Discover the benefits of chiropractic care for diabetic neuropathy in enhancing mobility and reducing discomfort in patients.
Understanding Diabetic Neuropathy: How Chiropractic Care Can Ease the Pain
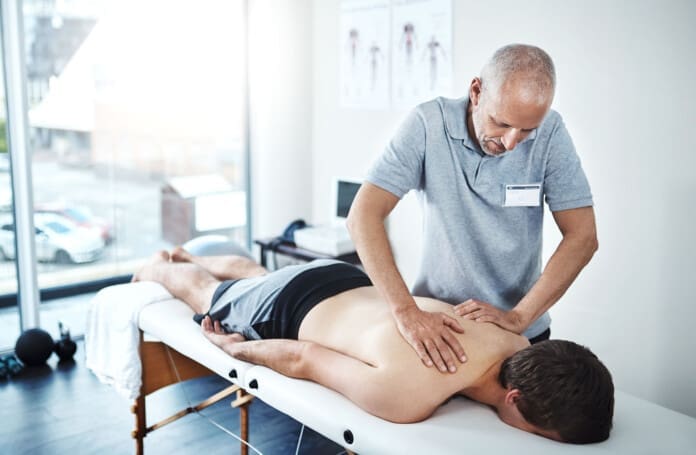
Living with diabetes can sometimes feel like you’re trying to juggle flaming torches while riding a unicycle. It’s tough, and one of the trickiest complications is diabetic neuropathy—a condition that brings nerve pain, tingling, and numbness to the party. About half of all people with diabetes deal with some form of neuropathy, which can make daily life feel like a prickly cactus hug (Feldman et al., 2019). But don’t worry—there’s hope! Chiropractic care, especially from experts like Dr. Alexander Jimenez, DC, APRN, FNP-BC, in El Paso, TX, can help soothe those cranky nerves without the need for surgery. Think of it as a superhero swooping in to calm the chaos.
In this 5,000+ word guide, we’ll break down diabetic neuropathy, its types, and how it messes with your body. We’ll explore why it happens, how your muscles and bones (also known as the musculoskeletal system) get involved, and why chiropractic care, paired with other non-surgical treatments, is a game-changer. We’ll also share practical lifestyle tips based on Dr. Jimenez’s clinical insights to help you manage your symptoms. Additionally, we’ll highlight Dr. Jimenez’s expertise in personal injury cases, demonstrating how he integrates medical care with legal needs for El Paso patients. So, grab a comfy chair (don’t slouch, your spine will thank you!), and let’s dive in.
What Is Diabetic Neuropathy?
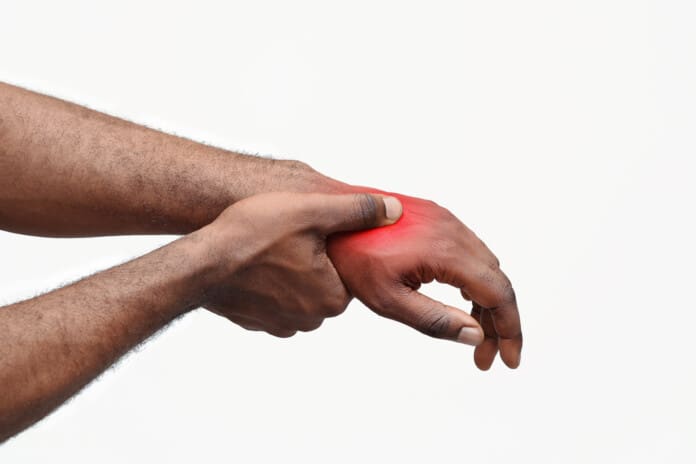
Diabetic neuropathy is like that one friend who shows up uninvited and makes everything awkward. It’s nerve damage caused by high blood sugar levels over time, which can affect nerves throughout the body (HealthCentral, n.d.). The most common type, distal symmetric polyneuropathy, often targets the feet and legs, causing tingling, burning, or numbness that can make walking feel like stepping on a Lego minefield (Feldman et al., 2019). It affects about 50% of people with diabetes, and if ignored, it can lead to serious issues like foot ulcers or infections (Sloan et al., 2025).
