Athletes regularly take an ice-water bath after training or playing. It is known as cold water immersion/cryotherapy. It is used to relieve and reduce muscle soreness and pain after intense training or competition. From runners to professional tennis and football players, taking an ice bath is a common recovery practice. Many athletes utilize ice baths to help with faster recovery, prevent injury, and cool down the body. Here we provide some research on cold-water immersion therapy.
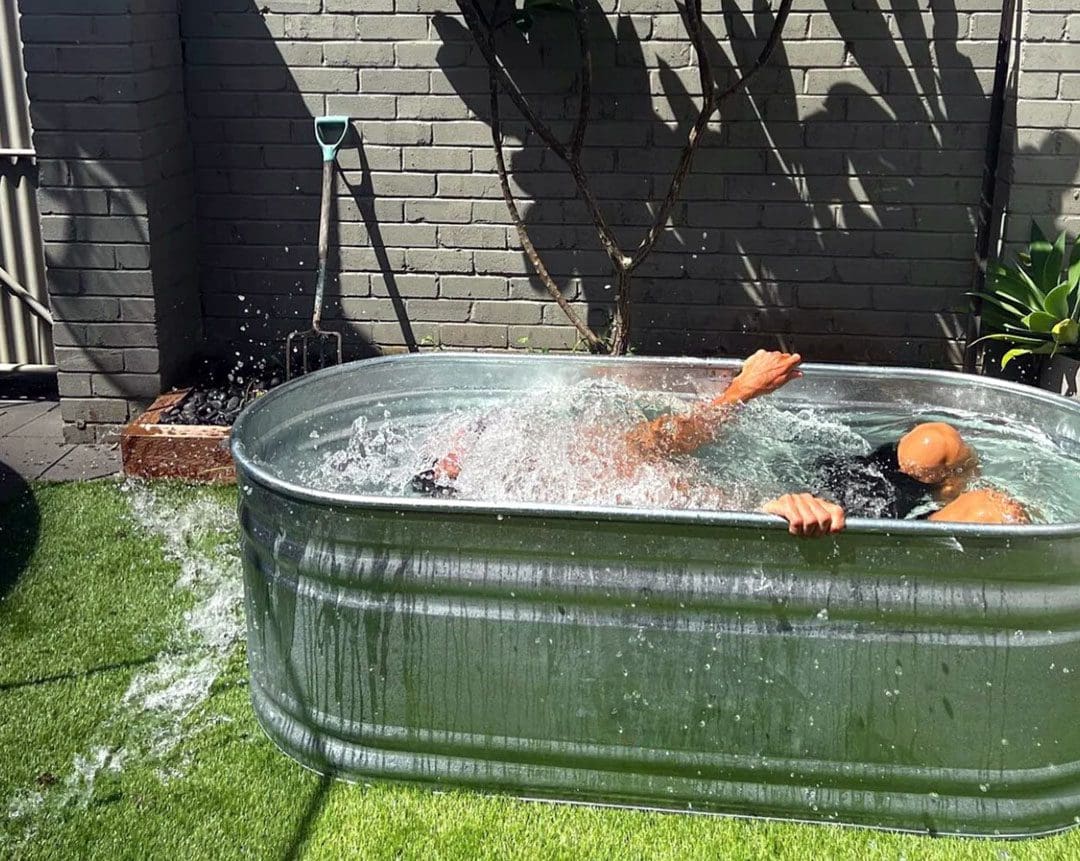

Table of Contents
Ice Water Bath
Cold Immersion After Exercise or Physical Activity
Exercise causes microtrauma/tiny tears in the muscle fibers. The microscopic damage stimulates muscle cell activity to repair the damage and strengthen the muscles/hypertrophy. However, hypertrophy is linked with delayed onset muscle soreness and pain/DOMS, between 24 and 72 hours after physical activity. An ice water bath works by:
- Constricting the blood vessels.
- Flushes out waste products (lactic acid), out of the muscle tissues.
- Decreases metabolic activity.
- Slows down physiological processes.
- Reduces inflammation, swelling, and tissue breakdown.
- Then, applying heat or warming up the water increases and speeds up blood circulation, improving the healing process.
- There is no current ideal time and temperature for cold immersion, but most athletes and trainers who use the therapy recommend a water temperature between 54 to 59 degrees Fahrenheit and immersion of five to 10 minutes, and depending on the soreness, sometimes up to 20 minutes.
Pros and Cons
The effects of ice baths and cold water immersion on exercise recovery and muscle soreness.
Relieves Inflammation but Can Slow Down Muscle Growth
- A study determined that cold water immersion can disrupt training adaptations.
