“For individuals training for long-distance walking marathons and/or events, can focusing on building a walking foundation and then increasing mileage progressively help condition the body for overall readiness?”
Table of Contents
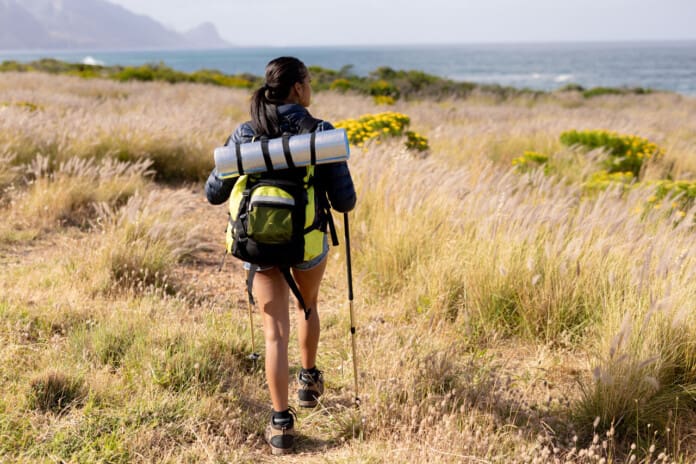
Long Distance Walking Training
- Training helps individuals be comfortable and safe for long-distance walking and events.
- Training should focus on building a walking pace and increasing mileage gradually.
- Individuals need endurance, not speed, and want to build mental stamina for walking for hours at a steady pace.
- To reduce the risk of training injuries, increasing the total mileage per week/the distance of the longest walk per week to no more than 10% is recommended.
- Individuals should also train to wear the gear worn during long-distance walks.
- Training could last a few months.
- Being methodical allows the body time to repair and build new muscle, blood supplies, and endurance.
Example Training Plans
Following a marathon training plan for mileage building and determining the proper hydration, nutrition, and gear for multi-day walks and treks is recommended. However, individuals must build back-to-back long days into their training sessions to assess any issues or problems resulting from walking long distances on back-to-back days.
Example Walking Training Plans
Multi-Day Walks/Treks Training Schedule
- 13 miles per day/21 kilometers
- Use this plan for marathons or other multi-day walks with hills and natural surfaces requiring a backpack.
Training to Walk a Marathon
- 26.2 miles/42 kilometers
- This will condition the body to go longer distances.
- When training for distances of 31 to 100 miles/50 to 161 kilometers, the longest distance to train should not need to exceed 20 to 25 miles,
- These should be performed at least twice two months before the marathon or event.
- Taper down the month before the event to a 12.4-mile/20-kilometer distance.
Gear
All clothing, shoes, sunscreen, backpacks, etc., must be tested on the longer training days before the event.
- Given the climate and terrain, plan for what will be needed and removed.
- Try things out, as individuals don’t want to be surprised with something unfamiliar at the event. From head to toe, test the gear, including:
- Shoes/boots, socks, underwear, bra, shirt, pants, hat, jacket, and rain gear.
- Choose shoes or walking boots and wear them on long training days to break them in and ensure they perform.
- Backpacks should be tested on longer training days to ensure they can be carried comfortably over long distances and have the necessary capacity.
- Choose wicking fabrics that allow the skin to breathe and cool, especially under layers. (Justin De Sousa et al., 2014)
- Individuals will want to wear gear similar to marathon walkers if the walk will mostly be on pavement or asphalt.
- Individuals can modify their gear if the route is off-road or during different seasons. Find out what other long-distance walkers have worn on the same route or event.
- Individuals can connect with fellow walkers via social media or find answers to frequently asked questions on the event’s or destination’s website.
- Individuals can also contact the event director via the website or social media.
Nutrition
Proper sports nutrition will prepare the body for endurance activity.
- For example, individuals are recommended to follow a diet comprising 70% carbohydrates, 20% protein, and 10% fat.
- Avoid high-protein diets, as they can cause hydration problems and strain your kidneys under endurance walking conditions. (Marta Cuenca-Sánchez et al., 2015)
- Train with the water, sports drinks, food, and snacks taken to the event, and do not deviate from them during the event.
- Water is needed for 20 kilometers and under events, but an electrolyte replacement sports drink may be better for longer walks.
- Diluting or leaving out some sugar can be easier on the stomach.
- Have snacks pre-packaged and labeled for the times to be eaten.
- Individuals need to eat fat and protein for ultramarathon distances – this can come from trail mix, peanut butter sandwiches, and chocolate bars with nuts.
- Carbohydrates can be provided by sports gels or energy bars.
It is recommended to avoid products made for short distances and power sports as they can cause digestive problems when walking longer distances.
Planning a Walk
Planning begins by setting goals. Considerations include:
- Time of year
- Distance
- Transportation to the event
- Event pace requirements
- Altitude and hill profile
- Climate
Individuals are recommended to:
- Prepare by researching routes and trails.
- Study the course maps to know what services are provided along the way and what individuals must bring.
- Walk a long distance without a supporting event.
- Contact individuals who have walked the course.
- Know the terrain and areas of total sun, hills, pavement, natural trails, and shade.
- If possible, drive the course to become familiar with it.
- Individuals may be able to find apps designed for their route.
Taking Breaks and Resting
- Regular breaks should be short – using the bathroom, eating a snack, rehydrating, tying shoes, or bandaging blisters.
- The body can stiffen up quickly during breaks and take several minutes to regain walking pace after a long break.
- Recommendations could be taking a walking break instead, which means continuing to walk but at a very slow pace.
Foot Care
Individuals will have found what works for them concerning shoes, boots, socks, etc., on the long training days to prevent blisters and injuries. It is recommended to try different strategies, which include:
- Sports tape
- Blister block pads
- Sprays
- Lubricants
- Wicking and/or double-layered socks
- Moleskin
- Stop at the first sign of irritation along the walk and doctor the foot with tape, blister bandages, or whatever method works best.
The body was built for walking. Planning and training properly before taking a long-distance or multi-day walk will ensure a safe and enjoyable marathon.
Move Better, Live Better
References
De Sousa, J., Cheatham, C., & Wittbrodt, M. (2014). The effects of a moisture-wicking fabric shirt on the physiological and perceptual responses during acute exercise in the heat. Applied ergonomics, 45(6), 1447–1453. doi.org/10.1016/j.apergo.2014.04.006
Cuenca-Sánchez, M., Navas-Carrillo, D., & Orenes-Piñero, E. (2015). Controversies surrounding high-protein diet intake: satiating effect and kidney and bone health. Advances in nutrition (Bethesda, Md.), 6(3), 260–266. doi.org/10.3945/an.114.007716