Your nerves are like the body’s electrical wiring, sending signals to control movement and sensation. When diabetes fries those wires, you get symptoms ranging from mild annoyance to severe pain. The good news? Treatments like chiropractic care can help rewire the system (or at least calm it down), and Dr. Jimenez’s clinic in El Paso is a go-to spot for relief (Sciatica Clinic, n.d.).
References
- Feldman, E. L., Callaghan, B. C., Pop-Busui, R., Zochodne, D. W., Wright, D. E., Bennett, D. L., … & Viswanathan, V. (2019). Diabetic neuropathy. Nature Reviews Disease Primers, 5(1), 41. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31197183/
- HealthCentral. (n.d.). Types of diabetic neuropathy. Retrieved from https://www.healthcentral.com/condition/diabetes/types-diabetic-neuropathy?legacy=ew
- Sciatica Clinic. (n.d.). Sciatica pain. Retrieved from https://sciatica.clinic/
- Sloan, G., Ali, N., & Tesfaye, S. (2025). Diabetic neuropathy: Cutting-edge research and future directions. Signal Transduction and Targeted Therapy, 10(1), 1-18. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/38245327/
Types of Diabetic Neuropathy and Their Effects
Diabetic neuropathy isn’t a one-trick pony—it comes in four main types, each with its own way of stirring up trouble. Let’s meet the gang and see how they mess with your body, based on insights from HealthCentral (n.d.) and research (Vinik et al., 2022).
1. Peripheral Neuropathy
This is the ringleader, affecting the nerves in your feet, legs, hands, and arms in a “stocking and glove” pattern (Vinik et al., 2022). Symptoms include:
- Tingling or numbness: Like your foot’s decided to take a nap.
- Burning or shooting pain: Think tiny firecrackers going off in your legs.
- Muscle weakness: Makes picking up groceries feel like lifting a car.
- Balance issues: You might wobble like a penguin on ice.
Peripheral neuropathy can make walking or even wearing shoes a chore. It also increases the risk of foot injuries, as you may not feel a cut, which can lead to infections (HealthCentral, n.d.).
2. Autonomic Neuropathy
This type interferes with your body’s autopilot—the autonomic nervous system that regulates functions such as heart rate and digestion. Symptoms include:
- Digestive drama: Nausea, bloating, or constipation that feels like your gut’s on strike.
- Heart rate hiccups: Your heart rate may speed up or slow down without an apparent reason.
- Bathroom troubles: Unpredictable bladder or bowel issues—yep, it’s awkward.
- Sweating quirks: Either you’re a human sprinkler or bone-dry.
It’s as if your body’s control panel is malfunctioning, making everyday functions a bit chaotic (Feldman et al., 2019).
3. Proximal Neuropathy
Also known as diabetic amyotrophy, this condition typically affects the thighs, hips, or buttocks, often on one side. Symptoms include:
- Deep pain: A nagging ache in your upper legs or hips.
- Muscle weakness: Climbing stairs feels like summiting a mountain.
- Trouble standing: Getting up from a chair might require a pep talk.
It’s more common in older adults with type 2 diabetes and can improve with time if managed well (HealthCentral, n.d.).
4. Focal Neuropathy
This is the wildcard, hitting specific nerves in your head, torso, or legs. Symptoms include:
- Sudden weakness: One muscle group might just clock out.
- Localized pain: Could be your wrist, thigh, or even face.
- Vision issues: Double vision or trouble focusing, as if your eyes are playing tricks.
Focal neuropathy strikes fast but often resolves on its own, though it’s no fun while it lasts (Vinik et al., 2022).
Each type can throw your musculoskeletal system into disarray, weakening muscles or disrupting your posture, which we’ll explore next.
