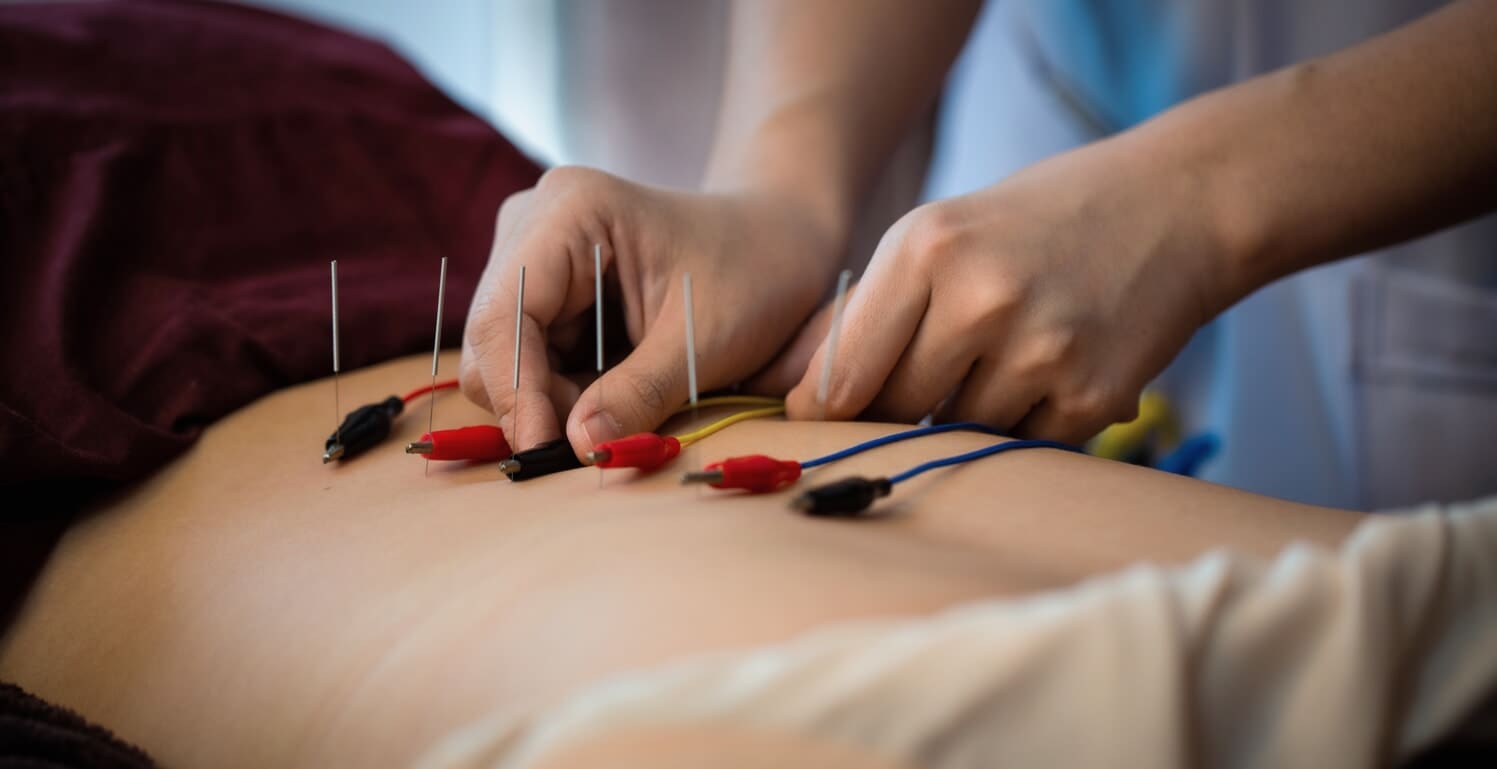
Can individuals with cervical spinal pain incorporate spinal decompression therapy to reduce neck pain and headaches?
Table of Contents
Introduction
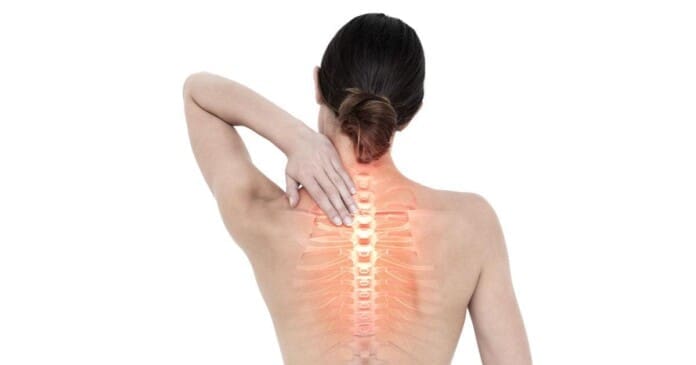
Many individuals deal with neck pain at some point, leading to many issues that can impact their daily lives. See, the neck is part of the cervical region of the musculoskeletal system. It is surrounded by muscles, soft tissues, and ligaments that protect the spinal cord while allowing the head to be mobile. Like back pain, neck pain is a common issue that causes pain and discomfort from associated environmental factors and traumatic injuries. When a person is dealing with neck pain, they are also coping with comorbidities that cause overlapping risk profiles like headaches and migraines. However, treatments like spinal decompression can help reduce cervical spinal pain affecting the neck and reduce the painful effects of headaches and migraines. Today’s article looks at the impact of cervical pain and headaches, how spinal decompression can reduce cervical spinal pain, and how it benefits from reducing headaches. We talk with certified medical providers who consolidate our patients’ information to assess how to mitigate cervical spinal pain from the neck. We also inform and guide patients on how spinal decompression can help reduce headaches caused by cervical spinal pain. We encourage our patients to ask their associated medical providers intricate and important questions about incorporating spinal decompression therapy as part of their routine to reduce headaches and migraines associated with the neck. Dr. Jimenez, D.C., includes this information as an academic service. Disclaimer.
