Table of Contents
Relieving Sciatica Pain: Chiropractic Solutions for Teachers’ Busy Lives
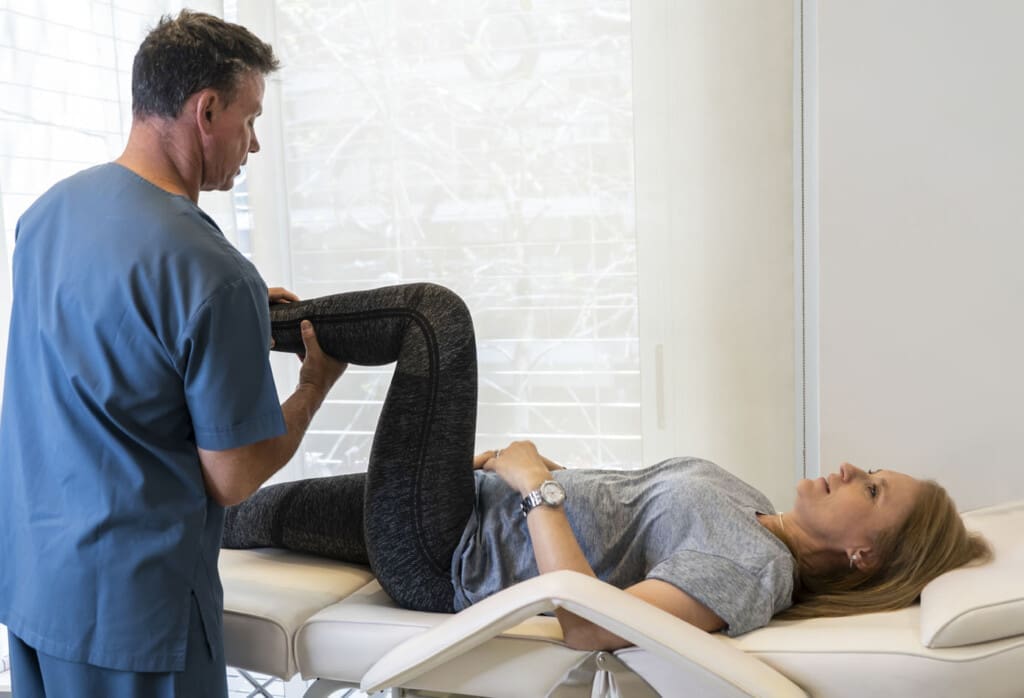
Introduction to Sciatica and Its Hidden Toll on Educators
Sciatica is a common issue that causes sharp pain, numbness, or tingling down the leg. It happens when the sciatic nerve, the longest nerve in the body, gets irritated or compressed. This nerve runs from the lower back through the hips and down each leg. For many people, sciatica is characterized by a shooting pain that makes daily tasks difficult. In the world of education, where days are long and full of movement, this pain can sneak up without warning.
Teachers often face unique challenges that raise the risk of sciatica. They spend hours standing in front of classes, sitting at desks to grade papers, and bending to help students. These actions can strain the back and irritate the nerve. Poor posture, often caused by hunching over books or computers, exacerbates the problem. The job’s physical demands, such as carrying heavy bags or chasing after kids, exacerbate the situation. Over time, these habits can lead to inflammation and nerve pressure.
But there’s hope. Chiropractic care provides a natural approach to alleviating sciatica. It focuses on fixing spine alignment to reduce nerve irritation. Simple changes, such as improved ergonomics and regular stretches, can help prevent flare-ups. This article examines the impact of sciatica on teachers, its underlying causes, and how chiropractic care and other therapeutic methods can offer relief. We’ll also examine real-world insights from experts, such as Dr. Alexander Jimenez, a chiropractor and nurse practitioner in El Paso, Texas. His work demonstrates how targeted care can effectively heal injuries and improve overall health.
By understanding these risks and solutions, teachers can stay active and pain-free. Let’s explore the causes first.
Understanding Sciatica: What It Is and Why It Hurts
The sciatic nerve starts in the lower spine and branches out like a tree. When something presses on it, like a bulging disc or tight muscles, sciatica begins. Symptoms include pain from the lower back to the foot, weakness in the leg, or a pins-and-needles feeling. It can hit one side of the body and last for days or months.
