Can individuals dealing with psoriatic arthritis find non-surgical treatments to reduce joint pain and improve skin health?
Table of Contents
Introduction
The body is a complex machine with a communal relationship with the joints, organs, bones, muscles, and tissues, each of which has a specific function to ensure the host is alive. The brain is the main control system that gives each body’s systems, organs, muscles and joints a job. When environmental factors or pathogens enter the body, the immune system is the first one to defend the body and eliminate the pathogens to initiate the natural healing process. However, when the immune system is attacking the body constantly, over time, it can lead to autoimmunity and cause overlapping risk profiles in the body. This, in turn, can lead the development of chronic conditions and cause individuals pain and discomfort. In today’s article, we look at an autoimmune disorder known as psoriatic arthritis, its causes and symptoms, and how treatment can help reduce its pain like effects. We discuss with certified medical providers who inform our patients how psoriatic arthritis can affect the joints. While asking informed questions to our associated medical providers, we advise patients to incorporate various non-surgical treatments to reduce psoriatic arthritis symptoms and help manage joint pain that affects a person’s quality of life. Dr. Alex Jimenez, D.C., encompasses this information as an academic service. Disclaimer.
What Is Psoriatic Arthritis?
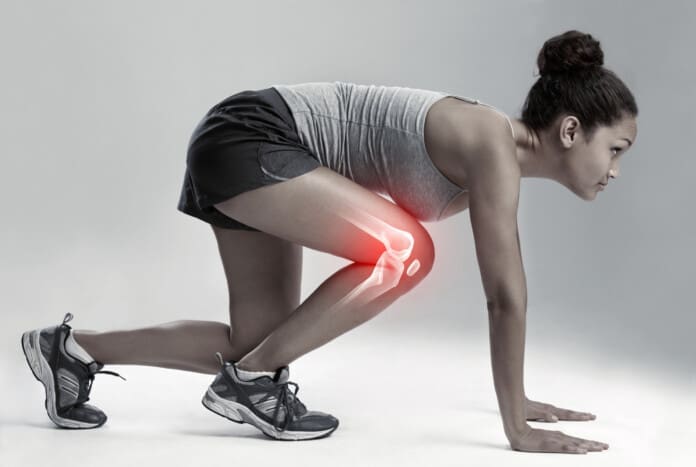
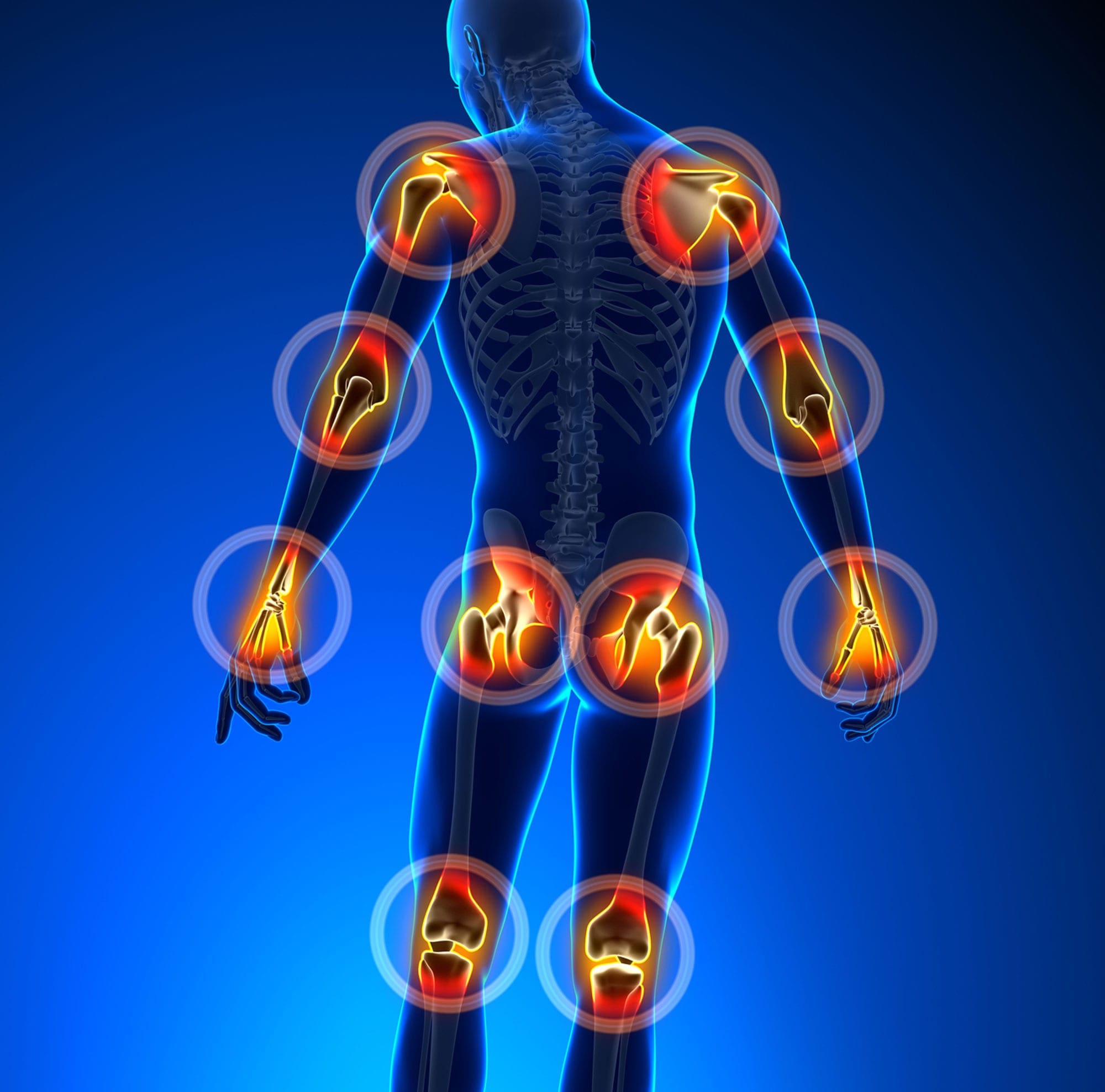
Do you experience swelling in your joints that causes pain and discomfort when moving? Do you feel your skin itchier and warmer than usual? Or have you noticed that everyday tasks are more difficult now than before? Many of these pain-like scenarios are associated with joint pain associated