The Effects Of Cervical Pain & Headaches
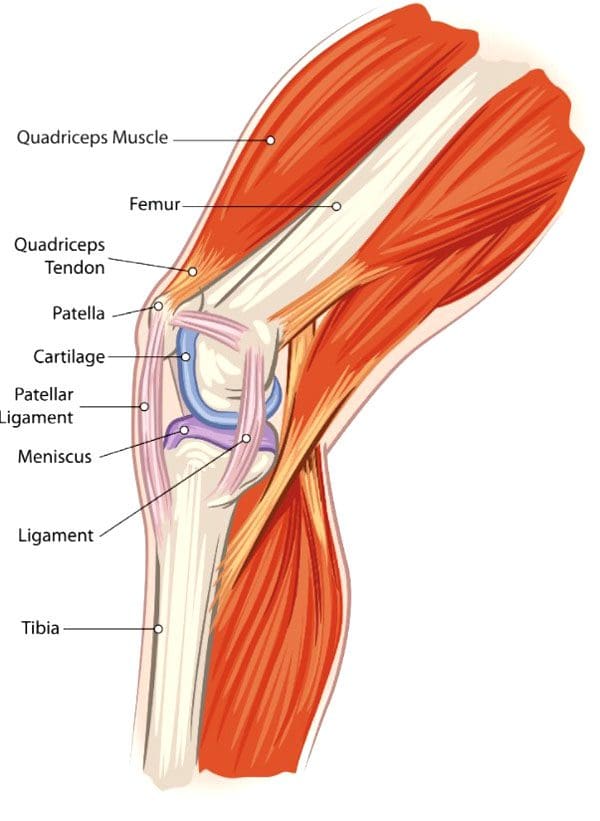
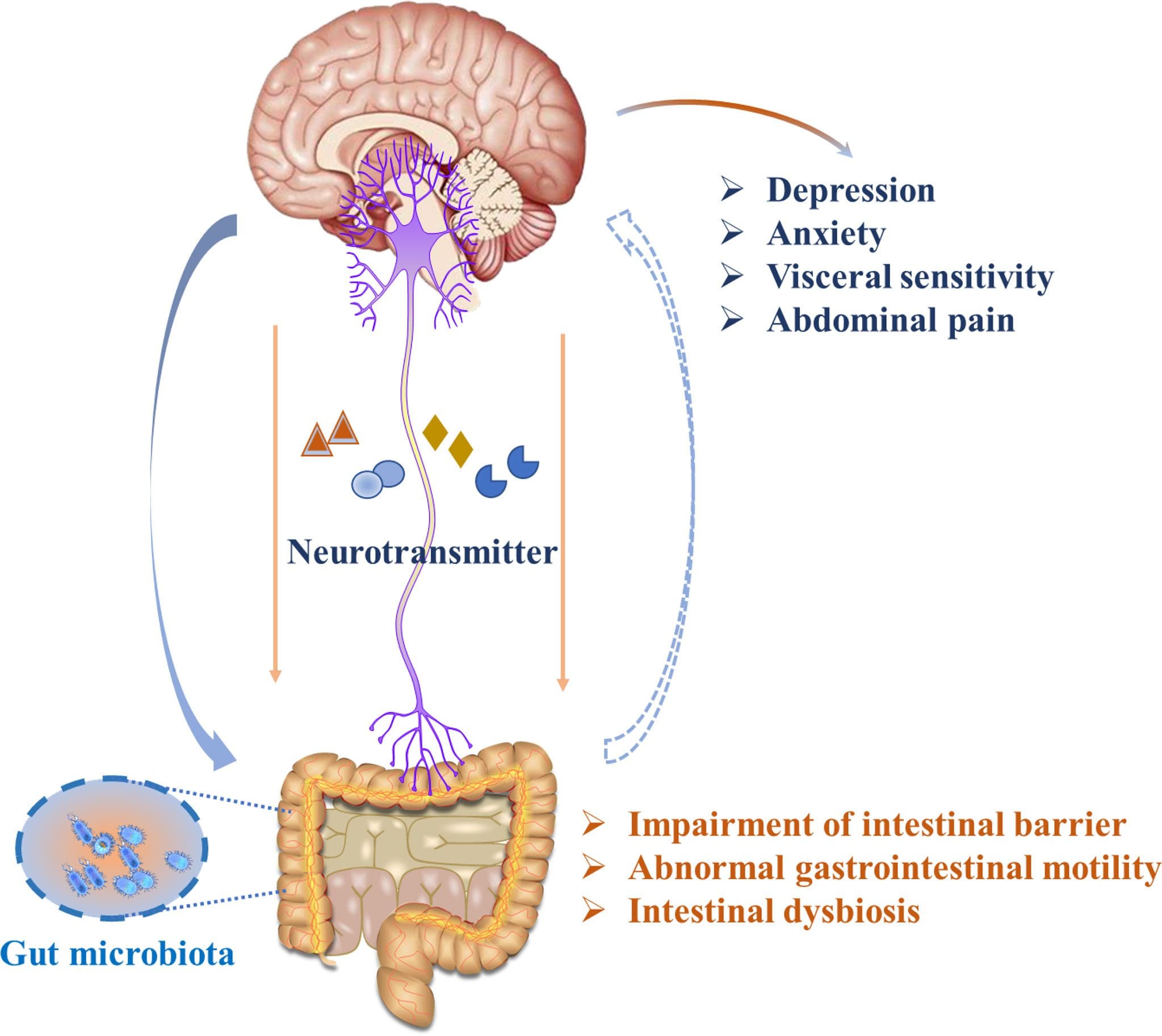
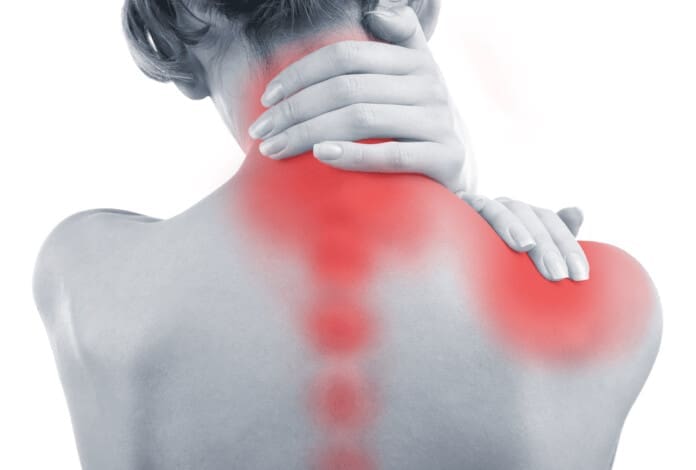
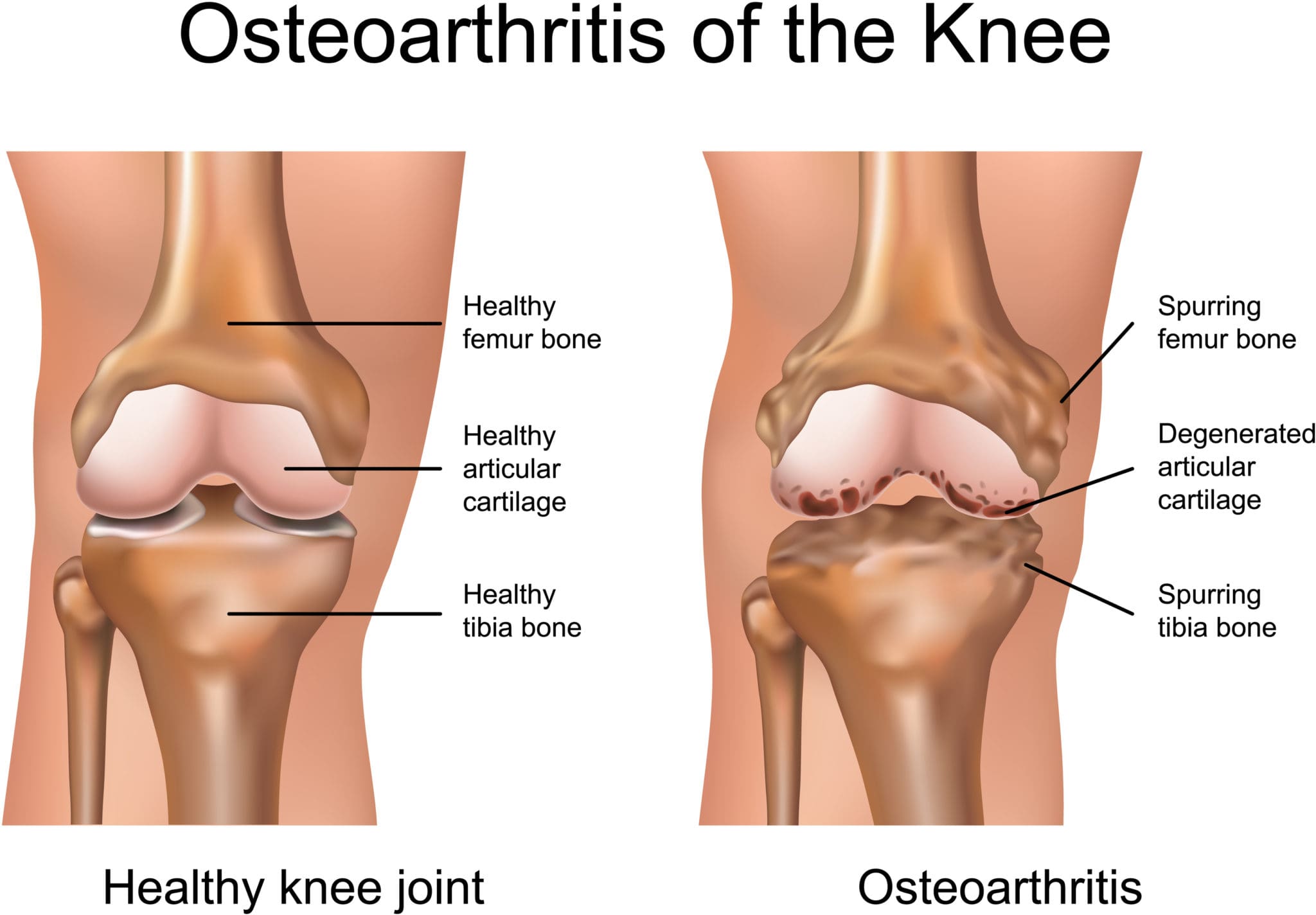
Do you feel stiffness on both sides of your neck that causes you limited mobility when you turn your neck? Have you experienced constant throbbing pain in your temples? Or do you feel muscle aches on your neck and shoulders from being hunched on the computer for an extended period? Many individuals dealing with these pain-like issues could be coping with cervical spinal pain. Various causes that can lead to the development of cervical spinal pain include herniated discs, pinched nerves, spinal stenosis, and muscle strain that originates from the neck region. This is because cervical spinal pain can be associated with environmental factors that can cause pain and discomfort, disability, and impaired quality of life as the surrounding neck muscles are overstretched and tight. (Ben Ayed et al., 2019) When people are dealing with cervical spinal pain, one of the symptoms it is associated with is headaches. This is because the intricated nerve pathways are connected to the neck and head. When cervical spinal pain is causing these issues, it can significantly impact a person’s daily body function as the pain is traveling upwards.