References
- Feldman, E. L., Callaghan, B. C., Pop-Busui, R., Zochodne, D. W., Wright, D. E., Bennett, D. L., … & Viswanathan, V. (2019). Diabetic neuropathy. Nature Reviews Disease Primers, 5(1), 41. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31197183/
- HealthCentral. (n.d.). Types of diabetic neuropathy. Retrieved from https://www.healthcentral.com/condition/diabetes/types-diabetic-neuropathy?legacy=ew
- Vinik, A. I., Nevoret, M. L., & Casellini, C. (2022). Diabetic neuropathies. Endotext. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/35428527/
Why Does Diabetic Neuropathy Happen? Risk Factors
Diabetic neuropathy doesn’t just show up like an uninvited guest—it’s more like a slow-building storm. Several factors contribute to its development, and they often tie into your musculoskeletal system. Let’s break them down.
1. High Blood Sugar Over Time
The main culprit is chronic high blood sugar, which damages the tiny blood vessels that feed your nerves (Feldman et al., 2019). Without sufficient oxygen and nutrients, nerves become irritated, leading to pain or numbness. It’s like your nerves are stuck in a low-battery mode.
2. How Long You’ve Had Diabetes
The longer you’ve had diabetes, the more likely neuropathy is to crash the party. Years of uncontrolled blood sugar can cause nerve damage, especially if you’re not keeping it in check (Vinik et al., 2022). Think of it as a snowball rolling downhill—it gets bigger over time.
3. Obesity
Excess weight puts stress on your spine, joints, and muscles, which can compress nerves and exacerbate pain (Sciatica Clinic, n.d.). Obesity also makes blood sugar control harder, feeding into neuropathy (Feldman et al., 2019). It’s like carrying a heavy backpack that keeps poking your nerves.
4. Heart Health Issues
High cholesterol, high blood pressure, or smoking can clog blood vessels, reducing blood flow to nerves (Sloan et al., 2025). Less blood flow means more nerve damage, like a plant wilting without water.
5. Musculoskeletal Problems
Here’s where your muscles and bones come in. Poor posture, spinal misalignments (subluxations), or muscle imbalances can pinch nerves, amplifying neuropathy symptoms (Sciatica Clinic, n.d.). For example, a misaligned spine might irritate the sciatic nerve, mimicking neuropathy pain. This overlap is why chiropractic care is so effective—it tackles these structural issues head-on.
6. Sedentary Lifestyle
Sitting for extended periods or experiencing repetitive strain from certain jobs can stress nerves or reduce blood flow, exacerbating neuropathy (HealthCentral, n.d.). It’s like your nerves are begging for a stretch break.
7. Genetics
Some individuals are more prone to nerve damage due to their genetic predisposition (Feldman et al., 2019). If neuropathy runs in your family, it’s like inheriting a quirky family trait—except this one stings.
These factors don’t just hurt your nerves; they can mess with your musculoskeletal system, creating a cycle of pain and dysfunction. Weakened leg muscles due to neuropathy can alter your walking pattern, placing additional stress on your spine and joints (Vinik et al., 2022). Let’s see how chiropractic care can break that cycle.
References
- Feldman, E. L., Callaghan, B. C., Pop-Busui, R., Zochodne, D. W., Wright, D. E., Bennett, D. L., … & Viswanathan, V. (2019). Diabetic neuropathy. Nature Reviews Disease Primers, 5(1), 41. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31197183/
- HealthCentral. (n.d.). Types of diabetic neuropathy. Retrieved from https://www.healthcentral.com/condition/diabetes/types-diabetic-neuropathy?legacy=ew
- Sciatica Clinic. (n.d.). Sciatica pain. Retrieved from https://sciatica.clinic/
- Sloan, G., Ali, N., & Tesfaye, S. (2025). Diabetic neuropathy: Cutting-edge research and future directions. Signal Transduction and Targeted Therapy, 10(1), 1-18. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/38245327/
- Vinik, A. I., Nevoret, M. L., & Casellini, C. (2022). Diabetic neuropathies. Endotext. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/35428527/
Diabetic Back Pain- Video
The Musculoskeletal Connection and Chiropractic Care
Your musculoskeletal system—your bones, muscles, and joints—is like the framework of a house. When diabetic neuropathy moves in, it can shake that framework, causing all sorts of problems. Here’s how it works and why chiropractic care, especially from Dr. Jimenez, is a powerful tool.
