Table of Contents
Introduction
One of the unique features of the body is when the gut and nervous systems have this communication partnership where information is transported back and forth throughout the entire body. The data transmitted to the brain and the gut travels through the nerve roots spread throughout the muscles, tissues, and ligaments that control the motor-sensory functions of the body. When the nerve roots become damaged or when there are gut issues affecting the organs in the gut system or even neurological disorders can cause the body to become dysfunctional and result in other matters affecting the muscles in the legs, arms, back, and neck. Today’s article looks at the functionality of the gut-brain axis, how this connection helps the body, and how disorders like inflammation and gut dysbiosis cause problems to the body and the gut-brain axis. Refer patients to certified, skilled providers specializing in gut treatments for individuals that suffer from gut dysbiosis and chronic inflammation. We guide our patients by referring to our associated medical providers based on their examination when it’s appropriate. We find that education is critical for asking insightful questions to our providers. Dr. Alex Jimenez DC provides this information as an educational service only. Disclaimer
Can my insurance cover it? Yes, it may. If you are uncertain, here is the link to all the insurance providers we cover. If you have any questions or concerns, please call Dr. Jimenez at 915-850-0900.
The Functionality Of The Gut-Brain Axis
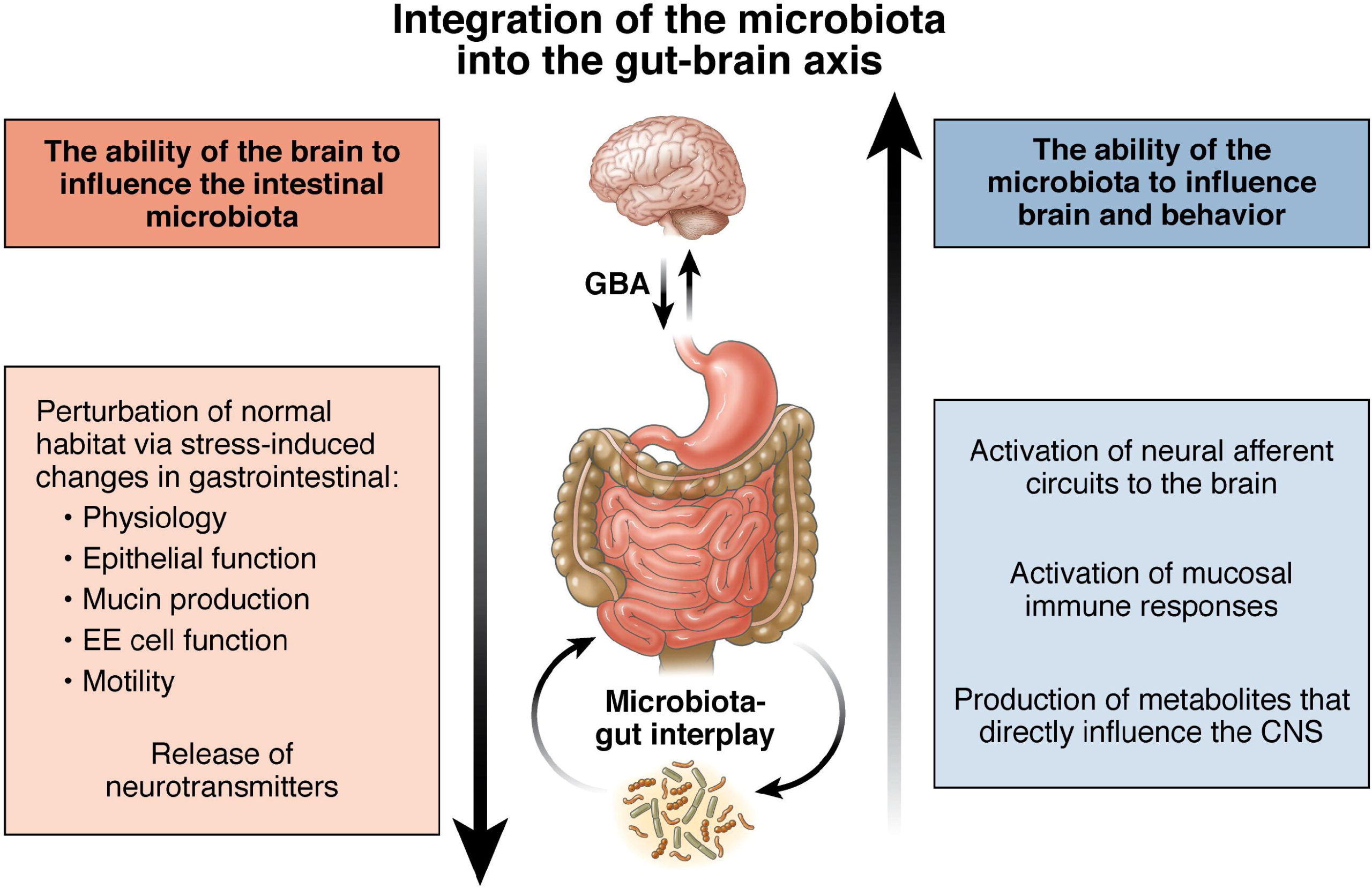
Have you been experiencing inflammation in your gut? How about feeling tired constantly throughout the entire day? Do any of your joints or muscles ache or feel stiff? Many of these are signs that the gut-brain axis is affected by common factors that the body has encountered. There is evidence that the bi-directional signaling between the gastrointestinal tract and the brain is connected with the vagus nerve. Research studies have mentioned that the vagus nerve is the modulator of the