“Postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome is a medical condition that causes lightheadedness and palpitations after standing. Can lifestyle adjustments and multidisciplinary strategies help reduce and manage symptoms?”
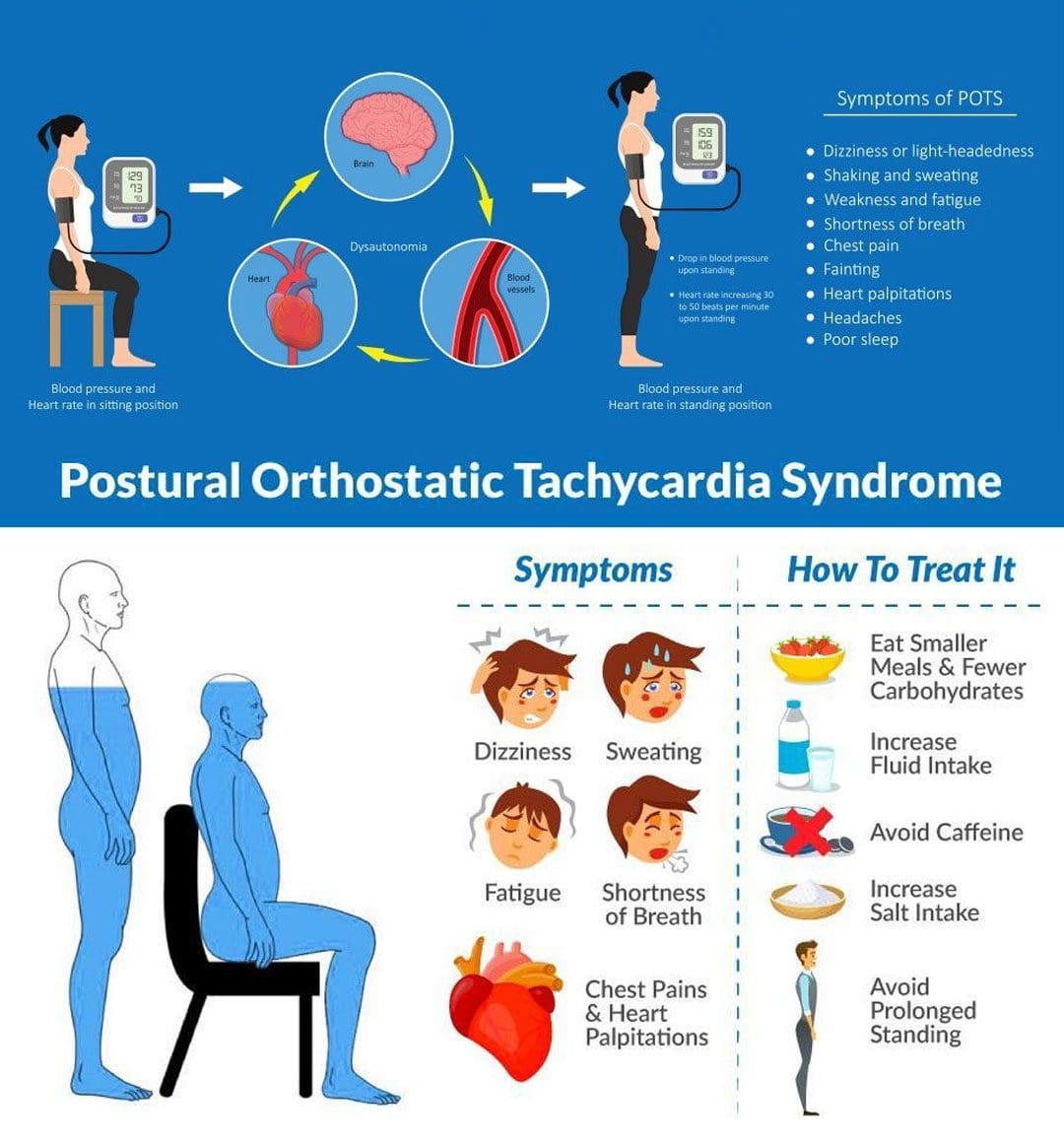
Table of Contents
Postural Orthostatic Tachycardia Syndrome – POTS
Postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome, or POTS, is a condition that varies in severity from relatively mild to incapacitating. With POTS:
- The heart rate increases dramatically with body position.
