Can incorporating these 7 exercises help individuals dealing with back pain help promote a healthy spine and functionality?
Table of Contents
Introduction
Many individuals have dealt with back pain in their body’s upper, middle, and lower portions, which can correlate with other issues in the upper and lower body extremities. This is due to how many environmental factors affect a person’s daily routine. From stressful days that impact a person’s day to physical inactivity or even spinal issues that have developed over time can cause back pain. When individuals decide to make changes in their health and wellness journey to not only reduce back pain but also improve how they present themselves. Many individuals can start with exercises to reduce back pain and help their spinal health by making sure that they are doing it correctly to prevent injuries. Today’s article looks at how spinal issues correlate with back pain and how these seven simple exercises and stretches can help reduce lower back pain and help you have a healthy spine. We talk with certified associated medical providers who provide our patients’ information to assess back pain correlated with their spine. We also inform patients while asking their associated medical provider intricate questions to formulate customized treatment plans to reduce back pain by integrating exercises to help reduce the pain and promote wellness. Dr. Alex Jimenez, D.C., includes this information as an academic service. Disclaimer.
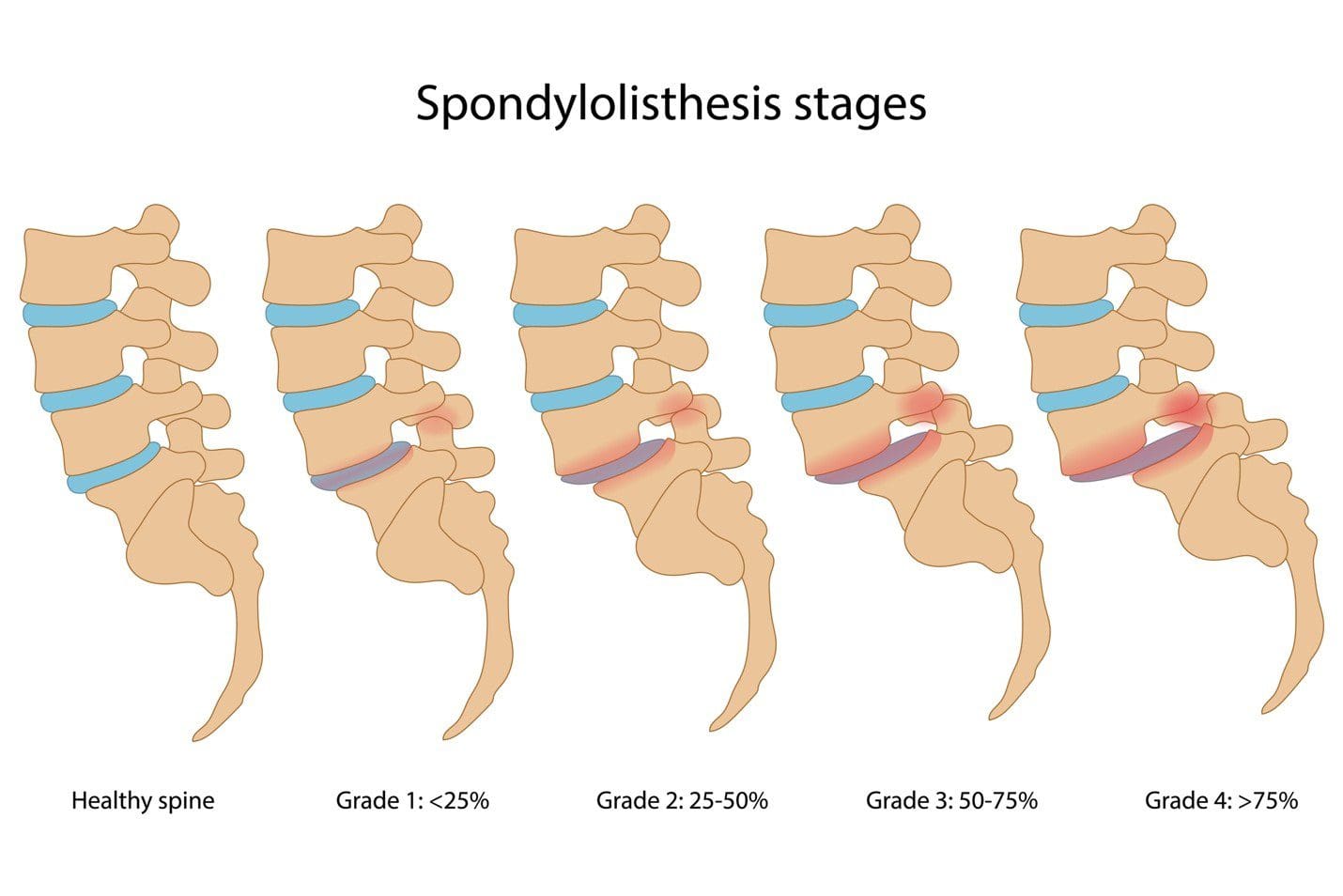
Spinal Issues Correlating To Back Pain
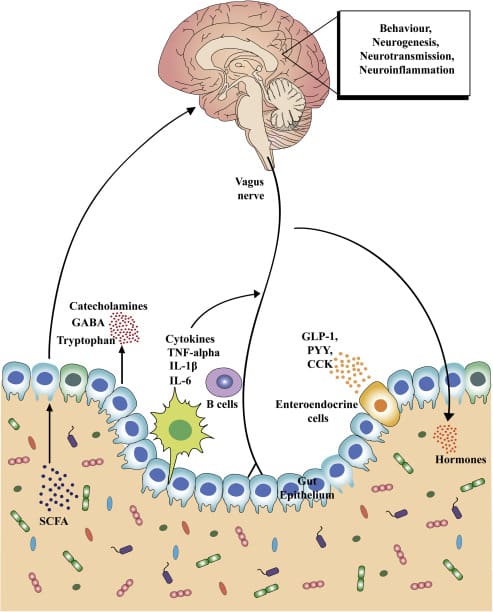
Do you feel stiffness or muscle aches in your back’s upper, middle, or lower areas? Have you noticed that your posture is hunched more than normal when looking at the phone or being on the computer for an extended period? Or does your back ache from lifting a heavy object or sleeping incorrectly? More often than not, these pain-related scenarios are associated with back pain combined with spinal issues. As one of the leading causes of disability, loss of productivity, and more visits to a health clinic, back pain can impact the body and cause individuals to be miserable. (Bang et al., 2021) Back pain can be specific or non-specific and can cause a person’s spine to degenerate through the spinal disc. The spinal disc provides stability, flexibility, and mobility to the spine, which then helps keep the host upright. However, as the body ages, so does the spine, as lower back pain is multifactorial. When the spinal disc degenerates, the spine has a reduced capacity for intrinsic self-repair within the tissues. (Mohd Isa et al., 2022)