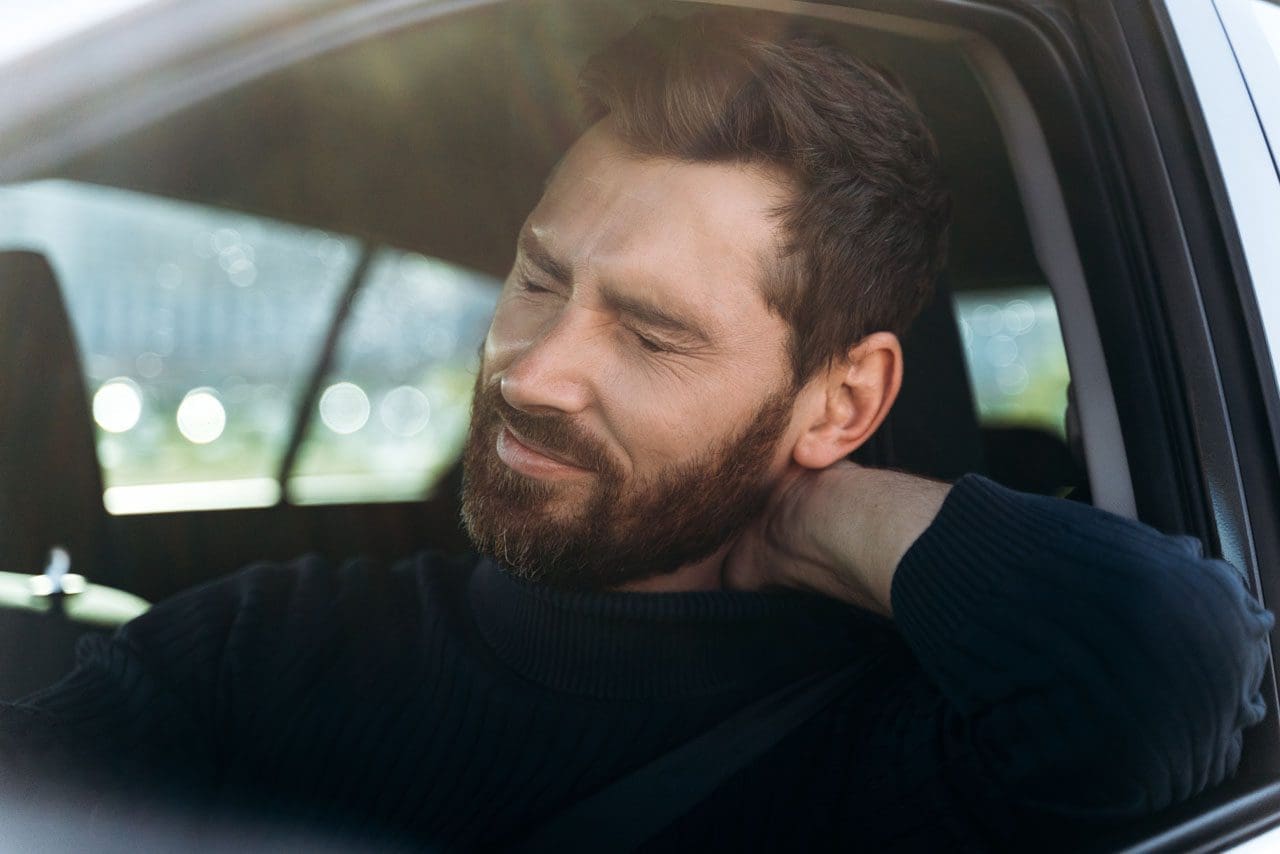

At the same time, neck pain is a multifactorial disease that can become a major issue worldwide. Like back pain, numerous risk factors can contribute to its development. (Kazeminasab et al., 2022) Some risk factors, like excessive phone usage, cause prolonged neck flexion to the neck and shoulders, causing static muscular loading with a lack of support to the upper extremities. (Al-Hadidi et al., 2019) To this point, environmental risk factors like excessive phone usage can make individuals develop a hunched position in their necks that can compress the spinal disc in the cervical region and aggravate the nerve roots to produce headaches and pain. However, many individuals have found ways to reduce cervical spinal pain and find pain relief from their headaches.
