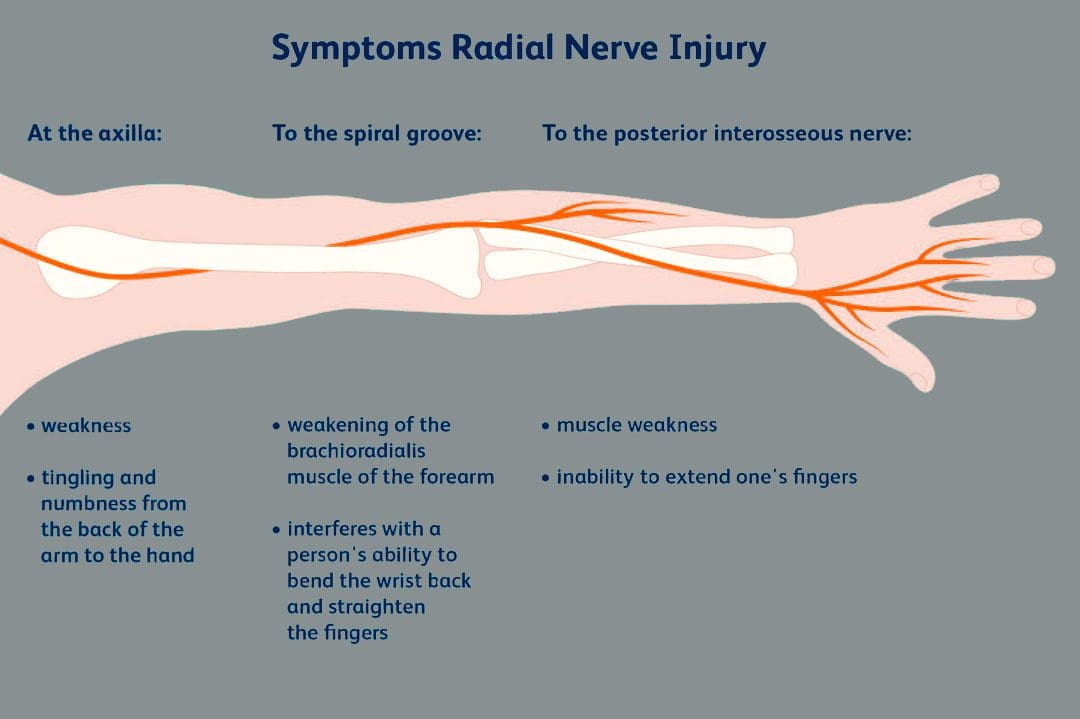
Golfing wrist injuries are common with treatment requiring 1-3 months of rest and immobilization and if tears are present surgery. Can chiropractic treatment help avoid surgery, expedite recovery, and rehabilitation?
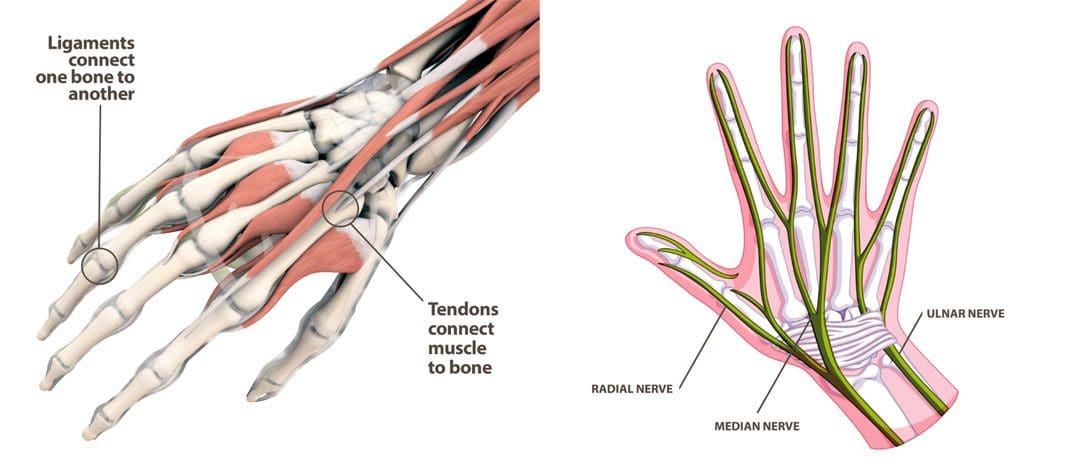
Table of Contents
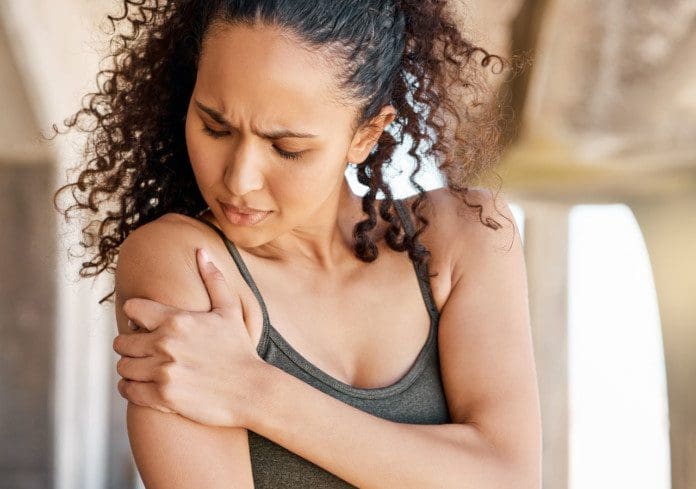
Golfing Wrist Injuries
Golfing Wrist Injuries: According to a study, there are over 30,000 golf-related injuries treated in American emergency rooms every year. (Walsh, B. A. et al, 2017) Nearly a third are related to a strain, sprain, or stress fracture.
