Table of Contents
Nerve Injuries After a Car Accident: Athletic Recovery Through Integrative Care

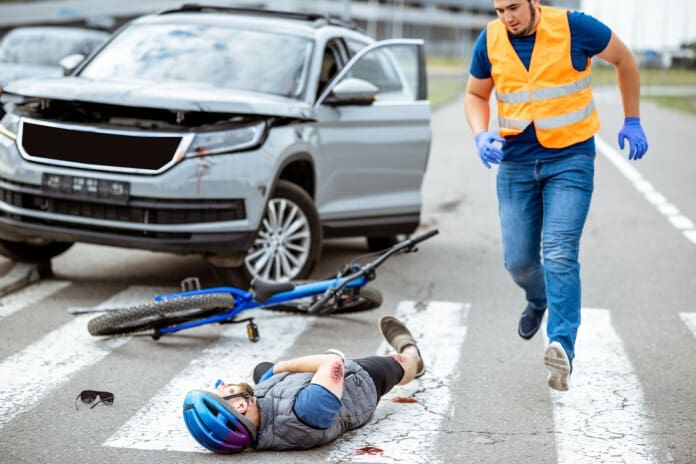
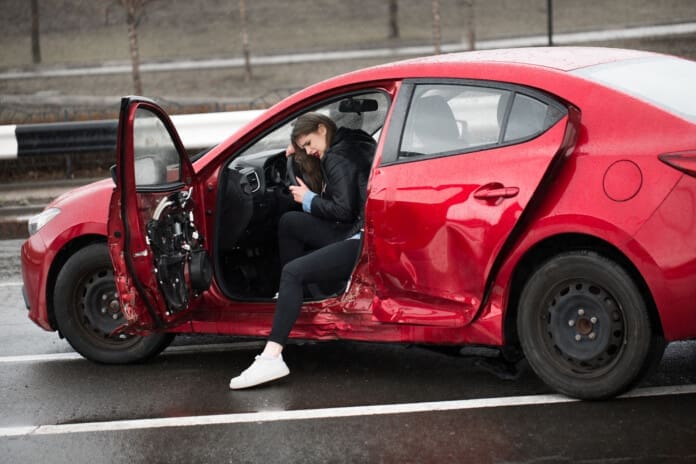
For individuals, a motor vehicle accident (MVA) can cause more than surface-level trauma—it can disrupt the nervous system in ways that impact strength, balance, reaction time, and recovery. While bruises and fractures often receive immediate attention, nerve injuries are frequently overlooked or misdiagnosed. Yet these injuries can limit mobility, delay healing, and reduce physical performance long after the crash.
At Sciatica.Clinic, we support post-accident nerve injury recovery through integrative care, including chiropractic adjustments, movement therapy, medical evaluation, and functional medicine. Understanding how accidents affect your nervous system is the first step toward full rehabilitation.
How Car Accidents Cause Nerve Injuries
Even low-speed collisions can affect the spine, joints, muscles, and nerves. In an accident, the body is rapidly accelerated and decelerated—causing shearing forces, joint misalignment, disc compression, and tissue inflammation. All of these can irritate or damage the nerves that run from the spinal cord through the limbs and internal organs.
Common Mechanisms of Nerve Injury in Accidents:
- Compression: A herniated disc or inflamed joint presses on nearby nerves
- Stretching: Whiplash or sudden force stretches nerves past their limit
- Crushing: Bone or muscle trauma crushes or cuts off nerve signals
- Inflammation: Swelling in tissues reduces the space around nerve pathways
These injuries disrupt the nerve’s ability to send and receive signals, often resulting in pain, numbness, weakness, or dysfunction. This results in slower muscle activation, impaired coordination, and an increased risk of injury upon returning to work.
Mayo Clinic, n.d.
Novus Spine Center, n.d.
Types of Nerves Affected by Motor Vehicle Accidents
The nervous system has three main types of nerves, and all of them can be impacted in a car crash:
1. Sensory Nerves
These control feelings—pain, pressure, heat, cold, and touch. Damage causes tingling, numbness, burning, or sensitivity in areas like the arms, hands, legs, or feet.
2. Motor Nerves
These control muscle strength and movement. When affected, individuals may feel muscle weakness, fatigue, cramping, or even loss of coordination.