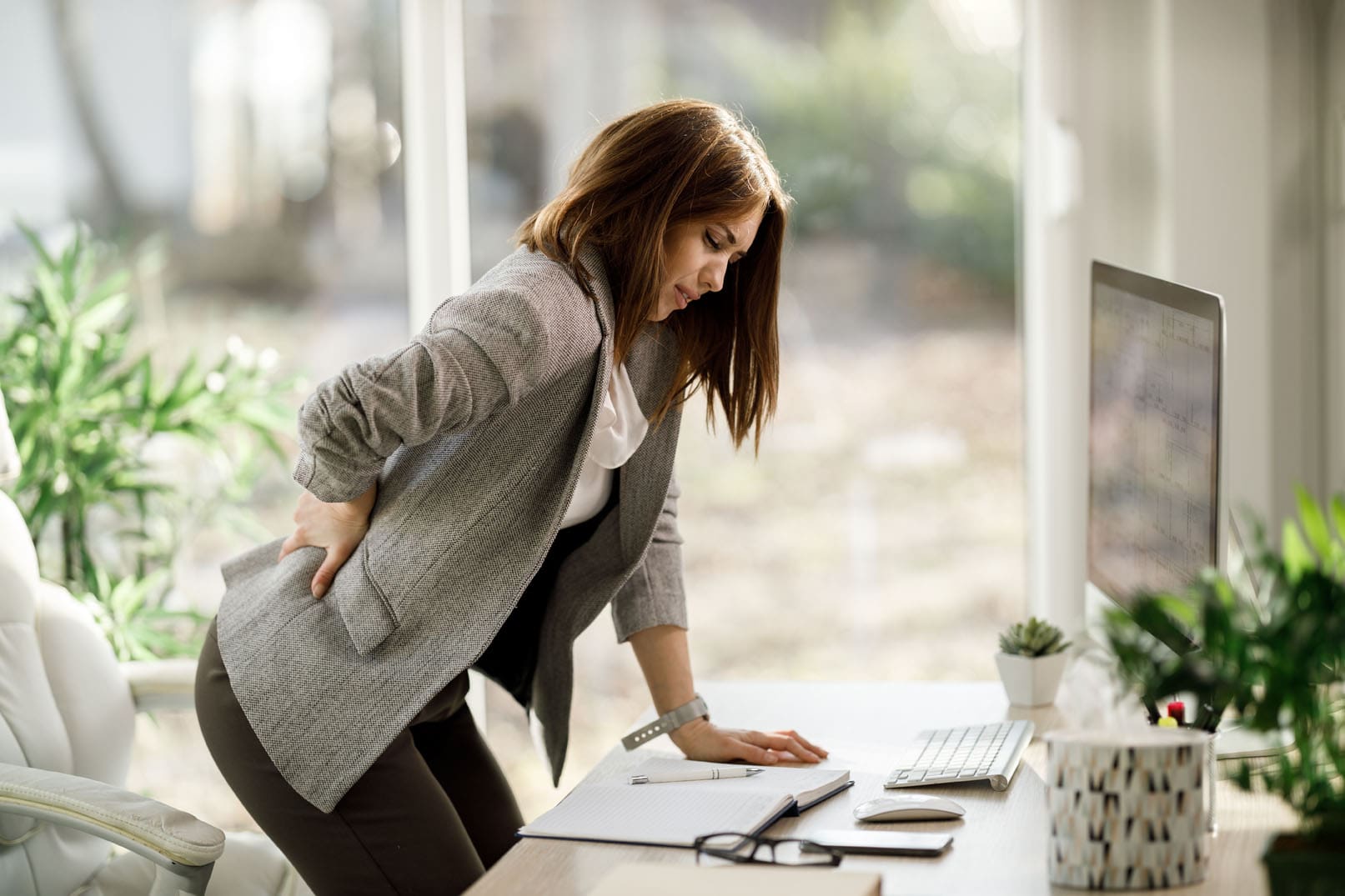

At the same time, when many individuals are dealing with low back pain, depending on the severity of the issue, they will often change their gait mechanics by adapting different strategies to mitigate the loading on the primary muscles associated with the locomotion that protects the pain-producing tissues. (Smith et al., 2022) When that happens, the pain from the lower back muscles can aggravate the spine further and lead to more chronic issues; however, there are ways to reduce the effects of lower back pain and to help keep the spine healthy.
Can Core Exercises Help with Back Pain?-Video

The 7 Exercises To Incorporate For Back Pain
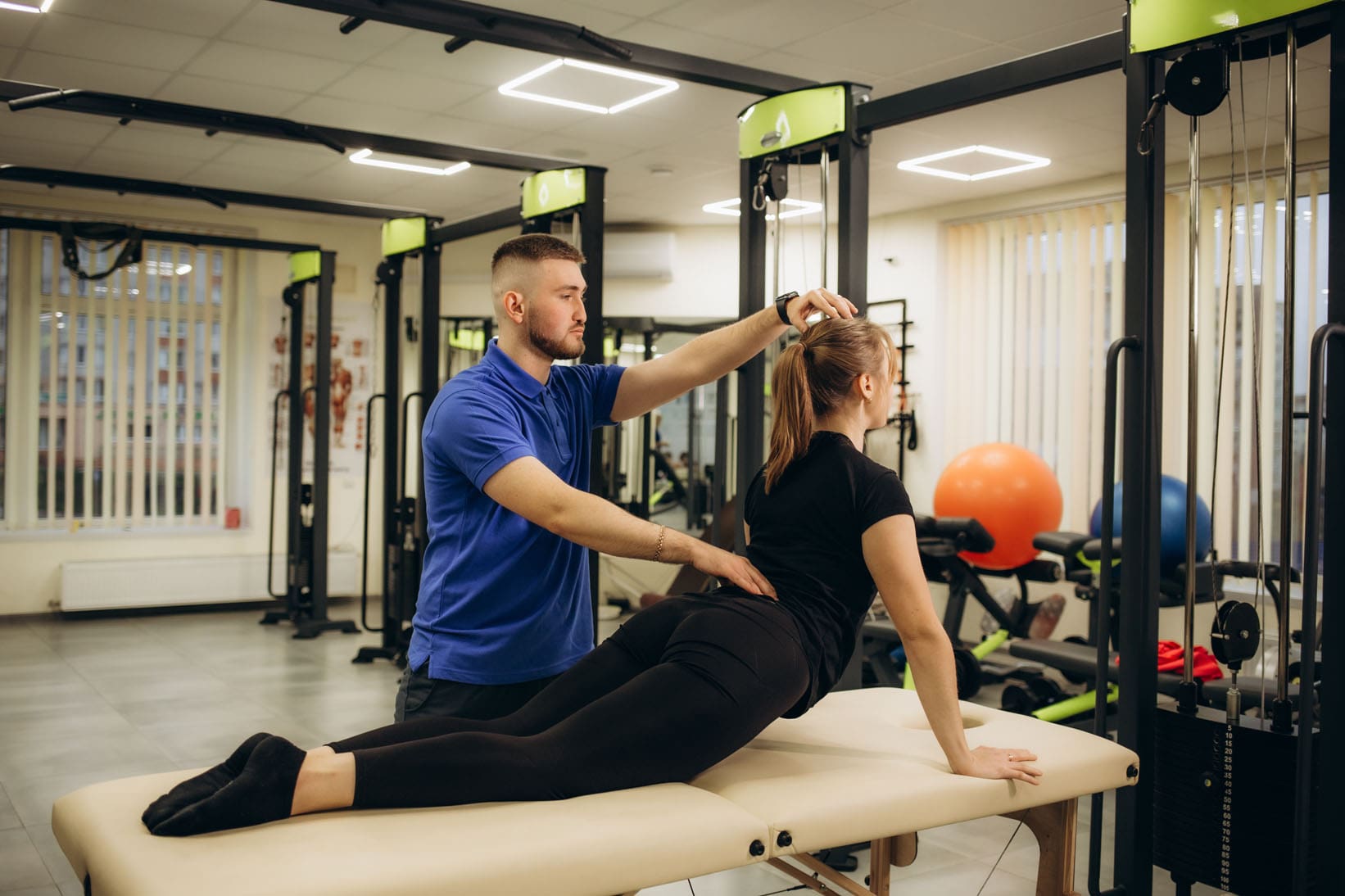
When it comes to making sure that lower back pain can be reduced and to help with keeping a healthy spine, many people often seek out physical therapy to reduce the pain. Since low back pain is costly in a clinical approach, physical therapy is cost-effective, non-invasive, and can help individuals get a kick start in their health journey. Physical therapy involves whole-body movement that emphasizes breathing coordination, reducing pain from the lower back, and helping stabilize the lumbar spine to improve physical function. (Li et al., 2023) By going through a treatment plan that incorporates physical therapy, many individuals will begin to notice their pain is improving and their quality of life is getting better. (Fischer et al., 2021) Additionally, stretching and core stability exercises can activate the deep and superficial spinal muscles by strengthening them and help stretch out sore muscles affected by low back pain to help many individuals recover. (Calatayud et al., 2019) Below are seven exercises that can help reduce back pain and, when done correctly and consecutively, can help many individuals have a healthier spine while being more mindful of their bodies.
Knee-To-Chest Exercise
This knee-to-chest exercise can help stretch the lower back muscles and can be done in the morning or evening.
- Lying on your back with knees bent and feet flat for stability.
- Pull one knee up with both hands and press it towards your chest.
- Keep the stomach muscles tight while pressing your spine to the floor, holding for at least 30 seconds before returning to position.
- Repeat with the other knee and do each stretch 2-3 times.
Lower Back Rotational Stretch (On the Floor)
This lower back rotational stretch can help stretch tight muscles in the lower back.
- Laying on the mat, ensure you are on your back with knees bent and feet flat.