- One of the most common causes of wrist pain is overuse. (Moon, H. W. et al, 2023)
- Repeated swinging generates added stress on the tendons and muscles, leading to inflammation and pain.
- Improper swing techniques can cause the wrists to twist uncomfortably, resulting in inflammation, soreness, and injuries.
- Golfers who grip the club too tightly can add unnecessary strain on their wrists, leading to pain and weakened grip.
Wrist Tendonitis
- The most common wrist injury is an inflammation of the tendons. (Ray, G. et al, 2023)
- This condition is often caused by overuse or repetitive motion.
- It usually develops in the leading hand from bending the wrist forward on the backswing and then extends backward at the finish.
Wrist Sprains
- These can occur when the golf club hits an object, like a tree root, and makes the wrist bend and/or twist awkwardly. (Zouzias et al., 2018)
Hamate Bone Fractures
- When the club hits the ground abnormally it can compress the handle against the bony hooks at the end of the smaller hamate/carpal bones.
Ulnar Tunnel Syndrome
- This can cause inflammation, and numbness, and is usually caused by an improper or loose grip.
- It causes nerve damage to the wrist from repeated bumping of the golf club handle against the palm.
de Quervain’s Tenosynovitis
- This is a repetitive motion injury below the thumb at the wrist. (Tan, H. K. et al, 2014)
- This causes pain and inflammation and is usually accompanied by a grinding sensation when moving the thumb and wrist.
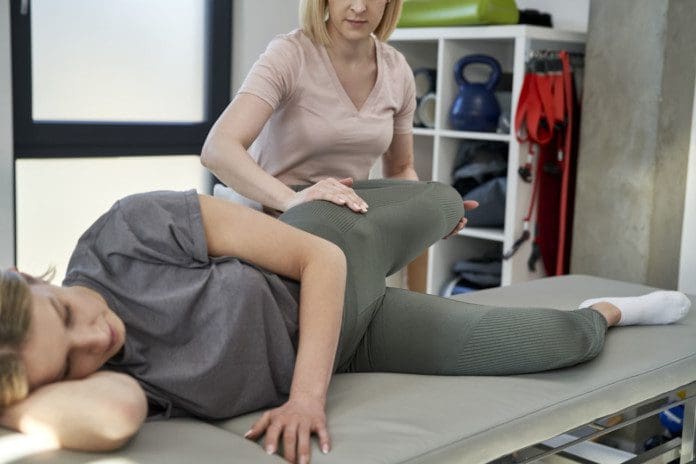
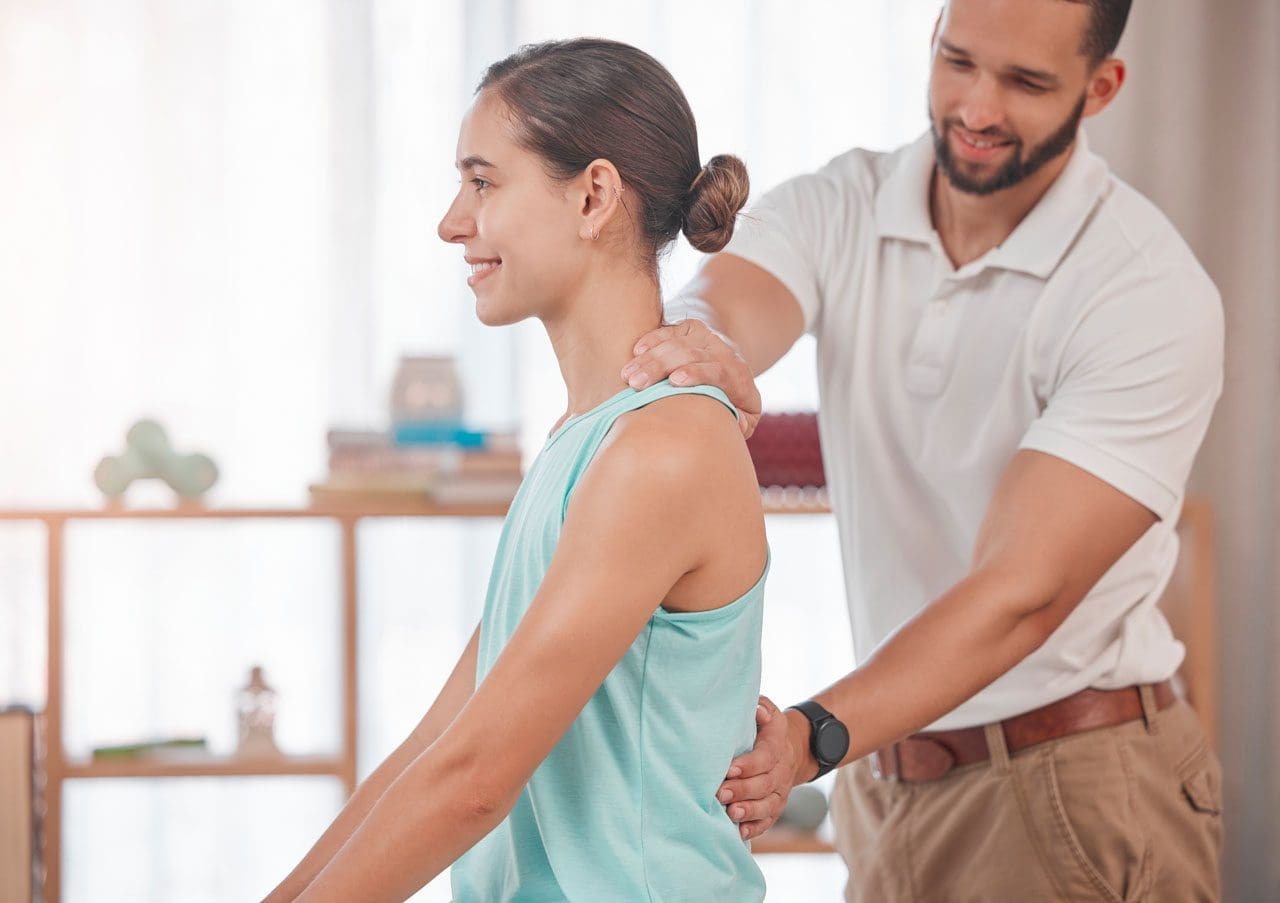
Chiropractic Treatment
Given the nature of these injuries, medical attention should be sought out for image scans to look at any damage and properly immobilize the wrist. Once a fracture has been ruled out or healed, golfing wrist injuries can benefit from chiropractic and physical therapy. (Hulbert, J. R. et al, 2005) A typical treatment may involve a multifaceted approach involving various therapies including:
