pankaj, et al. “Isolated Traumatic Brachialis Muscle Tear: A Case Report and Review of Literature.” Bulletin of Emergency and Trauma, Shiraz University of Medical Sciences, Oct. 2017, https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5694606/.
Suh, Mi Ri, et al. “Ultrasound-Guided Myofascial Trigger Point Injection into Brachialis Muscle for Rotator Cuff Disease Patients with Upper Arm Pain: A Pilot Study.” Annals of Rehabilitation Medicine, Korean Academy of Rehabilitation Medicine, Oct. 2014, https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4221396/.