Home Exercises for Pain Relief-Video

How Spinal Decompression Reduces Cervical Spinal Pain
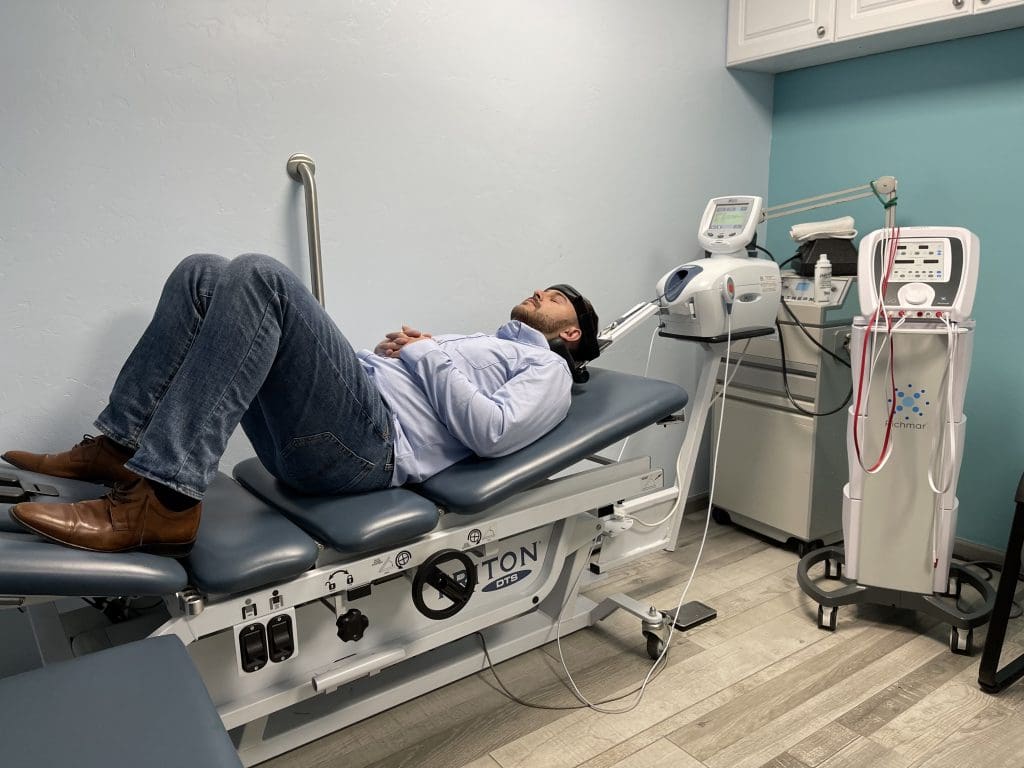
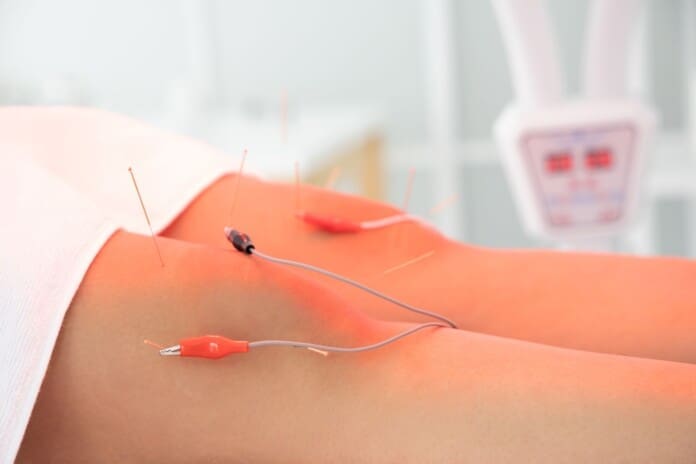
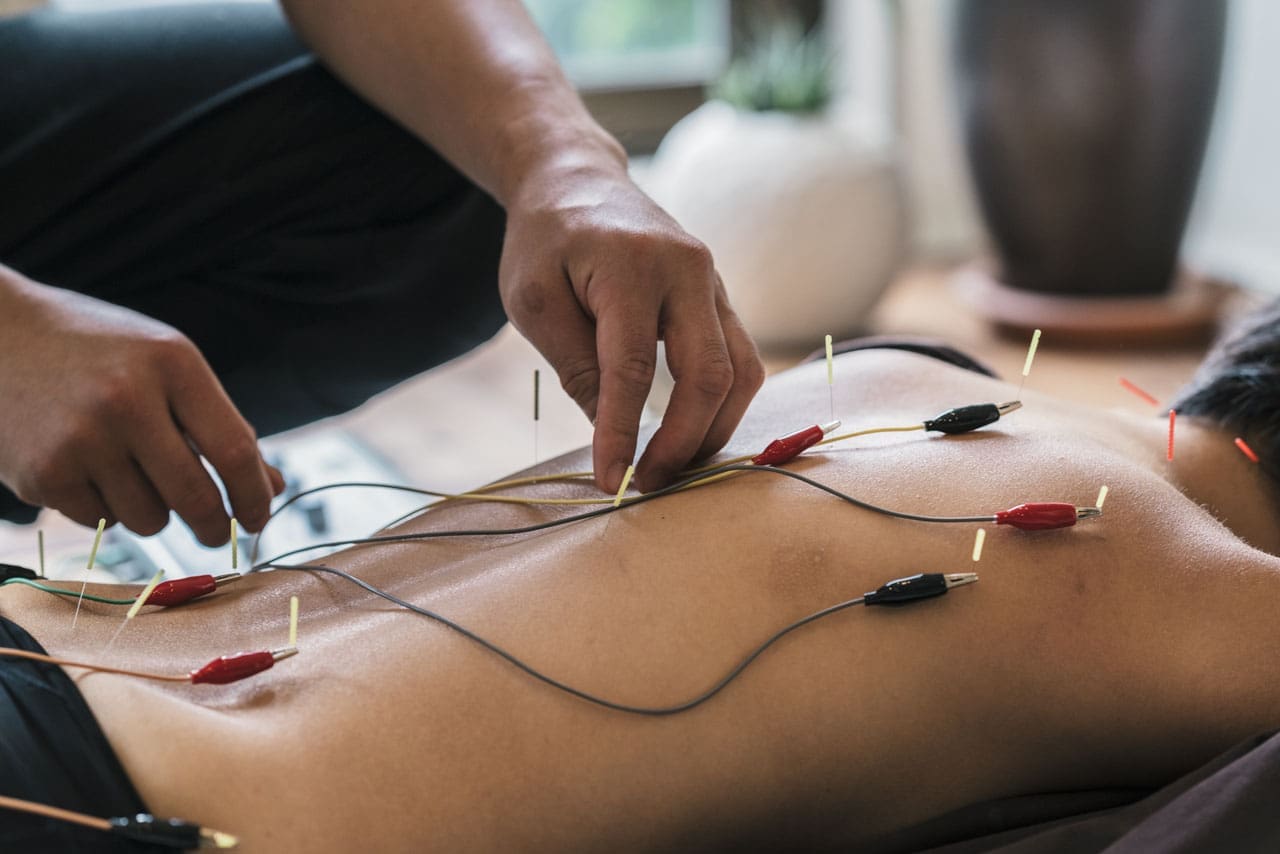
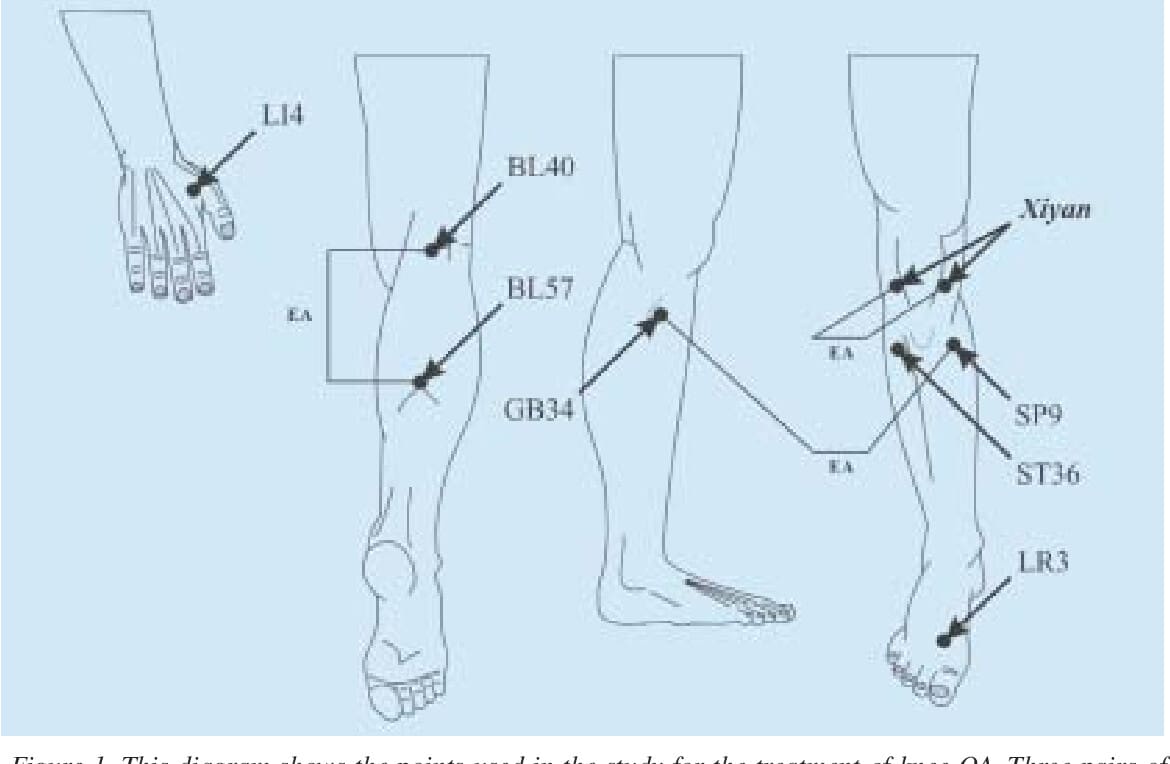
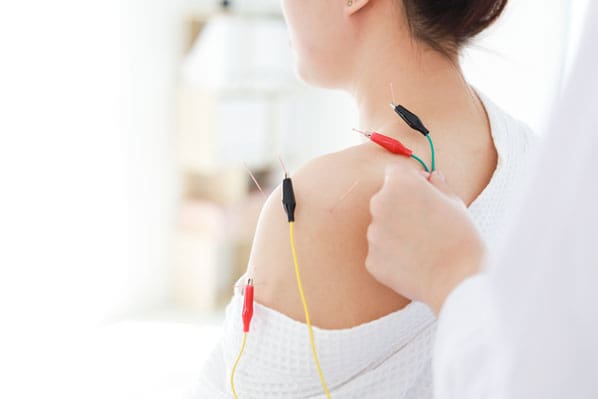
When it comes to reducing cervical spinal pain, many individuals have experienced that spinal decompression can help mitigate the effects of cervical pain. Spinal decompression has increasingly been recognized as an effective non-surgical treatment when it comes to alleviating cervical spinal pain. What spinal decompression does is that it allows negative pressure on the cervical spine to relieve any herniated disc of the aggravated nerve roots and help improve neurological symptoms. (Kang et al., 2016) This is due to a person being strapped comfortably on a traction machine that gently stretches and decompresses the spinal vertebrae. Additionally, some of the benefits of spinal decompression for cervical spinal pain include:
- Improved spinal alignment to reduce muscle strain on the neck muscles and joints.
