Table of Contents
Introduction
The heart is a fantastic muscle in the body that allows hormones, oxygenated blood, and nutrients to travel and transport to all the muscles, tissues, and organs, providing functionality to the body. As one of the main components of the cardiovascular system, the heart works together with the lungs to help carry the deoxygenated blood to the pulmonary system to dispose of waste from the body. The human body needs the heart to stay healthy; however, factors like stress, obesity, autoimmune diseases, and unhealthy habits can affect the heart, causing cardiac issues associated with various body problems. Today’s article focuses on coronary heart disease, what are the risks associated with coronary heart disease, and ways to prevent coronary heart disease from progressively getting worse. We refer patients to certified providers specializing in cardiology treatments that help those with issues of coronary heart disease. We also guide our patients by referring to our associated medical providers based on their examination when it’s appropriate. We find that education is the solution to asking our providers insightful questions. Dr. Alex Jimenez DC provides this information as an educational service only. Disclaimer
What Is Coronary Heart Disease?
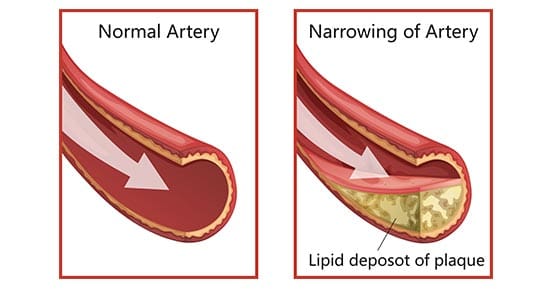