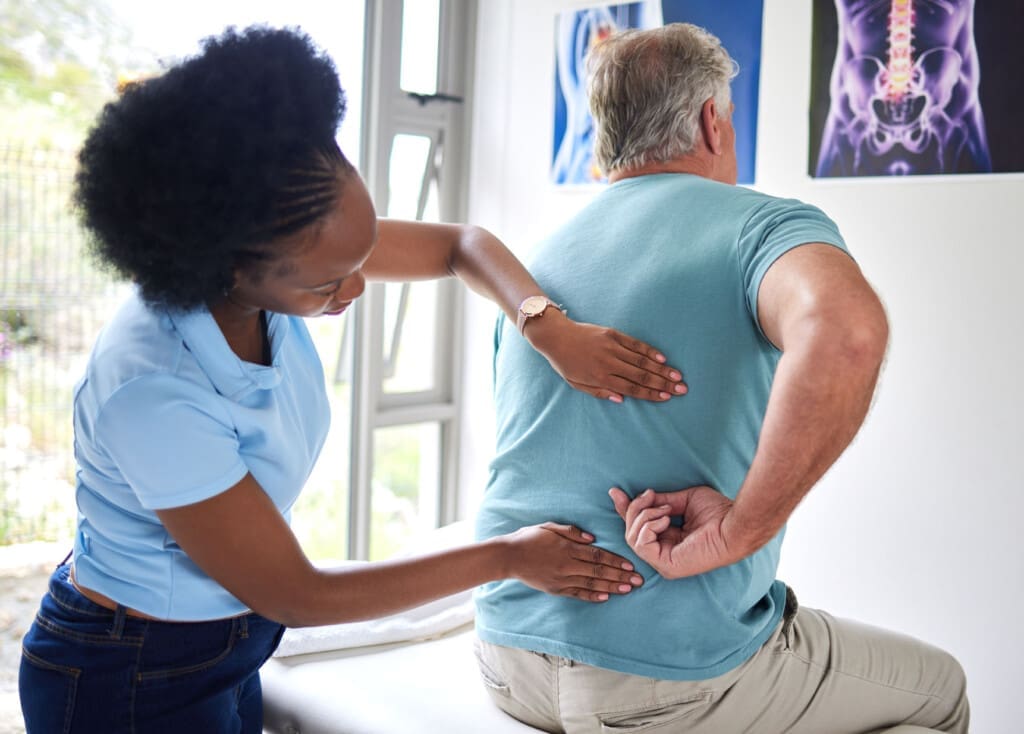
For teachers, this pain disrupts lesson planning or playground duty. Sitting for long periods, such as during parent-teacher meetings, compresses the spine and irritates the nerve (Bomberg Chiropractic, 2023). Standing all day without breaks can cause the muscles around the hips to tighten, adding pressure.
Common triggers include herniated discs from lifting stacks of papers or poor posture from leaning over desks. Stress from grading deadlines can tense muscles, worsening the issue (Paragon Chiropractic, n.d.). In classrooms, uneven floors or old chairs often force students into awkward positions that strain their backs.
Dr. Alexander Jimenez, a board-certified chiropractor and family nurse practitioner, notes in his clinical work that sciatica often links to everyday strains. At his El Paso clinic, he sees many patients with nerve pain resulting from repetitive tasks, such as those in the teaching profession. His dual-scope approach—combining chiropractic exams with advanced imaging—helps spot hidden issues early (Jimenez, n.d.a). This means teachers don’t have to wait for pain to peak before getting help.
Sciatica isn’t just uncomfortable; it can lead to missed workdays. Studies show up to 40% of adults face it yearly, with job demands playing a big role (Anchor to Health Chiropractic, 2021). Next, we’ll examine how teachers’ routines contribute to this risk.
Job Risks for Teachers: How Daily Demands Spark Sciatica
Teaching looks calm from afar, but it’s full of physical twists. Standing for hours delivers lessons or supervises lunch. This static pose fatigues lower back muscles, increasing disc pressure and nerve pinch (Boyne Ergonomics, n.d.). Then, there’s sitting—hunched over laptops during planning or tiny chairs in reading circles. Prolonged sitting shortens hip flexors and weakens the core, pulling the spine out of line (East Bay Chiropractic Office, 2023).
