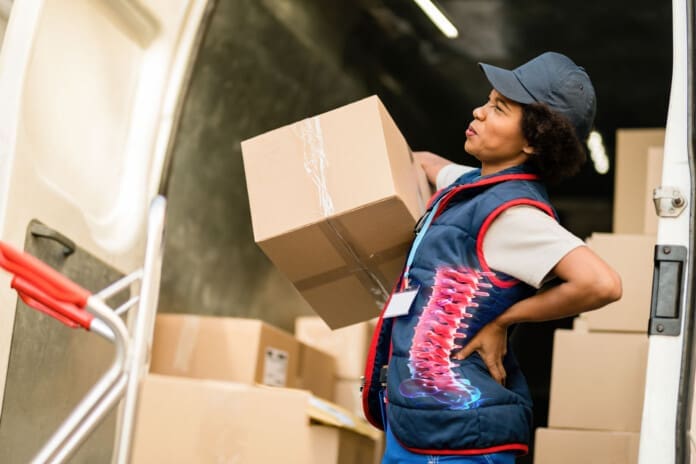
Individuals experiencing persistent pain, weakness, numbness, and tingling in the back could be suffering from nerve root encroachment. Could surgery ease nerve compression and improve symptoms for persistent and severe cases?
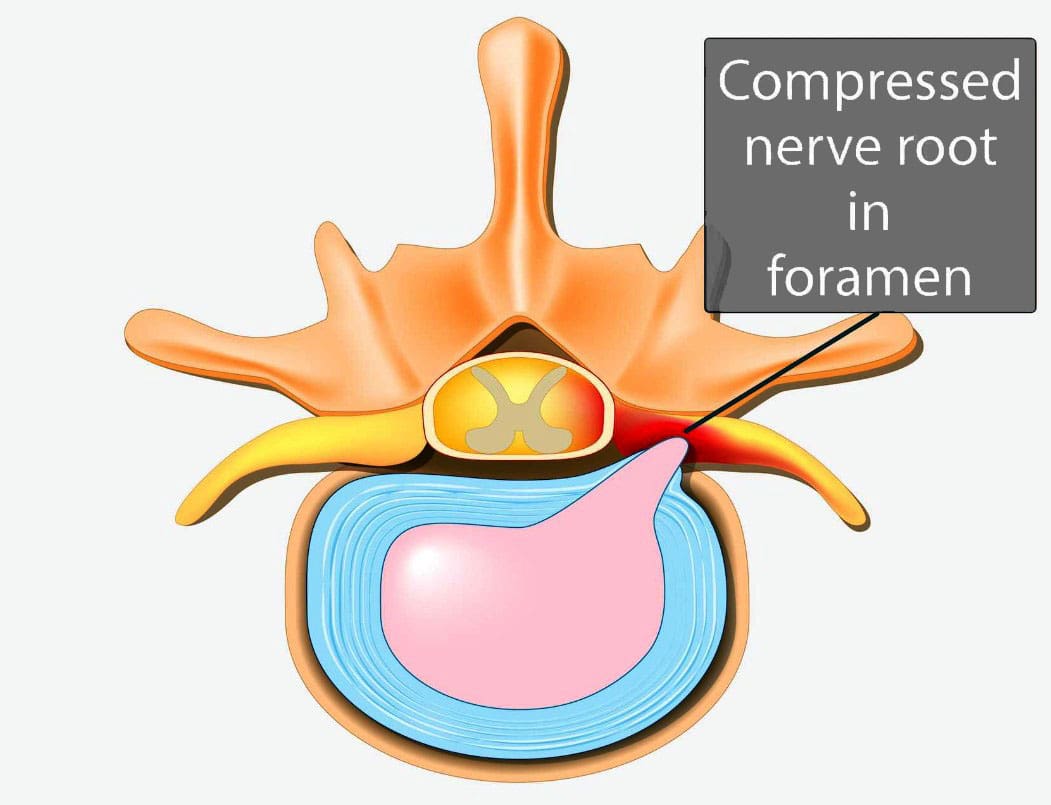
Table of Contents
Surgical Decompression
The pain, weakness, numbness, and tingling associated with nerve root encroachment are usually first treated with non-surgical therapies that include:
- Anti-inflammatory medications
- Physical therapy
This can be enough to address the irritation of the spinal nerve root. But when cases become severe, surgical decompression may be recommended and necessary. It can be done in a couple of different ways.
Causes and Symptoms
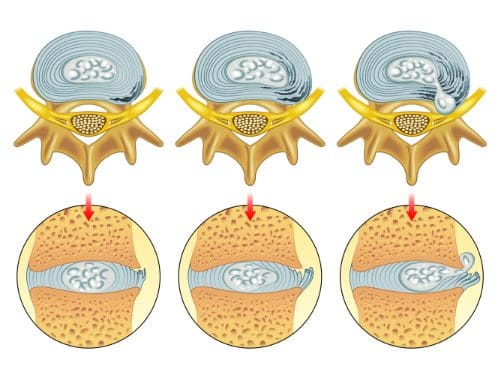
Vertebrae are bones in the spine. Small openings called foramina allow a spinal nerve root to pass through on each side of the vertebra. When nerve root encroachment is present, the spinal nerve root gets compressed, pinched, and trapped, which can cause peripheral symptoms such as numbness, tingling, pain, or weakness to develop. Nerve root encroachment is typically caused by normal aging degenerative wear and tear changes in the vertebrae. (Choi Y. K. 2019) These degenerative changes can include:
- Facet joint hypertrophy
- Ligament and bone hypertrophy
- Disc disorders
- Formation of bone spurs or osteophytes.