gut-brain axis and is considered the primary component in the parasympathetic nervous system that is vital for maintaining homeostasis in the body. The vagus nerve helps the body by overseeing every bodily function like heart rate, digestion responses, immune responses, and sending the brain information about the state of the inner organs. The vagus nerve is also involved in the etiology of several metabolic and mental dysfunctions/disorders that the body encounters that affect the muscles and internal organs. Additional research studies have shown that the vagus nerve has anti-inflammatory properties that are activated from the HPA axis and release the hormone cortisol in the body. The macrophages in the spleen make tumor necrosis factor (TNF) a potent inflammation-producing molecule when the vagus nerve is stimulating the TNF production in the spleen, causing it to decrease. At the same time, the survival portion increases in the body.
How Does The Gut-Brain Axis Help The Body?
With the bi-directional that the gut and brain have on the body, it is evident that environmental factors like oxidative stress, inflammation, and mood disorders cause changes in the glutamatergic pathways and neurotrophins in the body. Research studies have mentioned that the gut-brain axis helps influence the autonomic nervous system by activating the immune system. When the immune system is activated, the body can generally function like muscle endurance, provide microbiota-derived SCFAs to the blood-brain barrier, and regulate the body’s homeostasis. When the gut-brain axis starts to become dysfunctional, the immune system will begin to increase its production of cortisol which can cause muscle stiffness and spasms to affect the body. When there is inflammation in the gut system, it can cause the muscles in the body to become weak, and it can affect the spine causing low back pain issues to develop over time. Whenever the gut-brain axis is affected by environmental factors, the body will begin to start causing trouble with these symptoms and making the individual miserable.