Poor posture is a silent enemy. Teachers often lean forward to engage students, curving the spine into a “C” shape. This forward tilt compresses the lower back, irritating the sciatic nerve roots (Scoliosis Center of Utah, n.d.). Add carrying heavy tote bags with books and supplies—up to 20 pounds—and the load shifts to one side, unbalancing the pelvis.
The job’s demanding side doesn’t stop. Bending to pick up dropped crayons or kneeling to tie shoes strains the piriformis muscle, which can trap the sciatic nerve. Repetitive motions, such as writing on boards or erasing, can build tension over time. Even computer use for emails or slides requires neck craning, which can lead to issues in the lower back (Total Health Chiropractic, n.d.).
Psychosocial stress amps it up. Managing rowdy classes or tight deadlines can raise cortisol levels, which in turn can tighten muscles and increase inflammation (Innova Chiropractic, n.d.). Dr. Jimenez observes this in his practice: Teachers with work-related injuries often have multiple issues stemming from stress and poor ergonomics. His team utilizes neuromusculoskeletal imaging to connect daily habits to nerve compression, addressing root causes such as muscle imbalances resulting from uneven standing (Jimenez, n.d.b).
These risks aren’t rare. Surveys show that 70% of teachers report back pain annually, with sciatica being a common condition among them (Abundant Life Chiropractor, 2023). However, awareness is key—small tweaks can significantly reduce the odds.
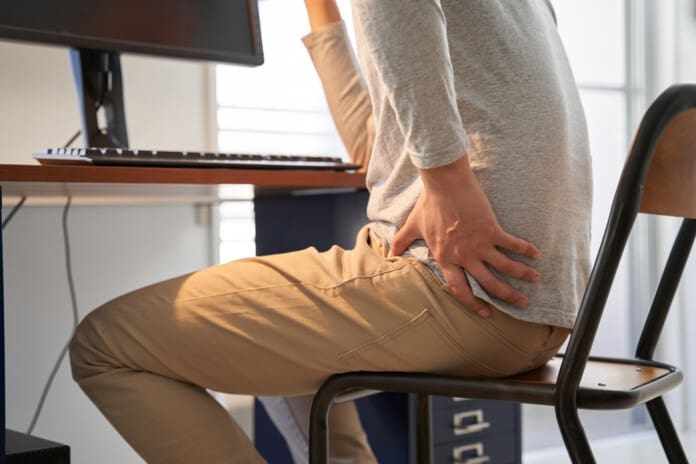
Prolonged Sitting and Standing: The Double-Edged Sword
Picture a typical school day: Morning assembly means standing tall for 45 minutes, feet aching. Then, desk time for lessons, butt glued to a hard chair. Switching between sitting and standing without proper form strains the spine endlessly.
Sitting compresses spinal discs by 30%, more than standing, per research. For teachers, this means that nerve roots can become compressed during grading marathons (Bomberg Chiropractic, 2023). Hip flexors shorten, tilting the pelvis and pinching the sciatic nerve. Standing, meanwhile, locks the pelvis if posture slumps, overloading the lower back.
Teachers alternate between these poses rapidly—standing to lecture and sitting to confer. This “yo-yo” effect fatigues stabilizers, leading to micro-tears in discs (Boyne Ergonomics, n.d.). In one study, educators who stood for over four hours daily had a 50% higher rate of back pain.
Dr. Jimenez’s clinic treats numerous cases resulting from motor vehicle accidents or slips and falls at school, but he emphasizes the importance of prevention. His diagnostic assessments, including X-rays and MRIs, reveal how prolonged positions cause disc bulges irritating nerves. Treatments blend adjustments with movement therapy to rebuild endurance (Jimenez, n.d.a).
To fight back, aim for balance. Alternate every 20 minutes: Stand for demos, sit for notes. Use anti-fatigue mats during duty. These habits ease pressure and keep nerves calm.
Poor Posture: The Sneaky Culprit Behind Nerve Irritation
Posture matters more than we think. Slouching compresses the lumbar spine, where the sciatic nerves reside. Teachers hunch over desks or boards, rounding their shoulders and jutting their heads forward. This “text neck” cascades to the lower back, tightening the piriformis and trapping the nerve (Scoliosis Center of Utah, n.d.).
