What are the advantages of being both a chiropractor and a nurse practitioner in cases of personal injury and car accidents?

Table of Contents
Chiropractic and Nurse Practitioner On Auto Accidents
In the aftermath of a motor vehicle accident, both chiropractors and nurse practitioners play vital roles in managing injuries and promoting recovery. Chiropractors focus on manual therapies, such as adjustments and manipulations, to address musculoskeletal issues and restore mobility, while nurse practitioners provide comprehensive care, including assessments, diagnoses, treatment plans, and education, often collaborating with specialists to optimize patient outcomes. (Physicians Group, LLC. 2024)
Chiropractors
Chiropractors treat musculoskeletal ailments, such as back and neck discomfort, which are common in motor vehicle accidents. They frequently employ hands-on techniques to reduce pain and enhance mobility instead of drugs. Their extensive records and expert testimony can also be used to support personal injury lawsuits, demonstrating the severity of injuries. (Dies, S., & Strapp, J. W., 1992)
Diagnosis and Treatment of Musculoskeletal Conditions
- Chiropractors can diagnose and treat spinal misalignments, muscle spasms, and soft tissue injuries that may occur following an accident. (The Neck and Back Clinics, 2025)
Pain Relief
- Manual therapy, such as spine adjustments and soft tissue mobilization, can help relieve pain and inflammation.
Improved mobility
- Chiropractors can assist in restoring range of motion and function by addressing joint and muscle limitations.
Holistic care
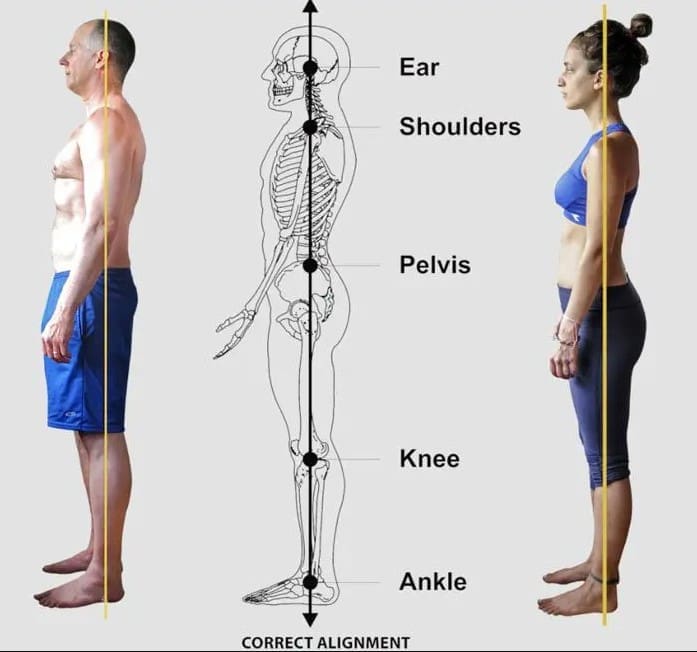
- Chiropractors frequently examine the complete body and can advise on maintaining excellent posture, ergonomics, and overall health to avoid future accidents.
Collaboration with Other Healthcare Professionals
- Chiropractors can collaborate with doctors, physical therapists, and other professionals to develop a holistic treatment plan for their patients. (Physicians Group, LLC, 2024)
Nurse practitioners
Nurse practitioners can offer complete care for motor vehicle accident injuries, such as: (Integrity Spine & Orthopedics, 2024)
Assessment and diagnosis
- Nurse practitioners can do physical exams, interpret diagnostic tests, and treat injuries like whiplash, soft tissue injuries, and concussions.
Treatment Plans
- They can create tailored treatment programs that include drugs, physical therapy, and other interventions to meet the patient’s specific requirements.
Patient Education
- Nurse practitioners can help patients understand their injuries, the recovery process, and self-care practices to improve healing and avoid problems.