- Research suggests that icing muscles right after maximum exercise decreases inflammation, but can slow down muscle fiber growth, and delay muscle regeneration.
- Athletes trying to increase muscle size and strength may need to adjust the therapy sessions.
Reduce Muscle Soreness
- A review concluded there was some evidence that ice water immersion reduced delayed onset muscle soreness when compared to resting and rehabilitation or no medical treatment.
- The most effects were seen in running athletes.
- There was no substantial evidence to conclude whether it improved fatigue or recovery.
- The studies did not have a standard for adverse effects or follow-up with the participants regularly.
- There was no difference in muscle soreness between cold water immersion, active recovery, compression, or stretching.
Pain Relief
- Cold water immersion after a physical activity offers temporary pain relief but can help with a faster recovery.
- A study of jiu-jitsu athletes found that following a workout with cold water immersion could lead to decreased muscle aches and help reduce lactate levels.
- Alternating cold water and warm water baths (contrast water therapy), may help athletes feel better and offer temporary pain relief.
Active Recovery Alternative
More research is needed before a firm conclusion can be reached on ice-water bath therapy. However, active recovery is a recommended alternative for athletes looking to recover faster.
- A study suggested that ice baths were equally effective, but not more effective, as active recovery for reducing inflammation.
- Cold water immersion is no greater than active recovery upon local and systemic inflammatory cellular stress.
- Research determined that active recovery is still the most widely used, and currently the best way to recover after intense exercise or physical activity.
- Low-impact workouts and stretches are still considered the most beneficial cool-down methods.
Cold Water Therapy
Ice Bath
- Individuals can use their tub at home to perform cold water therapy.
- Individuals may want to purchase a large bag of ice, but the cold water from the faucet will work.
- Fill the tub with cold water, and if desired, pour in some ice.
- Let the water and ice sit to get the cold temperature.
- Measure the temperature if necessary before getting in.
- Submerge the lower half of the body and adjust the temperature based on feel by adding more water, ice, or warm water if freezing.
- It’s like icing with an ice pack, but the whole body swelling reduces and relaxes the muscles.
- Don’t overdo it – one review found the best routine was 11 to 15 minutes of immersion at a temperature between 52 and 60 degrees Fahrenheit.
Cold Shower
- A few minutes in a cold shower is another way to perform the therapy.
- Individuals can get in a cold shower or start with warm water and slowly transition to cold.
- This is the easiest and most time-efficient method of cold water therapy.
Safety
- Consult with your doctor or a health care practitioner before practicing cold water therapy.
- Exposure to cold water can affect blood pressure, circulation, and heart rate.
- Cold water immersion can cause cardiac stress and can result in a heart attack.
- Be mindful that exposure to cold temperatures can result in hypothermia.
- Get out of the cold water if you experience numbness, tingling, discomfort, and/or pain.
Optimizing Wellness
References
Allan, R, and C Mawhinney. “Is the ice bath finally melting? Cold water immersion is no greater than active recovery upon local and systemic inflammatory cellular stress in humans.” The Journal of Physiology vol. 595,6 (2017): 1857-1858. doi:10.1113/JP273796
Altarriba-Bartes, Albert, et al. “The use of recovery strategies by Spanish first division soccer teams: a cross-sectional survey.” The Physician and sports medicine vol. 49,3 (2021): 297-307. doi:10.1080/00913847.2020.1819150
Bieuzen, François, et al. “Contrast water therapy and exercise-induced muscle damage: a systematic review and meta-analysis.” PloS one vol. 8,4 e62356. 23 Apr. 2013, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0062356
Fonseca, Líllian Beatriz et al. “Use of Cold-Water Immersion to Reduce Muscle Damage and Delayed-Onset Muscle Soreness and Preserve Muscle Power in Jiu-Jitsu Athletes.” Journal of athletic training vol. 51,7 (2016): 540-9. doi:10.4085/1062-6050-51.9.01
Forcina, Laura, et al. “Mechanisms Regulating Muscle Regeneration: Insights into the Interrelated and Time-Dependent Phases of Tissue Healing.” Cells vol. 9,5 1297. 22 May. 2020, doi:10.3390/cells9051297
Shadgan, Babak, et al. “Contrast Baths, Intramuscular Hemodynamics, and Oxygenation as Monitored by Near-Infrared Spectroscopy.” Journal of athletic training vol. 53,8 (2018): 782-787. doi:10.4085/1062-6050-127-17
Sutkowy, Paweł, et al. “Postexercise impact of ice-cold water bath on the oxidant-antioxidant balance in healthy men.” BioMed research international vol. 2015 (2015): 706141. doi:10.1155/2015/706141