In classrooms, engaging low kids means crouching awkwardly, arching the back. Over time, this can lead to uneven muscle pull, shifting vertebrae, and nerve inflammation. Computer screens are too low, forcing downward gazes, worsening the curve.
Chiropractors see this daily. Adjustments realign the spine, easing nerve flow (Anchor to Health Chiropractic, 2021). Dr. Jimenez integrates posture coaching in his plans. His functional medicine lens correlates poor alignment with inflammation from diet or stress, using acupuncture to relax tissues (Jimenez, n.d.b).
Fix it with cues: Ears over shoulders, chin tucked. Ergonomic setups—like raised monitors—help. Regular checks prevent chronic shifts.
Physically Demanding Nature: Lifting, Bending, and Beyond
Teaching isn’t desk-bound; it’s an active process. Lifting AV equipment, hauling art supplies, or corralling recess chaos strains the body. Sudden twists to grab a falling book can herniate a disc, pressing the sciatic nerve.
Bending forward repeatedly, like filing papers, overloads the lower back. Muscles fatigue, ligaments stretch, and nerves get caught (East Bay Chiropractic Office, 2023). Sports-like dashes after stray balls mimic injury risks.
Dr. Jimenez treats these as work-related injuries, documenting them for legal purposes. His clinic handles MVAs and slips, using massage and exercise to heal soft tissues. Dual-diagnosis spots if a bend caused a sprain plus nerve entrapment (Jimenez, n.d.a).
Safe lifts—knees bent, core tight—cut risks. Trolleys for supplies help too.
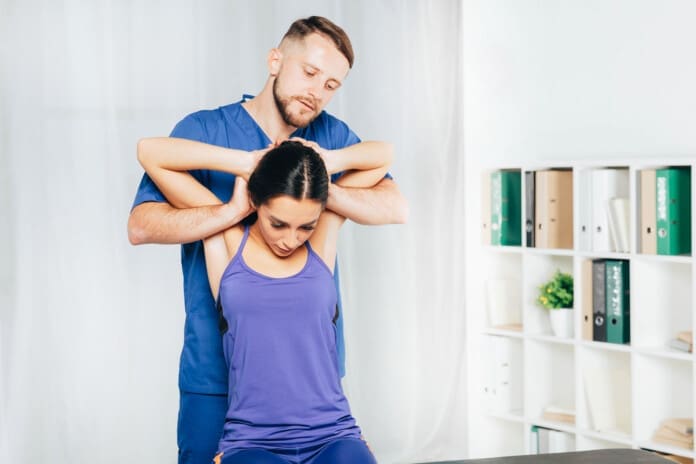
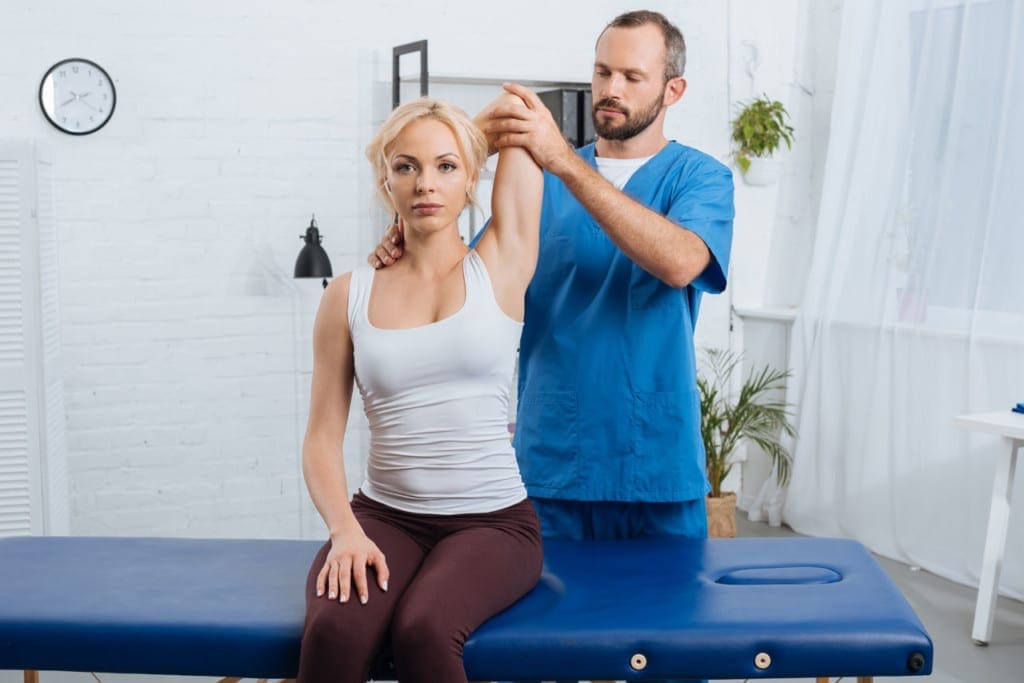
Chiropractic Care: A Natural Path to Nerve Relief
Chiropractic shines for sciatica. Manual adjustments nudge vertebrae back, freeing the nerve. This reduces inflammation and boosts mobility (Active Health Center, n.d.). Teachers feel less pain after sessions, standing taller.