The Microbiome Being Affected By Inflammation-Video

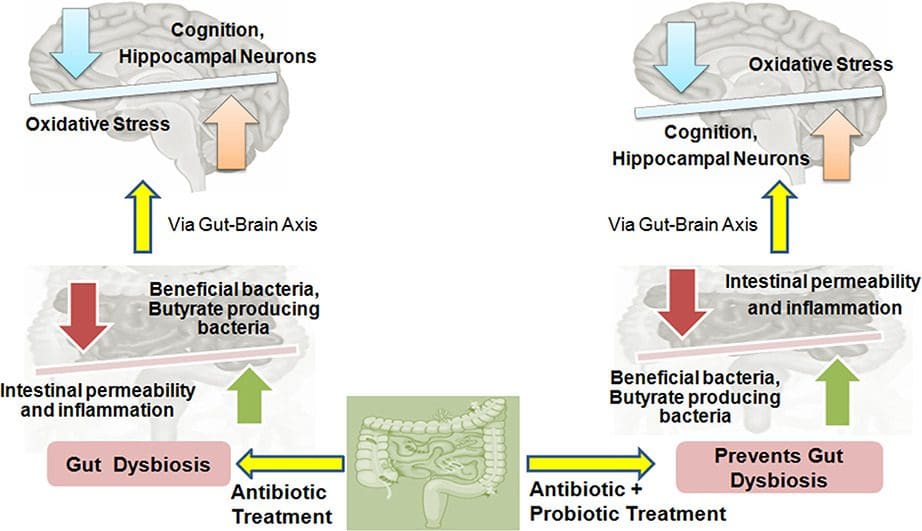
Are you experiencing muscle stiffness or weakness in your lower back, neck, or other body parts? Have you experienced mood swings or felt anxious constantly? Many of these symptoms you are experiencing are dysfunctional gut-brain axis affecting your body. The video above explained what happens when the gut microbiome is affected by inflammatory factors causing gut dysbiosis and neurological disorders. Research studies have mentioned that the composition between the gut and the brain as they communicate helps shape the body. When a person starts changing their dietary habits and lifestyle, their gut composition will not only be affected, but their nervous system begins to change too. Unwanted factors can cause many disturbances in the body and, if not treated right away, can develop into chronic issues that affect the joints, muscles, and tissues.
Inflammation And Gut-Brain Dysbiosis
When the gut-brain system is affected by unwanted factors, various symptoms will begin to rise in the body and start wreaking havoc on specific organs, tissues, muscles, and joints that need the gut-brain axis to keep the body functioning. Not only can inflammation cause these unwanted factors, but gut dysbiosis can also affect the T-cells in the immune system. Research studies have mentioned that when inflammatory markers start to translocate harmful bacteria across the gut-epithelial barrier to the blood-brain barrier, it can contribute to multiple sclerosis on the spine. Additional research studies have found that a stroke-induced gut dysfunction in the body allows the commensal bacteria to infect the peripheral tissue, causing infections like pneumonia and urinary tract infections. When individuals start to figure out what is causing their gut-brain axis to become dysfunctional, they can begin to heal their bodies.
Conclusion
The gut and nervous systems have a special bi-directional connection known as the gut-brain axis. The gut-brain axis helps the body function by metabolizing the immune system and regulating homeostasis with the vagus nerve. The vagus nerve is part of the parasympathetic nervous system that allows every bodily function like heart rate, digestion, and immune response while sending information about the state of the inner organs to the brain. The vagus nerve also makes sure that the inner organs are functioning correctly. When unwanted environmental factors like inflammation or gut dysbiosis start to affect the gut-brain axis, it can wreak havoc on the internal organs and cause the body to become dysfunctional. When people notice that their body becomes dysfunctional, they will find treatments available to relieve these issues in their bodies and continue on their health and wellness journey.
References
Appleton, Jeremy. “The Gut-Brain Axis: Influence of Microbiota on Mood and Mental Health.” Integrative Medicine (Encinitas, Calif.), InnoVision Health Media Inc., Aug. 2018, https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6469458/.
Bonaz, Bruno, et al. “Vagus Nerve Stimulation at the Interface of Brain-Gut Interactions.” Cold Spring Harbor Perspectives in Medicine, Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, 1 Aug. 2019, https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6671930/.
Breit, Sigrid, et al. “Vagus Nerve as Modulator of the Brain-Gut Axis in Psychiatric and Inflammatory Disorders.” Frontiers in Psychiatry, Frontiers Media S.A., 13 Mar. 2018, https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5859128/.
Gwak, Min-Gyu, and Sun-Young Chang. “Gut-Brain Connection: Microbiome, Gut Barrier, and Environmental Sensors.” Immune Network, The Korean Association of Immunologists, 16 June 2021, https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8263213/.