- Enhanced the body’s natural healing by increasing blood flow and nutrient exchange.
- Increased neck mobility by decreasing muscle stiffness.
- Reducing pain levels that are causing intense headaches.
The Benefits of Spinal Decompression For Headaches
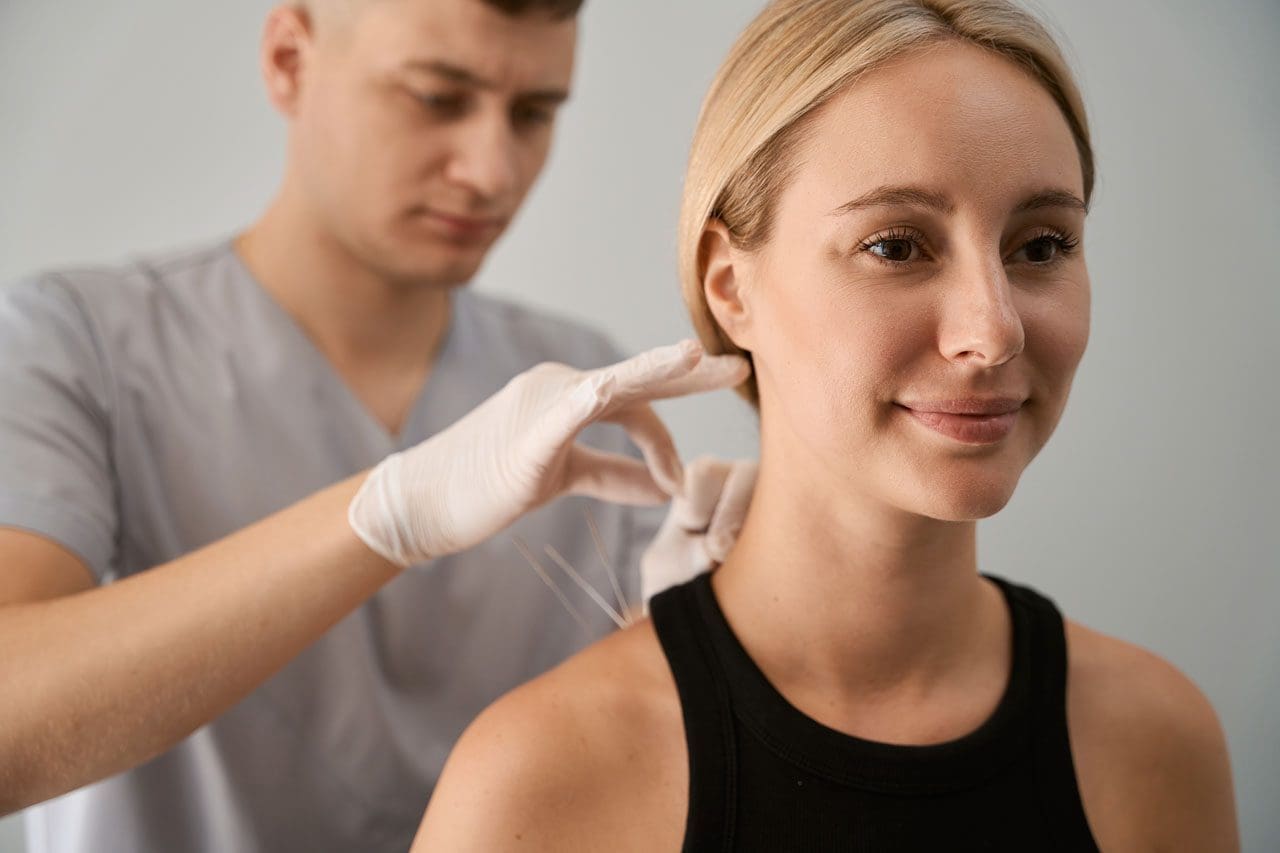
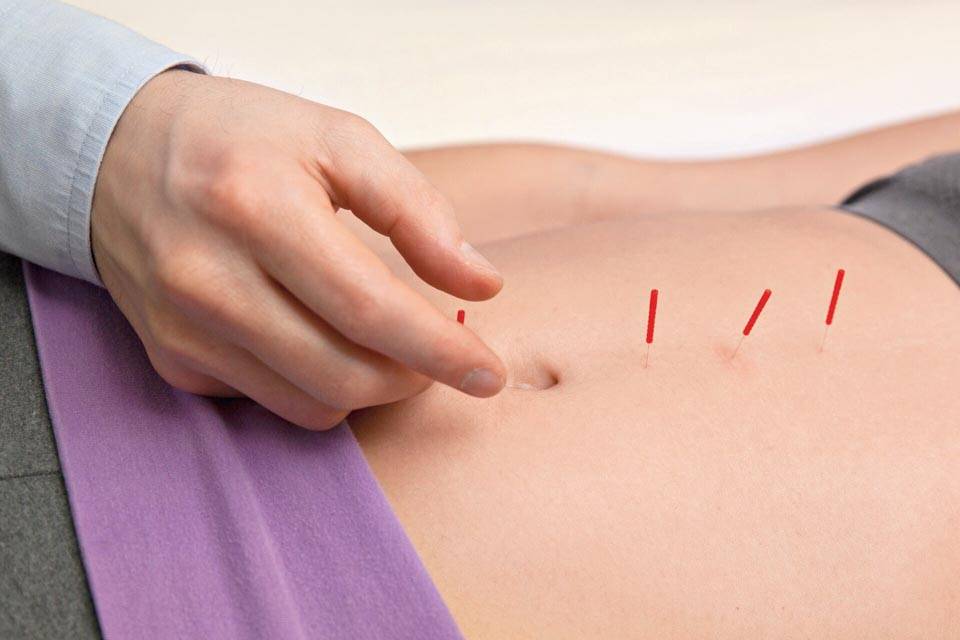
Additionally, spinal decompression can help reduce headaches associated with cervical spinal pain as spinal decompression can be combined with other therapies like acupuncture and physical therapy to relieve the protruding spinal dice and stabilize within the annulus by spinal elongation. (Van Der Heijden et al., 1995) This is due to gentle traction on the neck that is causing the prolapsed disc to reposition itself while restoring disc height to minimize the pressure on the nerves. (Amjad et al., 2022) When a person is doing spinal decompression therapy consecutively, the pain-like effects of cervical spinal pain and the associated headaches begin to reduce over time, and many people will start to notice how their habits are in correlation with their pain. By incorporating spinal decompression therapy as part of their treatment, many people can make small changes in their routine and be more mindful of their bodies to prevent the progression of cervical spinal pain from returning.