Have you been experiencing hypertension in your body or near your heart? How about unexplained chest pains that randomly showed up? Have you experienced pain running down your shoulders and arms? Many of these are signs that you could be experiencing coronary heart disease. Research studies have defined coronary heart disease as a common heart condition with plaque formation in the heart vessels that cuts off the supply of oxygenated blood to the heart and the rest of the body. As part of cardiovascular diseases, coronary heart disease can cause overlapping profile issues over time if it is not treated right away. Many disruptive factors can affect the heart muscle like:
- Age and gender
- Oxidative stress
- Inflammation
- Vascular immune dysfunction
- Lack of physical activities
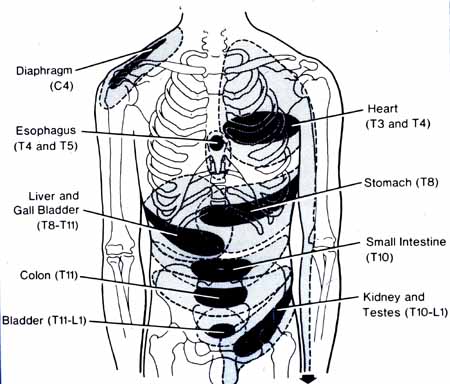
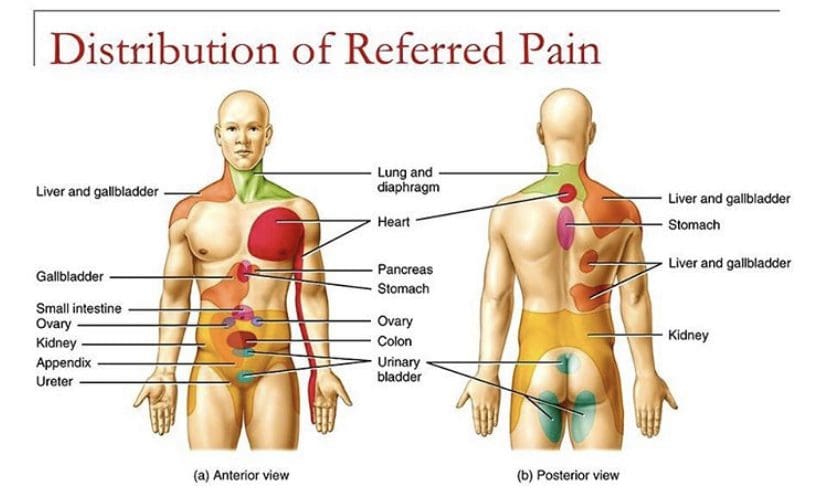
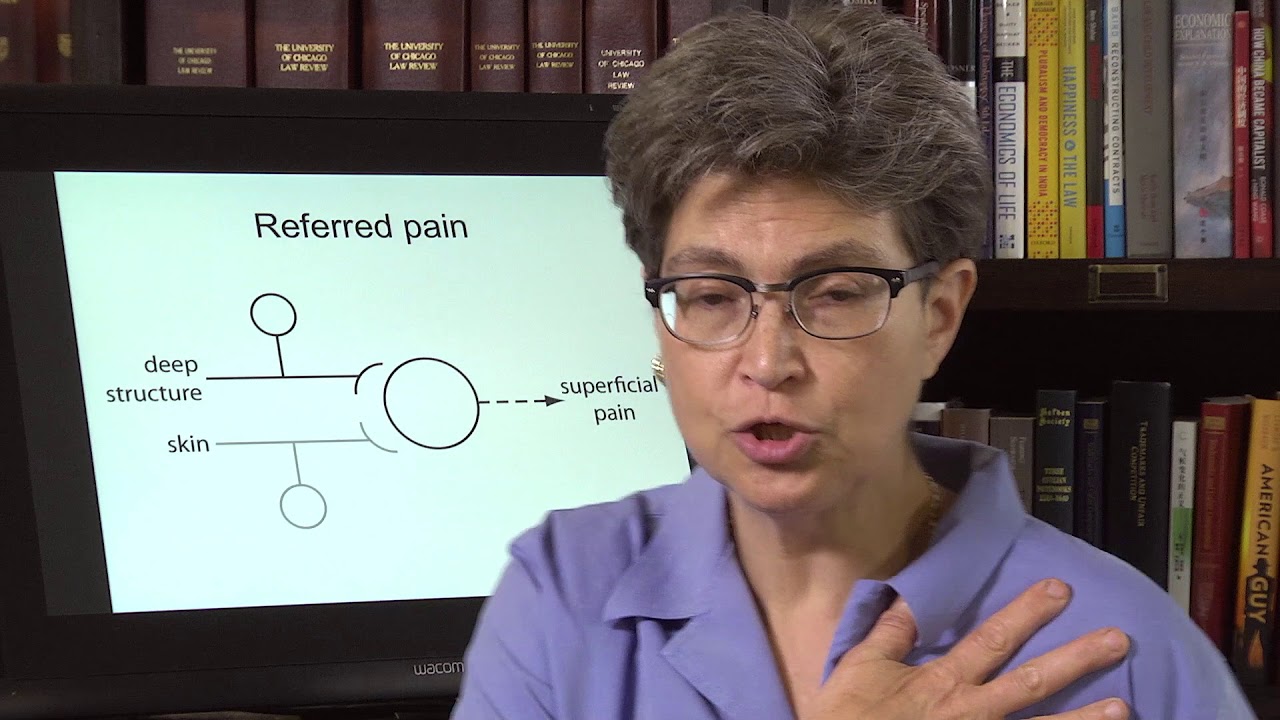
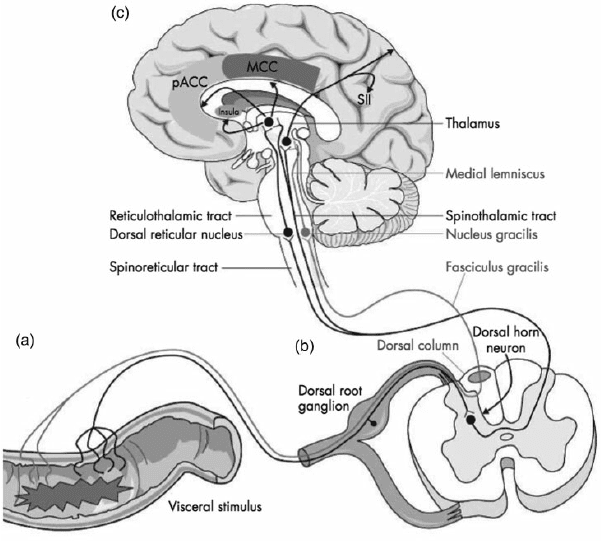
These disruptive factors can increase cardiovascular disease mortality that can affect the heart and be co-morbidities associated with different issues affecting the body. Studies reveal that the mechanisms of cardiac pain are associated with the chest and upper left arm pain. This is defined as referred pain where the sensory input from visceral organs mimics cardiac distress, and the corresponding muscles are affected. But how does this correlate to the heart muscle, and why does the chest experience pain? Visceral pain is a bit trickier to diagnose when cardiovascular disorders overlap the risk profiles associated with other issues affecting the body. For example, you could be experiencing pain in your chest and upper back, but your brain is telling you something is affecting your heart.