Spinal decompression gently pulls discs apart, retracting bulges (Bomberg Chiropractic, 2023). Soft tissue work releases tight spots.
Dr. Jimenez’s approach adds layers. His neuromusculoskeletal imaging pinpoints issues, guiding precise adjustments. For teachers with sports strains, he pairs chiropractic with acupuncture for a natural pain block (Jimenez, n.d.b).
Regular visits prevent returns, promoting healing without drugs.
Improving Spinal Alignment and Nerve Function Through Adjustments
Adjustments are chiropractic’s core. A quick thrust realigns joints, easing nerve pressure. For sciatica, lumbar focus relieves leg pain fast (AFC Adherence, n.d.).
Teachers benefit as alignment fights job slumps. Blood flow improves, aiding repair (Innova Chiropractic, n.d.). Dr. Jimenez uses advanced tools for safe, targeted care, correlating alignment to overall function (Jimenez, n.d.a).
Sessions build resilience against daily wear.
Reducing Inflammation: Chiropractic’s Gentle Approach
Inflammation swells tissues around the nerve. Adjustments calm it by improving drainage and motion (Active Health Center, n.d.). Heat or ice post-adjustment speeds relief.
For teachers, this means less swelling from standing. Dr. Jimenez adds nutrigenomics—diet tweaks to lower inflammation—enhancing results (Jimenez, n.d.b).
Lifestyle Recommendations: Ergonomics and Exercises for Lasting Change
Chiropractors don’t stop at adjustments. They teach ergonomics, including the use of adjustable chairs and screens at eye level (Boyne Ergonomics, n.d.). For teachers, desk risers allow stand-sit switches.
Exercises strengthen the core: Planks build stability, and piriformis stretches loosen the hips (Alliance Orthopedics, n.d.). Knee-to-chest pulls pressure off nerves.
Dr. Jimenez prescribes tailored routines that incorporate massage for recovery. His legal docs ensure work claims cover these (Jimenez, n.d.a).
Daily 5-minute breaks prevent buildup.
Managing Pain and Preventing Flare-Ups: Daily Habits That Work
Pain management starts with awareness. Track triggers such as long periods of inactivity, and then take action. Heat soothes tight muscles; cold numbs acute flares (Abundant Life Chiropractor, 2023).
Prevention: Engage in core workouts three times a week, and utilize posture apps for reminders. Stress-busters like yoga help ease tension (Paragon Chiropractic, n.d.).
In Dr. Jimenez’s view, preventing long-term issues means holistic care. His clinic’s exercise programs, post-injury, restore function and avoid scars (Jimenez, n.d.b).
Integrative Approaches: Beyond Chiropractic for Full Support
Chiropractic pairs well with others. Physical therapy builds strength via guided moves (Alliance Orthopedics, n.d.). Stress management techniques, such as meditation, can help reduce muscle tension.
Movement breaks: Every hour, march in place. Dr. Jimenez integrates acupuncture for nerve calm and massage for flow, particularly in work/sports cases (Jimenez, n.d.a). His team documents everything for insurance.
These combos heal naturally, preventing chronic pain.
Physical Therapy: Building Strength to Shield the Spine
PT complements chiropractic by focusing on function. Therapists teach bridges for the glutes and bird-dogs for balance (Active Health Center, n.d.). For teachers, home plans fit busy schedules.