Coordination of Care
- They can work with other professionals, such as surgeons, neurologists, and physical therapists, to provide a comprehensive approach to treatment.
Follow-Up Care
- Nurse practitioners can track the patient’s progress, modify treatment programs as appropriate, and offer ongoing care throughout the healing process.
Personal injury cases, particularly those resulting from car accidents, sometimes entail complex medical and legal issues. Chiropractors and nurse practitioners, with their specific areas of practice, play critical roles in diagnosis, treatment, and documentation.
Both chiropractors and NPs provide distinct advantages to personal injury cases. Chiropractors specialize in musculoskeletal difficulties and provide non-invasive treatments, whereas NPs manage a wider range of medical needs, such as drug prescriptions and care coordination. Their collaboration can improve patient outcomes, as seen in settings such as the Accident Treatment and Treatment Center, where NPs and physicians monitor treatment and supplement chiropractic interventions. (Accident Care, 2025)
Legal sources indicate that both professionals’ paperwork is crucial for insurance claims and settlements. Chiropractors’ detailed reports on spinal injuries, along with NPs’ comprehensive medical records on overall health, can build a strong compensation case. This synergy is especially noticeable in auto accident cases, when patients may need both physical changes and medical supervision to fully recover. (Chiropractic Economics, 2023)
Injury Medical Chiropractic and Functional Medicine Clinic
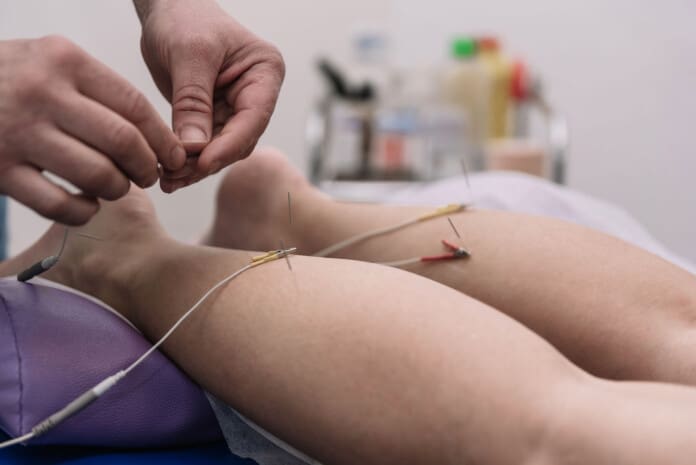
Dr. Jimenez is a family practice nurse practitioner who uses both sophisticated medical knowledge and chiropractic care to treat a variety of illnesses. We use functional medicine, acupuncture, electro-acupuncture, and sports medicine to make personalized treatment programs that help people heal naturally, move better, and stay healthy for a long time. We help people do well, no matter their age or health problems, by focusing on flexibility, agility, and strength. We at El Paso’s Chiropractic Rehabilitation Clinic & Integrated Medicine Center are very dedicated to helping people recover from accidents and chronic pain conditions. We work with people of all ages and impairments to help them get better through programs that improve their flexibility, mobility, and agility. We make sure that every patient gets tailored care and good health outcomes by using both in-person and online health coaching and full care plans.
Don’t Ignore Your Post-Accident Pain
References
Physicians Group, LLC. (2024). The Role of Nurse Practitioners in Managing Auto Injuries. Physicians Group, LLC. https://physiciansgroupllc.com/the-role-of-nurse-practitioners-in-managing-auto-injuries/#:~:text=Nurse%20Practitioners%20are%20vital%20in,improved%20outcomes%20and%20patient%20satisfaction.
Dies, S., & Strapp, J. W. (1992). Chiropractic treatment of patients in motor vehicle accidents: a statistical analysis. The Journal of the Canadian Chiropractic Association, 36(3), 139–145.
The Neck and Back Clinics. (2025). Why Seeing a Chiropractor After a Car Accident Is Crucial for Long-Term Recovery. https://theneckandbackclinics.com/long-term-recovery/#:~:text=Reducing%20Inflammation%20and%20Pain,each%20patient%20for%20optimal%20recovery.