If these degenerative changes progress, they can encroach and compress a nerve root, leading to peripheral symptoms. (Choi Y. K. 2019)
When Surgery Is Recommended
When symptoms occur, initial treatment will involve:
- Physical therapy
- Chiropractic realignment
- Massage therapies
- Rest
- Lifestyle adjustments
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatories – NSAIDs
- Corticosteroid injections into the spine
If conservative therapies don’t fully heal or improve symptoms or there are neurological problems like difficulty with balance or walking, then surgery may be recommended. Severe pain that limits normal function is an indication for surgery, and rapidly progressive weakness of the arms and/or legs or signs of cauda equina syndrome are indications for emergency surgery.
Surgery Options
Different types of spinal surgery may be performed. A neurosurgeon will decide the best procedure for each patient based on their case, age, medical conditions, and other factors. Specific spinal surgical decompression depends on what is causing the nerve compression. In most cases, it involves removing bone or tissue to relieve nerve pressure or provide support to stabilize the joint. The most common types of surgical decompression include: (Mayo Clinic Health System, 2022)
- Laminectomy
- Discectomy
- Laminotomy
- Foraminotomy
- Fusion
Spinal surgical goals are to: (American Association of Neurological Surgeons, 2024)
- Decompress pressure on the nerve roots.
- Relieve pressure on the nerve roots.
- Maintain the stability and alignment of the spine.
- Improve the stability and alignment of the spine.
Anterior Surgery
The anterior approach to surgery means that the spine is accessed through the anterior/front of the spine. In this surgery, one or more discs and bone spurs may be removed through an incision in the front of the neck. (American Association of Neurological Surgeons, 2024) For example, an anterior cervical discectomy may alleviate pressure on one or more nerve roots in the neck. With an anterior lumbar interbody fusion, a surgeon removes a degenerative disc in the lower spinal area by going through a patient’s lower abdomen. (American Association of Neurological Surgeons, 2024) After the disc is removed, a structural device, usually made of bone, fills the space where it once was. This device encourages bone healing and helps the vertebrae’s bodies fuse.
Posterior Surgery
Posterior surgery means the spine is accessed through the posterior/back of the spine. An example is removing a thickened ligament, bone spur, or disc material in the neck. To do this, a small incision in the back of the neck may be made to remove part of the back of the vertebrae called the lamina. This is called a posterior cervical laminectomy. (American Association of Neurological Surgeons, 2024) A posterior lumbar interbody fusion removes a degenerative disc by going through the back. (American Association of Neurological Surgeons, 2024) Like the anterior approach, a structural device often contains bone to fill the space where the disc once was to fuse the bones.
Potential Risks
As with any surgery, it’s important that the individual and their healthcare provider carefully discuss the benefits and risks. Spinal surgical decompression includes: (Proietti L. et al., 2013)
- Bleeding
- Blood clots
- Surgical site infection
- Urinary tract infection
- Lung infection
- Intestinal blockage
There are also specific risks to the area of the spine being operated on and how it is surgically approached. For example, a cervical anterior procedure may injure the esophagus, trachea, or carotid artery. Likewise, damage to the C5 nerve root/C5 palsy can occur from cervical spinal decompressive surgery. This complication causes weakness, numbness, and pain in the shoulders. (Thompson S. E. et al., 2017) The spinal cord may also be injured during surgery and result in paralysis, although this is rare. (American Association of Neurological Surgeons, 2024)
Injury Medical Chiropractic and Functional Medicine Clinic
Injury Medical Chiropractic and Functional Medicine Clinic works with primary healthcare providers and specialists to develop an optimal health and wellness solution. We focus on what works for you to relieve pain, restore function, and prevent injury. Regarding musculoskeletal pain, specialists like chiropractors, acupuncturists, and massage therapists can help mitigate the pain through spinal adjustments that help the body realign itself. They can also work with other medical professionals to integrate a treatment plan to resolve musculoskeletal issues.
The Non-Surgical Solution
References
Choi Y. K. (2019). Lumbar foraminal neuropathy: an update on non-surgical management. The Korean journal of pain, 32(3), 147–159. https://doi.org/10.3344/kjp.2019.32.3.147
Mayo Clinic Health System. (2022). Decompress and stabilize: understanding types of back surgery. Speaking of Health. https://www.mayoclinichealthsystem.org/hometown-health/speaking-of-health/understanding-types-of-back-surgery
American Association of Neurological Surgeons. (2024). Cervical spine. https://www.aans.org/patients/conditions-treatments/cervical-spine/
American Association of Neurological Surgeons. (2024). Lumbar spinal stenosis. https://www.aans.org/patients/conditions-treatments/lumbar-spinal-stenosis/
Proietti, L., Scaramuzzo, L., Schiro’, G. R., Sessa, S., & Logroscino, C. A. (2013). Complications in lumbar spine surgery: A retrospective analysis. Indian journal of orthopaedics, 47(4), 340–345. https://doi.org/10.4103/0019-5413.114909
Thompson, S. E., Smith, Z. A., Hsu, W. K., Nassr, A., Mroz, T. E., Fish, D. E., Wang, J. C., Fehlings, M. G., Tannoury, C. A., Tannoury, T., Tortolani, P. J., Traynelis, V. C., Gokaslan, Z., Hilibrand, A. S., Isaacs, R. E., Mummaneni, P. V., Chou, D., Qureshi, S. A., Cho, S. K., Baird, E. O., … Riew, K. D. (2017). C5 Palsy After Cervical Spine Surgery: A Multicenter Retrospective Review of 59 Cases. Global spine journal, 7(1 Suppl), 64S–70S. https://doi.org/10.1177/2192568216688189