- Make sure the shoulders are firmly on the floor, and slowly roll the knees to one side until 45 degrees.
- Hold that position for 30 seconds before slowly rotating the knees back to the starting position.
- Repeat on the other side and do each stretch 2-3 times.
Lower Back Flexibility Exercise
This lower back flexibility will help stretch and strengthen the lower back and core muscles.
- Lay flat on the mat. For stability, make sure that the knees are bent with feet are flat on the floor.
- Tighten the stomach muscles so the lower back can be pulled away from the floor.
- Hold the position for 5 seconds and relax, slowly lowering to the floor.
- Flatten the back as your belly button starts to go towards the floor, and hold the position for 5 seconds before relaxing.
- Do five repetitions a day to slowly work up to 30 reps.
Bridge Exercise
The bridge exercise can help with core stability and help strengthen core muscles.
- Laying flat on your back on the floor, with knees bent and feet flat. Make sure that your shoulders and head are relaxed.
- Tighten the core and glute muscles while slowly raising from the hips to form a straight line from the knees to the shoulders.
- Stay in that position for 30 seconds while taking deep breaths.
- Slowly go down to the floor and relax.
- Do five repetitions a day to slowly work up to 30 reps.
Cat-To-Cow Stretch
The cat-to-cow stretch helps with shoulders, upper back, and lower back muscles.
- On your hands and knees, hip-width apart on the mat, be in a neutral spine position.
- Slowly arch your back by pulling your belly towards the ceiling and your head down for 30 seconds.
- Then, slowly let the back and belly sag towards the floor as the head rises for 30 seconds.
- Return to the neutral spine position and repeat about 3-5 times twice daily.
Lower Back Rotational Stretch (Seated)
This lower back rotational stretch is seated if the floor is uncomfortable for individuals with severe back pain.
- Sitting in an armless chair or stool in a seated upright position, cross one leg over the other.
- Then, place the left elbow against the outside of the right knee and twist and stretch the side.
- Hold the postion for 10 seconds before slowly returning to a seated position.
- Repeat the stretch on the opposite side.
- Do this stretch 3-5 times on each side to stretch tight back muscles about twice daily.
Shoulder Blade Squeeze
This shoulder blade squeeze helps individuals properly posture while stretching and strengthening tight upper back and shoulder muscles.
- Start in a seated upright position on an armless chair or stool.
- Slowly pull the shoulder blades together in the upright position and hold for 5-30 seconds.
- Relax, return to the upright position, and repeat 3-5 times twice daily.
References
Bang, A. A., Bhojraj, S. Y., & Bang, A. T. (2021). Back pain and musculoskeletal pain as public health problems: Rural communities await solution. J Glob Health, 11, 01007. https://doi.org/10.7189/jogh.11.01007
Calatayud, J., Escriche-Escuder, A., Cruz-Montecinos, C., Andersen, L. L., Perez-Alenda, S., Aiguade, R., & Casana, J. (2019). Tolerability and Muscle Activity of Core Muscle Exercises in Chronic Low-back Pain. Int J Environ Res Public Health, 16(19). https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16193509
Fischer, S. C., Calley, D. Q., & Hollman, J. H. (2021). Effect of an Exercise Program That Includes Deadlifts on Low Back Pain. J Sport Rehabil, 30(4), 672-675. https://doi.org/10.1123/jsr.2020-0324
Li, Y., Yan, L., Hou, L., Zhang, X., Zhao, H., Yan, C., Li, X., Li, Y., Chen, X., & Ding, X. (2023). Exercise intervention for patients with chronic low back pain: a systematic review and network meta-analysis. Front Public Health, 11, 1155225. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpubh.2023.1155225
Mohd Isa, I. L., Teoh, S. L., Mohd Nor, N. H., & Mokhtar, S. A. (2022). Discogenic Low Back Pain: Anatomy, Pathophysiology and Treatments of Intervertebral Disc Degeneration. Int J Mol Sci, 24(1). https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24010208
Smith, J. A., Stabbert, H., Bagwell, J. J., Teng, H. L., Wade, V., & Lee, S. P. (2022). Do people with low back pain walk differently? A systematic review and meta-analysis. J Sport Health Sci, 11(4), 450-465. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jshs.2022.02.001