An Overview Of CAD-Video

Have you experienced shortness of breath? How about pain located in your chest or radiating from your shoulders and arms? Have you noticed inflammation occurring in your body? Many of these are signs and symptoms of you experiencing coronary artery disease in your body. The video above explains what coronary artery disease is and the risk factors associated with the progression of this common heart disease. Studies reveal that the risk factors can overlap in profiles that contribute to the development of coronary heart disease:
- Environmental factors
- Lifestyle habits
- Diabetes mellitus
- Obesity
- Symptomatic angina
- Smoking
When a person has these risk profiles overlapping different associated issues, their body becomes dysfunctional. Sometimes the symptoms affect other areas of the body, while the brain might be signaled that something is wrong with the heart. Since coronary artery disease progresses slowly over time, many individuals don’t experience the symptoms affecting their heart muscles.
Risk Issues Associated With CHD
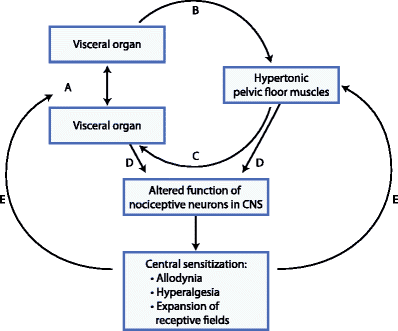
Some of these symptoms that overlap in risk profiles may seem like heart issues but may refer to different problems affecting the body. This is defined as viscero-somatic pain, where the pain in the internal organs is associated with the corresponding muscles that share the same nerve. Chest pain associated with heart issues is a perfect example. Studies reveal that chest pains can become indistinguishable from angina, which may result from abnormalities in the thoracic viscera that overlap in profiles with heart issues. So what does it mean? It implies that sensory neurons from different visceral organs might mimic cardiac pain-causing risk-associated problems that affect the thoracic region of the spine triggering neck and upper back issues. Everything is connected as chest pains, dyspnea, and dyspepsia are intertwined with the thoracic anteriority becoming a mediator for cardiovascular diseases.