with an autoimmune or musculoskeletal condition. Since autoimmunity is developed when environmental factors cause the immune system to attack healthy cells, it can envoke pain and discomfort to the body. When a person is dealing with an autoimmune condition, it can impact not only the individual but also the rest of the body’s system. For instance, if a person is dealing with an autoimmune condition, they could be dealing with skin issues that can cause them to develop scaly, itchy, red skin patches known as psoriasis. If they have joint pain combined with psoriasis, it can develop into psoriatic arthritis. (Skornicki et al., 2021) Now psoriatic arthritis is a heterogeneous autoimmune condition with musculoskeletal involvement that can manifest various symptoms including inflammation and arthritis. (Hackett et al., 2022) This in turn causes many individuals to think they are dealing with rheumatoid factors.
Causes & Symptoms
As a multifactorial pathology, psoriatic arthritis causes care often influenced by a complex interplay of immunological, environmental, and genetic factors that cause its development. (Zalesak et al., 2024) When the immune system starts to attack the healthy cells in the body, the inflammatory cytokines can become haywire and attack the “problem,” causing the development of autoimmunity. Within this integration, some of the causes can include predisposing genetic backgrounds with the presence of environmental factors that can activate the innate immune system precipitate the onset of psoriatic arthritis. (Azuaga et al., 2023) Some of the symptoms can many individuals with psoriatic arthritis can include:
- Tendon tenderness
- Joint pain
- Stiffness
- Fatigue
- Joint swelling
- Skin rash
- Musculoskeletal pain
However, there are ways to manage psoriatic arthritis, reduce joint pain from affecting a person, and help them manage the symptoms.