Integrity Spine & Orthopedics. (2024). The 9 Steps to Recovery After an Auto Accident. https://www.integrityspineortho.com/post/the-9-steps-to-recovery-after-an-auto-accident/#:~:text=CONTACT%20INTEGRITY%20SPINE%20AND%20ORTHOPEDICS%20AFTER%20A,concussions%2C%20soft%20tissue%20damage%20and%20spine%20damage.
Accident Care and Treatment Center, Inc. (2025). Comprehensive Therapies and Treatments in One Location. https://accidentcare.com/treatment/
Chiropractic Economics. (2023). Evidence-based chiropractic: the key to personal-injury cases. https://www.chiroeco.com/evidence-based-chiropractic-the-key-to-personal-injury-cases/


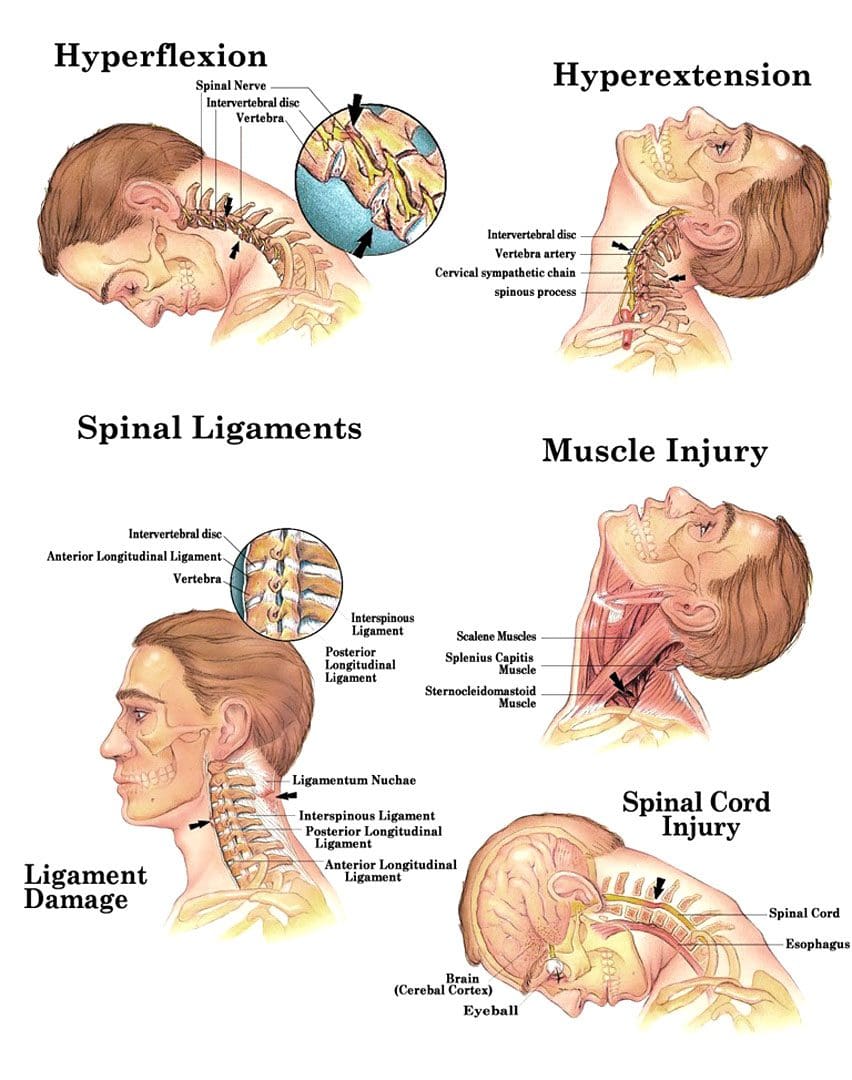 Common Causes Of Whiplash
Common Causes Of Whiplash