How Neuropathy Impacts Muscles and Bones
Diabetic neuropathy, particularly peripheral neuropathy, can throw your musculoskeletal system out of whack (Vinik et al., 2022). Here’s how:
- Muscle Weakness: Damaged nerves struggle to send signals to muscles, leading to weakness in your legs or feet. This can make walking feel like trudging through mud.
- Wonky Gait: Pain or numbness in your legs changes how you walk, putting extra stress on your spine, hips, or knees. It’s like driving with a flat tire—everything gets bumpy.
- Spinal Misalignments: To avoid pain, you may slouch or shift your weight, further misaligning your spine and compressing nerves (Sciatica Clinic, n.d.).
- Joint Stress: Weak muscles and poor alignment can overwork your joints, leading to pain or even symptoms similar to arthritis.
This creates a vicious cycle: neuropathy weakens muscles, which messes with your posture, which pinches nerves, which worsens pain. For example, sciatic nerve irritation from a misaligned spine can mimic or amplify neuropathy symptoms (Sciatica Clinic, n.d.).
The Chiropractic Solution
Chiropractic care is like hiring a skilled carpenter to fix your house’s foundation. Dr. Jimenez employs gentle spinal adjustments to realign the spine, reduce nerve pressure, and enhance blood flow to damaged nerves (Sciatica Clinic, n.d.). Here’s the clinical rationale for why it works:
- Easing Nerve Compression: Adjustments correct spinal misalignments, thereby reducing pressure on nerves, such as the sciatic nerve, which can help alleviate neuropathic pain (Jensen et al., 2020).
- Boosting Circulation: Proper alignment enhances blood flow, delivering oxygen and nutrients to nerves, which may aid in their healing (Feldman et al., 2019).
- Restoring Muscle Function: Better spinal alignment supports muscle coordination, reducing weakness and improving mobility (Sciatica Clinic, n.d.).
- Natural Pain Relief: Adjustments can help lower inflammation and trigger the release of endorphins, your body’s natural painkillers (Jensen et al., 2020).
Dr. Jimenez begins with a thorough examination, often utilizing advanced imaging techniques such as X-rays or MRIs to pinpoint issues like herniated discs or subluxations (Jimenez, n.d.). His dual training as a chiropractor and nurse practitioner enables him to craft personalized plans that address both nerve pain and musculoskeletal issues, ensuring you return to feeling like yourself.
References
- Feldman, E. L., Callaghan, B. C., Pop-Busui, R., Zochodne, D. W., Wright, D. E., Bennett, D. L., … & Viswanathan, V. (2019). Diabetic neuropathy. Nature Reviews Disease Primers, 5(1), 41. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31197183/
- Jensen, R. K., Kongsted, A., Kjaer, P., & Koes, B. (2020). Diagnosis and treatment of sciatica. BMJ, 367, l6273. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32036431/
- Jimenez, A. (n.d.). LinkedIn profile. Retrieved from https://www.linkedin.com/in/dralexjimenez/
- Sciatica Clinic. (n.d.). Sciatica pain. Retrieved from https://sciatica.clinic/
- Vinik, A. I., Nevoret, M. L., & Casellini, C. (2022). Diabetic neuropathies. Endotext. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/35428527/
Non-Surgical Treatments to Boost Chiropractic Care
Chiropractic care is a superstar, but it shines even brighter when teamed up with other non-surgical treatments. Think of it as assembling the Avengers to tackle neuropathy pain. Here are some treatments Dr. Jimenez often pairs with chiropractic care, based on his clinical expertise (Sciatica Clinic, n.d.; Jimenez, n.d.).
1. Physical Therapy
Physical therapy strengthens muscles, improves flexibility, and fixes gait issues caused by neuropathy (Sloan et al., 2025). Core and leg exercises reduce stress on your spine and joints, making chiropractic adjustments even more effective. Dr. Jimenez often suggests specific exercises to maintain proper posture.