3. Autonomic Nerves
These regulate involuntary functions, such as heart rate, digestion, and body temperature. Damage can cause dizziness, irregular heartbeat, digestive changes, or sweating problems.
Understanding which nerves are affected helps guide rehabilitation planning and long-term care. At Sciatica.Clinic, we use a dual-discipline evaluation model to assess all of these systems.
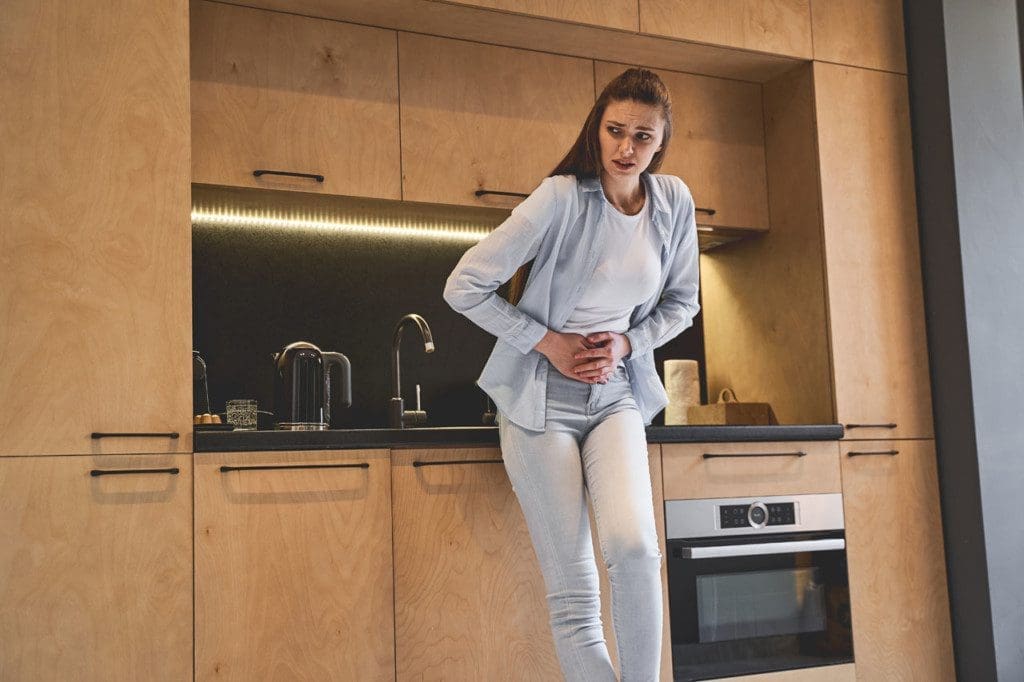
Recognizing Nerve Injury Symptoms
Individuals may experience nerve injury symptoms differently from sedentary patients. Because their bodies are finely tuned for movement, even minor dysfunctions in nerve signaling can have noticeable effects on performance, endurance, and proprioception (body awareness).
Signs of Post-Accident Nerve Injury in Active Patients:
- Sudden loss of coordination or imbalance while engaged in physical activities like lifting
- Delayed muscle firing, leading to weaker starts or slower reactions
- Persistent tingling or numbness in arms, legs, or feet during exercise
- Muscle weakness in previously strong areas
- Unexplained fatigue after a short while
- Tightness or stiffness that does not respond to stretching
- Loss of grip strength or precision during physical-specific tasks
These subtle deficits may be overlooked early on, but over time, they increase the risk of further injury—especially in environments where peak performance is crucial.