It reduces reliance on medication, promoting the release of natural endorphins. Dr. Jimenez refers for PT in complex injuries, like MVA whiplash with sciatica (Jimenez, n.d.b).
Stress Management: Easing Tension to Protect Nerves
Stress tightens backs, worsening sciatica. Deep breaths or walks release it (Paragon Chiropractic, n.d.). Teachers can journal post-class.
Mindfulness apps guide short sessions. In Jimenez’s practice, stress links to inflammation; his functional plans include yoga (Jimenez, n.d.a).
Movement Breaks: Small Steps for Big Relief
Breaks recharge the body. Stand and twist gently every 30 minutes (Boyne Ergonomics, n.d.). In class, lead stretches.
This boosts circulation, easing nerve pressure. Dr. Jimenez’s protocols include timed walks for recovery (Jimenez, n.d.b).
Insights from Dr. Alexander Jimenez: Real-World Clinical Wisdom
Dr. Jimenez, with over 30 years of experience in El Paso, combines chiropractic and nursing expertise. His clinic treats sciatica resulting from work-related lifts, sports-related twists, personal falls, and car crashes. Dual diagnosis combines exams with imaging to map injuries—such as a teacher’s bend, revealing a disc herniation along with a strain.
Treatments target the causes: adjustments free the nerves, exercises rebuild, and acupuncture soothes. For legal cases, detailed reports support claims, ensuring access to care.
Integrative medicine shines here. Massage helps ease scars, and a balanced diet helps fight inflammation. Jimenez’s patients, including educators, gain mobility without surgery, thereby preventing issues such as chronic weakness (Jimenez, n.d.a; Jimenez, n.d.b).
His story: From bodybuilder to healer, he empowers others through education, such as podcasts on spine care.
Case Studies: Teachers Finding Relief Through Targeted Care
Consider Maria, a third-grade teacher with shooting leg pain from desk slumps. Chiropractic adjustments plus stretches cut her flares by 80% in weeks (Inspired by Anchor to Health Chiropractic, 2021).
Or Tom, high school coach with sciatica from field runs. Dr. Jimenez-like care—imaging, decompression, core work—got him back coaching (Jimenez, n.d.a).
These show integrative paths work.
Daily Exercises: Simple Routines to Ease and Prevent Pain
Start with cat-cow: On all fours, arch your back and round it 10 times. It loosens the spine (Active Health Center, n.d.).
Piriformis stretch: Cross ankle over knee, lean forward. Hold 30 seconds per side.
Bridges: Lie back, lift hips—strengthens support.
Do these mornings. Teachers, weave into warm-ups.
Dr. Jimenez customizes for injuries, adding resistance for athletes (Jimenez, n.d.b).
Ergonomic Tips for Classrooms and Home Offices
Raise boards to waist height; use pointers. Chairs with lumbar pillows support curves (AFC Adherence, n.d.).
At home, footrests for grading. Dr. Jimenez coaches on setups to avoid strains (Jimenez, n.d.a).
Nutrition and Wellness: Fueling Healing from Within
Anti-inflammatory foods—such as berries and fish—can calm the nerves. Hydration keeps discs plump.
Jimenez’s nutrigenomics tailors plans, boosting recovery in injury cases (Jimenez, n.d.b).
When to Seek Help: Signs It’s Time for Professional Care
If pain lasts over a week, weakens your legs, or disrupts your sleep, see a professional. Early intervention prevents worsening.
Dr. Jimenez urges prompt visits for accurate diagnosis (Jimenez, n.d.a).
Long-Term Spinal Health: Building a Pain-Free Future
Consistent care sustains gains. Annual check-ups catch shifts early.
Integrative habits—such as yoga and walks—fortify. Jimenez’s programs empower lifelong wellness (Jimenez, n.d.b).
Conclusion: Empowering Teachers with Knowledge and Tools
Sciatica doesn’t have to sideline educators. By addressing sitting/standing strains, posture pitfalls, and physical demands with chiropractic care, exercises, and smart strategies, relief is within reach. Dr. Jimenez’s insights prove targeted, natural care heals and prevents.