2. Massage Therapy
Massage isn’t just for fancy spa days—it boosts blood flow, relaxes tight muscles, and calms irritated nerves (Sciatica Clinic, n.d.). Patients at Dr. Jimenez’s clinic rave about therapists like Adrian, who help ease pain alongside adjustments (Sciatica Clinic, n.d.).
3. Acupuncture
Acupuncture uses tiny needles to stimulate nerves and reduce pain. It’s like giving your nerves a gentle pep talk. Research indicates that it can help alleviate neuropathic pain by calming nerve signals and reducing inflammation (Zhang et al., 2021).
4. Nutritional Guidance
What you eat matters. Dr. Jimenez recommends anti-inflammatory foods, such as greens, berries, and salmon, to support nerve health and control blood sugar (Jimenez, n.d.). Ditching sugary snacks is like telling nerve-damaging sugar to take a hike.
5. TENS (Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation)
TENS uses low-voltage currents to block pain signals, like turning down the volume on your nerves’ complaints. Studies suggest it offers short-term relief for neuropathy pain (Gibson et al., 2020).
6. Lifestyle Tweaks
Small changes can make a big difference. Dr. Jimenez suggests:
- Get Moving: Low-impact exercises like walking or yoga improve circulation and ease symptoms.
- Wear Good Shoes: Supportive footwear protects your feet, especially if you have peripheral neuropathy.
- Manage Stress: Meditation and deep breathing help lower stress hormones that can exacerbate pain (Sciatica Clinic, n.d.).
These treatments work in conjunction with chiropractic care to address both nerve pain and musculoskeletal issues, providing a comprehensive plan for relief.
References
- Gibson, W., Wand, B. M., & O’Connell, N. E. (2020). Transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENS) for neuropathic pain in adults. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews, 2020(9). https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32999525/
- Jimenez, A. (n.d.). LinkedIn profile. Retrieved from https://www.linkedin.com/in/dralexjimenez/
- Sciatica Clinic. (n.d.). Sciatica pain. Retrieved from https://sciatica.clinic/
- Sloan, G., Ali, N., & Tesfaye, S. (2025). Diabetic neuropathy: Cutting-edge research and future directions. Signal Transduction and Targeted Therapy, 10(1), 1-18. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/38245327/
- Zhang, R., Lao, L., Ren, K., & Berman, B. M. (2021). Mechanisms of acupuncture in persistent pain. Current Pain and Headache Reports, 25(12), 1-10. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34901069/
Dr. Alexander Jimenez: El Paso’s Personal Injury Expert
In El Paso, TX, Dr. Alexander Jimenez is a standout for patients dealing with neuropathy or personal injuries from accidents. His unique combo of chiropractic expertise, nursing knowledge, and diagnostic skills makes him a trusted choice (Jimenez, n.d.).
Why Dr. Jimenez Shines in Personal Injury Care
Car accidents or falls can worsen neuropathy by causing spinal misalignments or nerve compression (Sciatica Clinic, n.d.). Dr. Jimenez’s approach is thorough:
- Advanced Imaging: He uses X-rays, MRIs, or CT scans to spot issues like herniated discs or subluxations.
- Detailed Diagnostics: Neurological and musculoskeletal exams pinpoint nerve damage and its effects.
- Dual-Scope Expertise: As a chiropractor and nurse practitioner, he provides detailed medical reports for legal cases, linking injuries to symptoms and treatments (Jimenez, n.d.).
- Holistic Plans: He combines adjustments, physical therapy, and other methods for comprehensive healing.
Patients love his care—Gale Grijalva, for example, said Dr. Jimenez’s treatments transformed her life after other doctors only offered pain pills (Sciatica Clinic, n.d.). His ability to bridge the gap between medical and legal needs makes him a vital ally for personal injury victims.
References
Practical Lifestyle Changes to Manage Neuropathy
You don’t need to flip your life upside down to manage neuropathy—small changes can work wonders. Dr. Jimenez shares these tips to ease nerve pain and support your musculoskeletal health (Sciatica Clinic, n.d.). Here’s a lighthearted take:
- Get Up and Groove: Aim for 30 minutes of walking or swimming most days. It’s like giving your nerves a coffee break to recharge (Sloan et al., 2025).