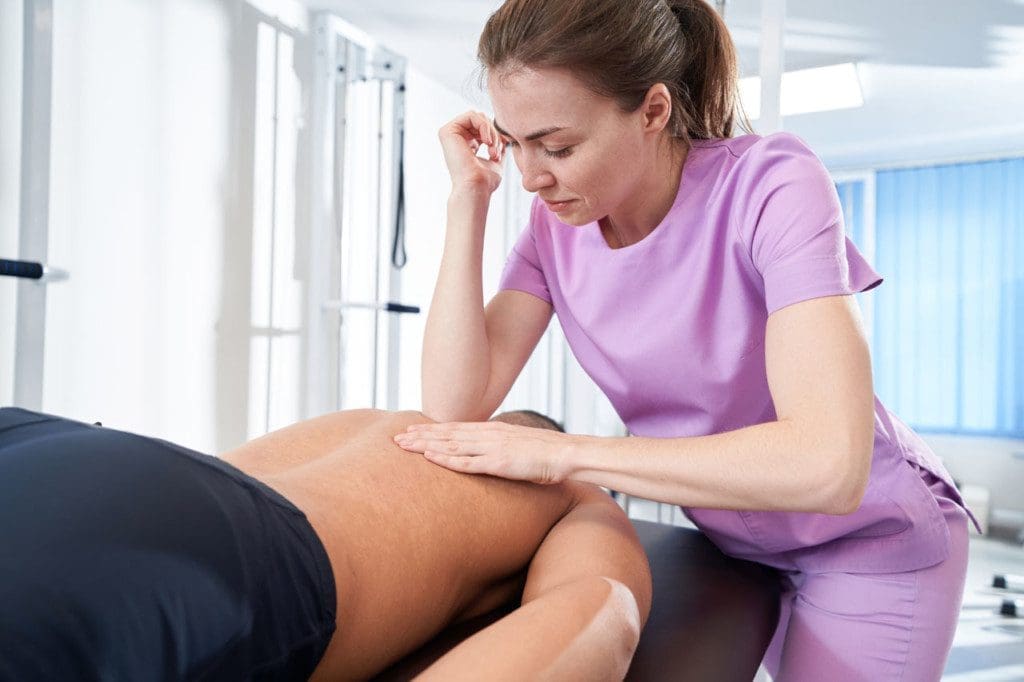
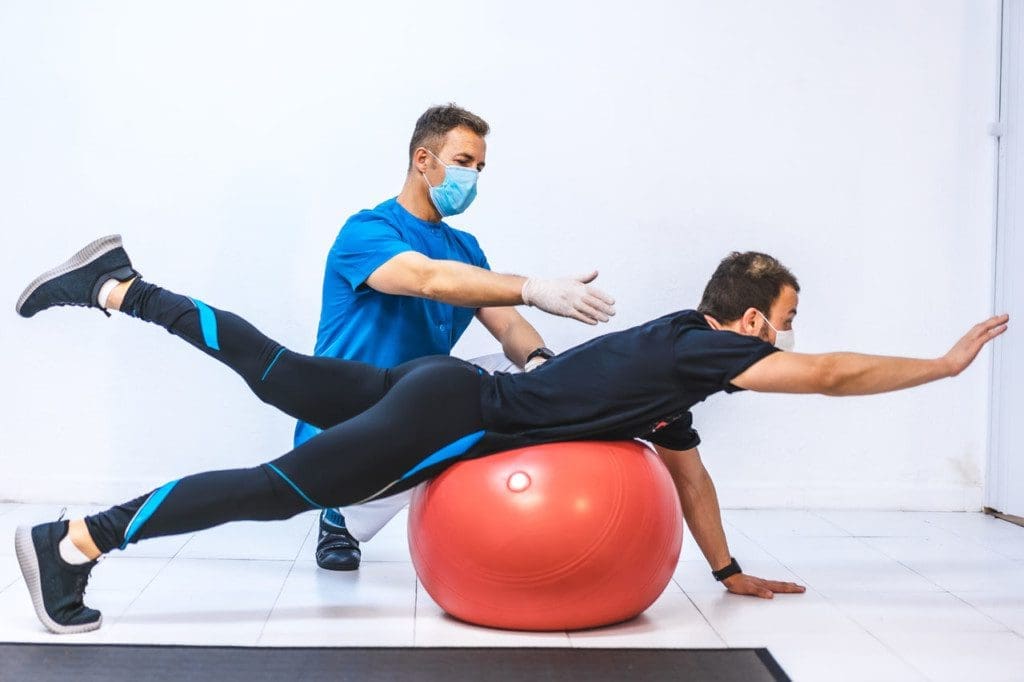
Chiropractic and Imaging for Post-Accident Nerve Diagnosis
At Sciatica.Clinic, we believe that identifying the full extent of nerve injury is the foundation for effective care. Our providers—including Dr. Alexander Jimenez, DC, APRN, FNP-BC—use a combination of biomechanical assessments, neurological testing, and advanced imaging to determine the source and severity of nerve-related symptoms.