- Active release therapy, myofascial release, athletic taping, corrective exercise, and stretching.
- A chiropractor will examine the wrist and its functioning to determine the nature of the injury.
- A chiropractor may recommend using a splint to immobilize the wrist, particularly in cases of overuse.
- They will relieve pain and swelling first, then focus on strengthening the joint.
- They may recommend a regimen of icing the hand.
- Adjustments and manipulations will relieve pressure on the nerves to reduce swelling and restore mobility.
Peripheral Neuropathy Successful Recovery
References
Walsh, B. A., Chounthirath, T., Friedenberg, L., & Smith, G. A. (2017). Golf-related injuries treated in United States emergency departments. The American journal of emergency medicine, 35(11), 1666–1671. doi.org/10.1016/j.ajem.2017.05.035
Moon, H. W., & Kim, J. S. (2023). Golf-related sports injuries of the musculoskeletal system. Journal of exercise rehabilitation, 19(2), 134–138. doi.org/10.12965/jer.2346128.064
Ray, G., Sandean, D. P., & Tall, M. A. (2023). Tenosynovitis. In StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing.
Zouzias, I. C., Hendra, J., Stodelle, J., & Limpisvasti, O. (2018). Golf Injuries: Epidemiology, Pathophysiology, and Treatment. The Journal of the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons, 26(4), 116–123. doi.org/10.5435/JAAOS-D-15-00433
Tan, H. K., Chew, N., Chew, K. T., & Peh, W. C. (2014). Clinics in diagnostic imaging (156). Golf-induced hamate hook fracture. Singapore medical journal, 55(10), 517–521. doi.org/10.11622/smedj.2014133
Hulbert, J. R., Printon, R., Osterbauer, P., Davis, P. T., & Lamaack, R. (2005). Chiropractic treatment of hand and wrist pain in older people: systematic protocol development. Part 1: informant interviews. Journal of chiropractic medicine, 4(3), 144–151. doi.org/10.1016/S0899-3467(07)60123-2