- This condition often affects young individuals.
- Most individuals with postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome are women between the ages of 13 and 50.
- Some individuals have a family history of POTS; some individuals report POTS began after an illness or stressor, and others report it began gradually.
- It usually resolves over time.
- Treatment can be beneficial.
- Diagnosis is based on assessing blood pressure and pulse/heart rate.
Symptoms
Postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome can affect young individuals who are otherwise healthy and can begin suddenly. It usually happens between the ages of 15 and 50, and women are more likely to develop it than men. Individuals can experience various symptoms within a few minutes of standing up from a lying or seated position. The symptoms can occur regularly and daily. The most common symptoms include: (National Institutes of Health. National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences. Genetic and Rare Diseases Information Center. 2023)
- Anxiety
- Lightheadedness
- A feeling like you’re about to pass out.
- Palpitations – sensing rapid or irregular heart rate.
- Dizziness
- Headaches
- Blurred vision
- Legs turn to reddish-purple.
- Weakness
- Tremors
- Fatigue
- Sleep problems
- Trouble concentrating/brain fog.
- Individuals may also experience recurrent episodes of fainting, usually without any trigger/s other than standing up.
- Individuals can experience any combination of these symptoms.
- Sometimes, individuals cannot handle sports or exercise and may feel light-headed and dizzy in response to mild or moderate physical activity, which can be described as exercise intolerance.
Associated Effects
- Postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome can be associated with other dysautonomia or nervous system syndromes, like neurocardiogenic syncope.
- Individuals are often co-diagnosed with other conditions like:
- Chronic fatigue syndrome
- Ehlers-Danlos syndrome
- Fibromyalgia
- Migraines
- Other autoimmune conditions.
- Bowel conditions.
Causes
Usually, standing up causes blood to rush from the torso to the legs. The sudden change means less blood is available for the heart to pump. To compensate, the autonomic nervous system sends signals to the blood vessels to constrict to push more blood to the heart and maintain blood pressure and a normal heart rate. Most individuals do not experience significant changes in blood pressure or pulse when standing up. Sometimes, the body is unable to perform this function correctly.
- If blood pressure drops from standing and causes symptoms like lightheadness, it is known as orthostatic hypotension.
- If the blood pressure remains normal, but the heart rate gets faster, it is POTS.
- The exact factors that cause postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome are different in individuals but are related to changes in:
- The autonomic nervous system, adrenal hormone levels, total blood volume, and poor exercise tolerance. (Robert S. Sheldon et al., 2015)
Autonomic Nervous System
The autonomic nervous system controls blood pressure and heart rate, which are the areas of the nervous system that manage internal bodily functions like digestion, respiration, and heart rate. It is normal for blood pressure to drop slightly and the heart rate to speed up a little when standing. With POTS, these changes are more pronounced.
- POTS is considered a type of dysautonomia, which is diminished regulation of the autonomic nervous system.
- Several other syndromes are also thought to be related to dysautonomia, like fibromyalgia, irritable bowel syndrome, and chronic fatigue syndrome.
- It isn’t clear why the syndrome or any of the other types of dysautonomia develop, but there seems to be a familial predisposition.
Sometimes the first episode of POTS manifests after a health event like:
- Pregnancy
- Acute infectious illness, for example, a severe case of influenza.
- An episode of trauma or concussion.
- Major surgery
Diagnosis
- A diagnostic evaluation will include a medical history, a physical examination, and diagnostic tests.
- The healthcare provider will take blood pressure and pulse at least twice. Once while lying down and once while standing.
- Blood pressure measurements and pulse rate lying down, sitting, and standing are orthostatic vitals.
- Typically, standing up increases the heart rate by 10 beats per minute or less.
- With POTS, heart rate increases by 30 beats per minute while blood pressure remains unchanged. (Dysautonomia International. 2019)
- The heart rate stays elevated for over a few seconds upon standing/usually 10 minutes or more.