Take charge: Adjust your setup, stretch daily, seek adjustments. A healthier spine means more energy for what matters—shaping young minds.
Expanded Section: Detailed Exercise Guide with Variations
For deeper dives, consider the knee-to-chest stretch. Lie on your back, pull one knee to your chest, and hold for 20 seconds. Variation: Both knees for balanced relief. Do 3 sets daily. This targets hamstrings, easing nerve pull (Active Health Center, n.d.).
Seated twist: In a chair, turn the torso gently. Great for desk breaks. Teachers, do during silent reading.
Bird-dog: Extend opposite arm/leg. Builds core without strain. Jimenez adapts for post-MVA patients (Jimenez, n.d.a).
Classroom Integration: Making Wellness Part of the Day
Incorporate group stretches, such as “Simon Says” with bends. Reduces collective risks (Abundant Life Chiropractor, 2023).
Home: Yoga mats for evenings. Stress tips: Breathing before bed.
Advanced Chiropractic Techniques Explained
Flexion-distraction: The Table gently rocks the spine. Ideal for disc issues (AFC Adherence, n.d.).
Graston: Tools break scar tissue. For chronic teacher strains.
Jimenez’s electro-acupuncture: Needles with current for deep relief (Jimenez, n.d.b).
Nutrition Deep Dive: Foods That Fight Inflammation
Omega-3s in salmon reduce swelling. Turmeric tea daily. Jimenez’s plans include gut health for better absorption (Jimenez, n.d.a).
Recipes: Berry smoothies. Avoid sugars that spike pain.

References
[Anchor to Health Chiropractic]. (2021, August 20). How chiropractic care can help teachers. https://anchortohealth.com/2021/08/20/how-chiropractic-care-can-help-teachers/
[Active Health Center]. (n.d.). Sciatica and chiropractic care: Natural solutions for nerve pain. https://activehealthcenter.com/sciatica-and-chiropractic-care-natural-solutions-for-nerve-pain/
[AFC Adherence]. (n.d.). Aligning your spine: How chiropractors target sciatica pain. https://afcadence.com/aligning-your-spine-how-chiropractors-target-sciatica-pain/
[Alliance Orthopedics]. (n.d.). Do I need a chiropractor or physical therapy for sciatica relief? https://allianceortho.com/do-i-need-a-chiropractor-or-physical-therapy-for-sciatica-relief/
[Abundant Life Chiropractor]. (2023). Back-to-school spine health: Sciatica prevention. https://abundantlifechiropractor.com/back-to-school-spine-health-sciatica-prevention/
[Bomberg Chiropractic]. (2023). Sedentary job? Here’s how to keep your body healthy while you sit. https://www.bombergchiropractic.com/Company-Information/Blog/entryid/60/sedentary-job-heres-how-to-keep-your-body-healthy-while-you-sit
[Boyne Ergonomics]. (n.d.). Reducing ergonomic risk among teachers. https://boyneergonomics.ie/reducing-ergonomic-risk-among-teachers/
[East Bay Chiropractic Office]. (2023). Benefits of chiropractic care for teachers. https://eastbaychiropracticoffice.com/blog/benefits-of-chiropractic-care-for-teachers/
[Innova Chiropractic]. (n.d.). The top 10 benefits of chiropractic care for teachers: A detailed guide. https://www.innervatechiropractic.com/the-top-10-benefits-of-chiropractic-care-for-teachers-a-detailed-guide
[Jimenez, A.]. (n.d.a). Injury specialists. https://dralexjimenez.com/
[Jimenez, A.]. (n.d.b). Dr. Alexander Jimenez, DC, APRN, FNP-BC, IFMCP, CFMP, ATN ♛ – Injury Medical Clinic PA. https://www.linkedin.com/in/dralexjimenez/
[Paragon Chiropractic]. (n.d.). What lifestyle changes are most effective in preventing sciatica? https://www.paragonchiropractic.com/What-Lifestyle-Changes-Are-Most-Effective-In-Preventing-Sciatica
[Scoliosis Center of Utah]. (n.d.). Posture and sciatica relief. https://scoliosiscenterofutah.com/posture-and-sciatica-relief/
[Total Health Chiropractic]. (n.d.). Can chiropractic help teachers? https://totalhealthchiropractic.com.au/can-chiropractic-help-teachers/