Ways To Prevent CHD
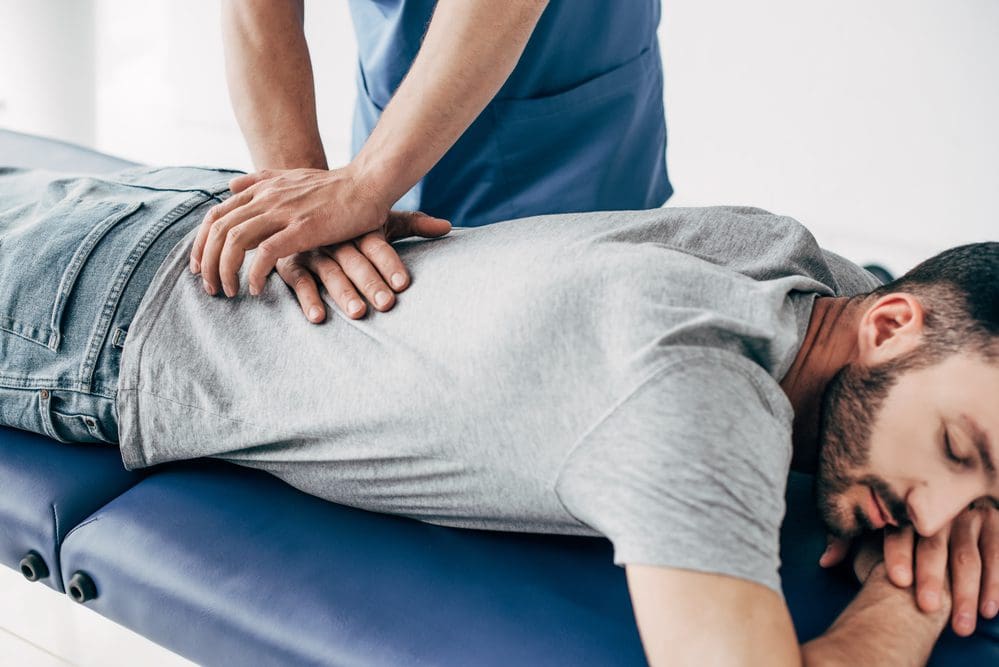
So let’s visualize a person going to their primary physician due to them experiencing heart issues associated with chest pains after the doctor goes through a manual examination on checking the individual’s heart and chest to see what problems are affecting the body. What does this implicates, and how do chest and back pains correlate with each other if there are heart issues? Studies reveal that the peripheral tissues in the body might be damaged from traumatic events that cause an inflammatory swelling in the cervical and thoracic region of the spine, causing muscle stiffness. Chiropractic care might be the answer to relieving pain and swelling triggering cervical and thoracic pain. Chiropractors use chiropractic adjustments to deliver a non-invasive, gentle treatment that reduces spinal misalignments to enhance the functionality of the musculoskeletal system. This will improve spinal health in the cervical and thoracic regions of the body by decreasing inflammatory swelling associated with heart issues. Chiropractic care, a healthy diet, and exercise also work hand in hand by positively impacting co-morbidities of coronary heart disease and other body problems like obesity to reduce cholesterol, help strengthen the weak muscles along the neck and upper back, and promote blood flow to the heart.
Conclusion
As part of the cardiovascular system, the heart supplies hormones, oxygenated blood, and nutrients throughout the entire body by ensuring that the muscles, tissues, and organs are functioning. When factors like stress, obesity, and unhealthy habits begin to affect the heart, it can develop cardiac issues like coronary heart disease associated with various body problems. Chest pains associated with heart issues that trigger neck and back pain in the body are known as viscero-somatic pain. Available treatments like chiropractic care and changing unhealthy habits work hand in hand to positively impact co-morbidities of coronary heart disease and reduce muscle stiffness along the neck and back muscles of the cervical and thoracic spine.
References
Börjesson, M. “Visceral Chest Pain in Unstable Angina Pectoris and Effects of Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation. (TENS). A Review.” Herz, U.S. National Library of Medicine, Apr. 1999, https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/10372297/.
Foreman, Robert D, et al. “Mechanisms of Cardiac Pain.” Comprehensive Physiology, U.S. National Library of Medicine, Apr. 2015, https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25880519/.
Malakar, Arup Kr, et al. “A Review on Coronary Artery Disease, Its Risk Factors, and Therapeutics.” Journal of Cellular Physiology, U.S. National Library of Medicine, Aug. 2019, https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30790284/.
Shahjehan, Rai Dilawar, and Beenish S Bhutta. “Coronary Artery Disease – Statpearls – NCBI Bookshelf.” In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL), StatPearls Publishing, 9 Feb. 2022, https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK564304/.