Tools We Use Include:
- Orthopedic and neurological exams to test strength, reflexes, sensation, and joint function
- Digital posture analysis to find imbalances that may irritate nerve roots
- MRI or CT scans to evaluate disc herniations, fractures, or joint trauma
- Electromyography (EMG) and nerve conduction studies (NCS) to assess how well nerves and muscles are communicating
This dual-scope approach—blending chiropractic science and medical diagnostics—ensures that individuals receive a full, evidence-based understanding of their injury.
LWW Journal of Neurorehabilitation, 2019
The Role of Dr. Alex Jimenez in Recovery
Dr. Alexander Jimenez’s unique dual-license as both a Doctor of Chiropractic (DC) and Advanced Practice Registered Nurse (APRN, FNP-BC) makes him a leader in post-MVA recovery. He is trained to treat injuries from both a medical and biomechanical lens—essential for individuals who need precision care and long-term prevention.
Dr. Jimenez Offers:
- Full-scope diagnostic evaluation
- Chiropractic adjustments to relieve nerve compression
- Injury documentation for legal and insurance support
- Nutritional and anti-inflammatory protocols for tissue healing
- Movement screening for return-to-work planning
By combining neuromuscular re-education, spinal correction, and functional medicine, Dr. Jimenez helps restore physical performance while preventing future setbacks.
Dr. Jimenez – Clinical Website
Dr. Jimenez – LinkedIn
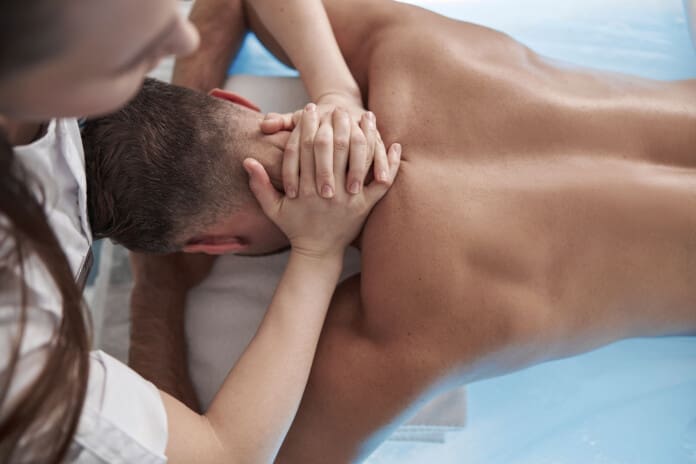
Chiropractic Adjustments and Nerve Healing After MVAs
Chiropractic care plays a central role in restoring nerve health and spinal function after a motor vehicle accident. For individuals, even minor spinal misalignments can affect power, flexibility, and coordination. These misalignments (called subluxations) often pinch or irritate nerves, contributing to pain, weakness, and slowed recovery.
How Chiropractic Helps Nerve Injury Recovery:
- Spinal adjustments relieve pressure on compressed nerves
- Joint mobilization improves range of motion and biomechanics
- Posture correction reduces compensatory muscle patterns
- Inflammation reduction promotes tissue healing and circulation
- Nerve decompression alleviates disc herniation-related pain
By reestablishing proper alignment and movement, chiropractic treatments reduce strain on the nervous system. Individuals often report improved coordination, energy, and reduced nerve-related symptoms within weeks of starting care.
Integrative Therapies for Total Nervous System Recovery
At Sciatica.Clinic, chiropractic care is only one piece of the puzzle. Our integrative model also includes functional movement training, nutritional guidance, lifestyle modification, and mind-body therapies—all of which are crucial for complete nervous system recovery.
Key Integrative Therapies Include:
- Neuromuscular re-education: retrains nerve-muscle pathways to restore strength and agility
- Physical therapy: focuses on mobility, stability, and balance for optimal movement
- Anti-inflammatory diet protocols: reduce systemic inflammation that slows nerve healing
- Cold laser therapy and PEMF: stimulate cellular regeneration and circulation
- Breathing and mindfulness coaching: calms the autonomic nervous system, aiding recovery
These therapies support nerve regeneration, enhance the healing environment, and improve outcomes for individuals with nerve injuries.