- Symptoms happen frequently.
- Lasts more than a few days.
Positional pulse changes are not the only diagnostic consideration for postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome, as individuals can experience this change with other conditions.
Tests
- Some experts use a tilt-table test for the initial diagnosis and monitor therapy. (National Institutes of Health. National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences. Genetic and Rare Diseases Information Center. 2023)
- During this test, blood pressure and pulse are measured several times when lying on a table and when the table is moved to an upright position.
Differential Diagnosis
- There are various causes of dysautonomia, syncope, and orthostatic hypotension.
- Throughout the evaluation, the healthcare provider may look at other conditions, like dehydration, deconditioning from prolonged bed rest, and diabetic neuropathy.
- Medications like diuretics or blood pressure medication can cause similar effects.
Treatment
Several approaches are used in managing POTS, and individuals may require a multidisciplinary approach. The healthcare provider will advise regularly checking blood pressure and pulse at home to discuss the results when going in for medical checkups.
Fluids and Diet
- Drinking non-caffeinated fluids can keep the body hydrated.
- A healthcare provider can calculate the right amount of fluids that are needed each day.
- Overnight dehydration is common, so it is especially important to drink fluids first thing in the morning, preferably before getting out of bed and standing.
- It is also important to maintain adequate sodium levels. (National Institutes of Health. National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences. Genetic and Rare Diseases Information Center. 2023)
Exercise Therapy
- Exercise and physical therapy can help the body learn to adjust to an upright position.
- Because it can be challenging to exercise when dealing with POTS, a targeted exercise program under supervision may be required.
- An exercise program may begin with swimming or using rowing machines, which do not require upright posture. (Dysautonomia International. 2019)
- After a month or two, walking, running, or cycling may be added.
- Studies have shown that individuals with POTS, on average, have smaller cardiac chambers than individuals who don’t have the condition.
- Regular aerobic exercise has been shown to increase cardiac chamber size, slow heart rate, and improve symptoms. (Qi Fu, Benjamin D. Levine. 2018)
- Individuals must continue an exercise program for the long term to keep symptoms from returning.
Medication
- Prescription medications to manage POTS include midodrine, beta-blockers, pyridostigmine – Mestinon, and fludrocortisone. (Dysautonomia International. 2019)
- Ivabradine, used for the heart condition of sinus tachycardia, has also been used effectively in some individuals.
Conservative Interventions
Other ways to help prevent symptoms include:
- Sleeping in the head-up position by elevating the head of the bed off the ground 4 to 6 inches utilizing an adjustable bed, blocks of wood, or risers.
- This increases the blood volume in circulation.
- Performing countermeasure maneuvers like squatting, squeezing a ball, or crossing the legs. (Qi Fu, Benjamin D. Levine. 2018)
- Wearing compression stockings to prevent too much blood from flowing into the legs when standing can help avoid orthostatic hypotension. (Dysautonomia International. 2019)
Conquering Congestive Heart Failure
References
National Institutes of Health. National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences. Genetic and Rare Diseases Information Center (GARD). (2023). Postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome.
Sheldon, R. S., Grubb, B. P., 2nd, Olshansky, B., Shen, W. K., Calkins, H., Brignole, M., Raj, S. R., Krahn, A. D., Morillo, C. A., Stewart, J. M., Sutton, R., Sandroni, P., Friday, K. J., Hachul, D. T., Cohen, M. I., Lau, D. H., Mayuga, K. A., Moak, J. P., Sandhu, R. K., & Kanjwal, K. (2015). 2015 heart rhythm society expert consensus statement on the diagnosis and treatment of postural tachycardia syndrome, inappropriate sinus tachycardia, and vasovagal syncope. Heart rhythm, 12(6), e41–e63. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hrthm.2015.03.029
Dysautonomia International. (2019). Postural Orthostatic Tachycardia Syndrome
Fu, Q., & Levine, B. D. (2018). Exercise and non-pharmacological treatment of POTS. Autonomic neuroscience : basic & clinical, 215, 20–27. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.autneu.2018.07.001