References
Al-Hadidi, F., Bsisu, I., AlRyalat, S. A., Al-Zu’bi, B., Bsisu, R., Hamdan, M., Kanaan, T., Yasin, M., & Samarah, O. (2019). Association between mobile phone use and neck pain in university students: A cross-sectional study using numeric rating scale for evaluation of neck pain. PLOS ONE, 14(5), e0217231. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0217231
Amjad, F., Mohseni-Bandpei, M. A., Gilani, S. A., Ahmad, A., & Hanif, A. (2022). Effects of non-surgical decompression therapy in addition to routine physical therapy on pain, range of motion, endurance, functional disability and quality of life versus routine physical therapy alone in patients with lumbar radiculopathy; a randomized controlled trial. BMC Musculoskelet Disord, 23(1), 255. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12891-022-05196-x
Ben Ayed, H., Yaich, S., Trigui, M., Ben Hmida, M., Ben Jemaa, M., Ammar, A., Jedidi, J., Karray, R., Feki, H., Mejdoub, Y., Kassis, M., & Damak, J. (2019). Prevalence, Risk Factors and Outcomes of Neck, Shoulders and Low-Back Pain in Secondary-School Children. J Res Health Sci, 19(1), e00440. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/31133629
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6941626/pdf/jrhs-19-e00440.pdf
Kang, J.-I., Jeong, D.-K., & Choi, H. (2016). Effect of spinal decompression on the lumbar muscle activity and disk height in patients with herniated intervertebral disk. Journal of Physical Therapy Science, 28(11), 3125-3130. https://doi.org/10.1589/jpts.28.3125
Kazeminasab, S., Nejadghaderi, S. A., Amiri, P., Pourfathi, H., Araj-Khodaei, M., Sullman, M. J. M., Kolahi, A. A., & Safiri, S. (2022). Neck pain: global epidemiology, trends and risk factors. BMC Musculoskelet Disord, 23(1), 26. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12891-021-04957-4
Van Der Heijden, G. J., Beurskens, A. J., Koes, B. W., Assendelft, W. J., De Vet, H. C., & Bouter, L. M. (1995). The Efficacy of Traction for Back and Neck Pain: A Systematic, Blinded Review of Randomized Clinical Trial Methods. Physical Therapy, 75(2), 93-104. https://doi.org/10.1093/ptj/75.2.93