Arthritis Explained-Video

Treatments For Psoriatic Arthritis
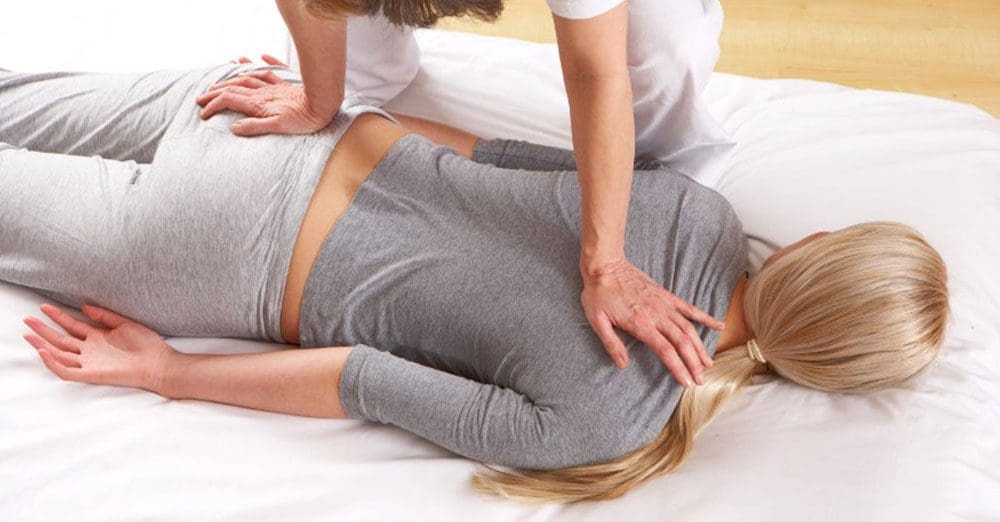
When it comes to treating psoriatic arthritis, healthcare professionals need to develop therapeutic options to educate the individual and develop a treatment plan that can include conventional therapies and non-pharmacological therapies that are affordable and customized with the individual’s condition. (Ogdie et al., 2020) Since psoriatic arthritis is a complex inflammatory musculoskeletal condition and skin disease, individuals must try to find ways to reduce the inflammatory effects of causing more joint issues. Non-surgical treatments like chiropractic care, physical therapy, and diet changes can help mitigate the burden of psoriatic arthritis by reducing the complications and the socio-economic impact. (McGonagle et al., 2022)
Another way individuals can reduce the inflammatory effects of psoriatic arthritis is by consuming anti-inflammatory foods to dampen the inflammatory cytokines attacking the joints and going to physical therapy sessions like water aerobics to help stabilize the joints and help people be more mindful about their bodies. Since psoriatic arthritis can be managed through non-surgical therapy, low-weight bearing exercise regimes and incorporating anti-inflammatory foods to reduce inflammation can help people minimize psoriatic arthritis symptoms from impacting their health and wellness journey.
References
Azuaga, A. B., Ramirez, J., & Canete, J. D. (2023). Psoriatic Arthritis: Pathogenesis and Targeted Therapies. Int J Mol Sci, 24(5). https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24054901
Hackett, S., Ogdie, A., & Coates, L. C. (2022). Psoriatic arthritis: prospects for the future. Ther Adv Musculoskelet Dis, 14, 1759720X221086710. https://doi.org/10.1177/1759720X221086710
McGonagle, D. G., Zabotti, A., Watad, A., Bridgewood, C., De Marco, G., Kerschbaumer, A., & Aletaha, D. (2022). Intercepting psoriatic arthritis in patients with psoriasis: buy one get one free? Ann Rheum Dis, 81(1), 7-10. https://doi.org/10.1136/annrheumdis-2021-221255
Ogdie, A., Coates, L. C., & Gladman, D. D. (2020). Treatment guidelines in psoriatic arthritis. Rheumatology (Oxford), 59(Suppl 1), i37-i46. https://doi.org/10.1093/rheumatology/kez383
Skornicki, M., Prince, P., Suruki, R., Lee, E., & Louder, A. (2021). Clinical Burden of Concomitant Joint Disease in Psoriasis: A US-Linked Claims and Electronic Health Records Database Analysis. Adv Ther, 38(5), 2458-2471. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12325-021-01698-7
Zalesak, M., Danisovic, L., & Harsanyi, S. (2024). Psoriasis and Psoriatic Arthritis-Associated Genes, Cytokines, and Human Leukocyte Antigens. Medicina (Kaunas, Lithuania), 60(5). https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina60050815