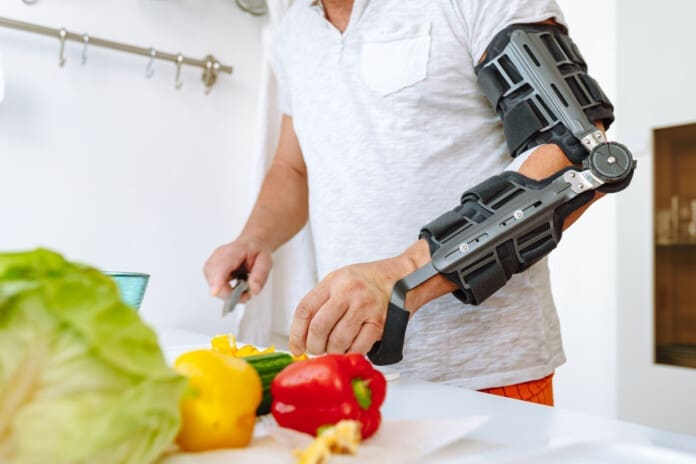
Returning to Regular Activities After a Nerve Injury
One of the top concerns for individuals recovering from a motor vehicle accident is: “When can I go back to regular activities again?”
The answer depends on nerve function, not just pain levels. At Sciatica.Clinic, we use functional movement assessments and specific metrics to determine when an individual is safe to return to their daily activities. These include:
- Balance and proprioception tests
- Reaction time and neuromuscular control assessments
- Core strength and spinal loading evaluations
- Gait, jump, and mobility analysis
By customizing your return-to-work protocol, we help reduce the risk of re-injury while restoring peak performance.
Legal and Documentation Support for Personal Injury Cases
Many athletes involved in car accidents face not only physical challenges, but legal and insurance complexities as well. Proper documentation of nerve injuries is essential for building a strong personal injury claim and securing necessary care.
At Sciatica.Clinic, Dr. Alex Jimenez provides:
- Detailed injury documentation for attorneys and insurance providers
- Objective diagnostic imaging that demonstrates nerve and spinal damage
- Clear functional assessments that outline how injuries impact daily life and work
- Progress reports showing treatment effectiveness over time
With his experience in both clinical care and legal coordination, Dr. Jimenez helps individuals protect their rights while recovering their health and well-being. His dual credentials make him a trusted resource in El Paso personal injury cases, especially for those seeking comprehensive post-accident care.
McNicholas Law, n.d.
Hoffmann Personal Injury, n.d.
Take the First Step Toward Nerve Recovery
If you’re struggling with nerve symptoms after a car accident—whether it’s pain, numbness, weakness, or reduced mobility—don’t wait. Nerve injuries can worsen without early intervention, especially for active adults.
At Sciatica.Clinic, we offer a complete recovery system grounded in:
- Chiropractic realignment
- Functional movement therapy
- Diagnostic imaging and testing
- Lifestyle and nutritional guidance
- Legal and documentation support
Whether you’re returning to work or simply seeking relief from chronic nerve pain, Dr. Alex Jimenez and team are here to guide you back to peak health—safely and sustainably.
References
Alexander Orthopaedics. (n.d.). Common car accident injuries. https://alexanderorthopaedics.com/blog/common-car-accident-injuries/
Grabban & Durando. (n.d.). Different types of nerve injuries. https://grabbanddurando.com/blog/different-types-of-nerve-injuries/
Hoffmann Personal Injury. (n.d.). 4 types of nerve injuries you may suffer in a car accident. https://www.hoffmannpersonalinjury.com/4-types-of-nerve-injuries-you-may-suffer-in-a-car-accident/
Hopkins Medicine. (n.d.). Types of peripheral nerve damage that may need surgery. https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/health/conditions-and-diseases/types-of-peripheral-nerve-damage-that-may-need-surgery
LWW Journal of Neurorehabilitation. (2019). Peripheral nerve injuries: Electrophysiology for prognosis and management. https://journals.lww.com/neur/fulltext/2019/67060/peripheral_nerve_injuries__electrophysiology_for.5.aspx
Mayo Clinic. (n.d.). Peripheral nerve injuries: Symptoms and causes. https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/peripheral-nerve-injuries/symptoms-causes/syc-20355631
McNicholas Law. (n.d.). Permanent nerve damage after a car accident. https://www.mcnicholaslaw.com/permanent-nerve-damage-after-a-car-accident/
Novus Spine Center. (n.d.). Pain conditions: Types of pain following an accident. https://novusspinecenter.com/pain-conditions/motor-vehicle-injuries-types-pain-following-accident
Physio-Pedia. (n.d.). Classification of peripheral nerve injury. https://www.physio-pedia.com/Classification_of_Peripheral_Nerve_Injury