- Eat Smart: Load up on veggies and healthy fats, and skip the sugary treats. Your nerves will thank you for not feeding them candy chaos (Jimenez, n.d.).
- Foot Check-Ups: Inspect your feet daily for cuts, blisters, or other signs of injury. Think of it as a daily high-five to your toes (HealthCentral, n.d.).
- Posture Power: Sit tall and use a rolled towel for lumbar support. Your spine will feel like it’s getting a gold star (Sciatica Clinic, n.d.).
- Chill Out: Try meditation or yoga to lower stress. It’s like telling your nerves to take a spa day (Zhang et al., 2021).
These tweaks, when paired with chiropractic care, can help you manage neuropathy and maintain a strong body framework.
References
- HealthCentral. (n.d.). Types of diabetic neuropathy. Retrieved from https://www.healthcentral.com/condition/diabetes/types-diabetic-neuropathy?legacy=ew
- Jimenez, A. (n.d.). LinkedIn profile. Retrieved from https://www.linkedin.com/in/dralexjimenez/
- Sciatica Clinic. (n.d.). Sciatica pain. Retrieved from https://sciatica.clinic/
- Sloan, G., Ali, N., & Tesfaye, S. (2025). Diabetic neuropathy: Cutting-edge research and future directions. Signal Transduction and Targeted Therapy, 10(1), 1-18. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/38245327/
- Zhang, R., Lao, L., Ren, K., & Berman, B. M. (2021). Mechanisms of acupuncture in persistent pain. Current Pain and Headache Reports, 25(12), 1-10. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34901069/
Conclusion
Diabetic neuropathy is a challenging condition, but with the right approach, you can find relief and improve your quality of life. Chiropractic care, led by experts like Dr. Alexander Jimenez in El Paso, TX, provides a non-surgical approach to alleviating nerve pain by addressing musculoskeletal issues such as spinal misalignments and muscle weakness. Combined with physical therapy, massage, acupuncture, and lifestyle changes, it tackles the root causes of neuropathy and its overlap with diabetes-related risks. Dr. Jimenez’s expertise in personal injury cases also makes him a trusted partner for accident victims, providing advanced diagnostics and legal documentation to support recovery.
Disclaimer: This blog post is for informational purposes only and is not a substitute for professional medical advice. Always consult a qualified healthcare provider, such as a chiropractor or physician, before starting any treatment for diabetic neuropathy or related conditions. The information is based on current research and clinical insights but does not replace a professional evaluation.
References
- Feldman, E. L., Callaghan, B. C., Pop-Busui, R., Zochodne, D. W., Wright, D. E., Bennett, D. L., … & Viswanathan, V. (2019). Diabetic neuropathy. Nature Reviews Disease Primers, 5(1), 41. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31197183/
- Gibson, W., Wand, B. M., & O’Connell, N. E. (2020). Transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENS) for neuropathic pain in adults. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews, 2020(9). https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32999525/
- HealthCentral. (n.d.). Types of diabetic neuropathy. Retrieved from https://www.healthcentral.com/condition/diabetes/types-diabetic-neuropathy?legacy=ew
- Jensen, R. K., Kongsted, A., Kjaer, P., & Koes, B. (2020). Diagnosis and treatment of sciatica. BMJ, 367, l6273. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32036431/
- Jimenez, A. (n.d.). LinkedIn profile. Retrieved from https://www.linkedin.com/in/dralexjimenez/
- Sciatica Clinic. (n.d.). Sciatica pain. Retrieved from https://sciatica.clinic/
- Sloan, G., Ali, N., & Tesfaye, S. (2025). Diabetic neuropathy: Cutting-edge research and future directions. Signal Transduction and Targeted Therapy, 10(1), 1-18. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/38245327/
- Vinik, A. I., Nevoret, M. L., & Casellini, C. (2022). Diabetic neuropathies. Endotext. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/35428527/
- Zhang, R., Lao, L., Ren, K., & Berman, B. M. (2021). Mechanisms of acupuncture in persistent pain. Current Pain and Headache Reports, 25(12), 1-10. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34901069/