Günther, Claudia, et al. “The Gut-Brain Axis in Inflammatory Bowel Disease-Current and Future Perspectives.” International Journal of Molecular Sciences, MDPI, 18 Aug. 2021, https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8396333/.
Stopińska, Katarzyna, et al. “The Microbiota-Gut-Brain Axis as a Key to Neuropsychiatric Disorders: A Mini Review.” Journal of Clinical Medicine, MDPI, 10 Oct. 2021, https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8539144/.
Disclaimer
Professional Scope of Practice *
The information herein on "The Connection Of Inflammatory Markers & The Gut-Brain Axis" is not intended to replace a one-on-one relationship with a qualified health care professional or licensed physician and is not medical advice. We encourage you to make healthcare decisions based on your research and partnership with a qualified healthcare professional.
Blog Information & Scope Discussions
Welcome to El Paso's Premier Wellness and Injury Care Clinic & Wellness Blog, where Dr. Alex Jimenez, DC, FNP-C, a Multi-State board-certified Family Practice Nurse Practitioner (FNP-BC) and Chiropractor (DC), presents insights on how our multidisciplinary team is dedicated to holistic healing and personalized care. Our practice aligns with evidence-based treatment protocols inspired by integrative medicine principles, similar to those found on this site and our family practice-based chiromed.com site, focusing on restoring health naturally for patients of all ages.
Our areas of multidisciplinary practice include Wellness & Nutrition, Chronic Pain, Personal Injury, Auto Accident Care, Work Injuries, Back Injury, Low Back Pain, Neck Pain, Migraine Headaches, Sports Injuries, Severe Sciatica, Scoliosis, Complex Herniated Discs, Fibromyalgia, Chronic Pain, Complex Injuries, Stress Management, Functional Medicine Treatments, and in-scope care protocols.
Our information scope is multidisciplinary, focusing on musculoskeletal and physical medicine, wellness, contributing etiological viscerosomatic disturbances within clinical presentations, associated somato-visceral reflex clinical dynamics, subluxation complexes, sensitive health issues, and functional medicine articles, topics, and discussions.
We provide and present clinical collaboration with specialists from various disciplines. Each specialist is governed by their professional scope of practice and their jurisdiction of licensure. We use functional health & wellness protocols to treat and support care for musculoskeletal injuries or disorders.
Our videos, posts, topics, and insights address clinical matters and issues that are directly or indirectly related to our clinical scope of practice.
Our office has made a reasonable effort to provide supportive citations and has identified relevant research studies that support our posts. We provide copies of supporting research studies upon request to regulatory boards and the public.
We understand that we cover matters that require an additional explanation of how they may assist in a particular care plan or treatment protocol; therefore, to discuss the subject matter above further, please feel free to ask Dr. Alex Jimenez, DC, APRN, FNP-BC, or contact us at 915-850-0900.
We are here to help you and your family.
Blessings
Dr. Alex Jimenez DC, MSACP, APRN, FNP-BC*, CCST, IFMCP, CFMP, ATN
email: [email protected]
Multidisciplinary Licensing & Board Certifications:
Licensed as a Doctor of Chiropractic (DC) in Texas & New Mexico*
Texas DC License #: TX5807, Verified: TX5807
New Mexico DC License #: NM-DC2182, Verified: NM-DC2182
Multi-State Advanced Practice Registered Nurse (APRN*) in Texas & Multi-States
Multi-state Compact APRN License by Endorsement (42 States)
Texas APRN License #: 1191402, Verified: 1191402 *
Florida APRN License #: 11043890, Verified: APRN11043890 *
Colorado License #: C-APN.0105610-C-NP, Verified: C-APN.0105610-C-NP
New York License #: N25929, Verified N25929
License Verification Link: Nursys License Verifier
* Prescriptive Authority Authorized
ANCC FNP-BC: Board Certified Nurse Practitioner*
Compact Status: Multi-State License: Authorized to Practice in 40 States*
Graduate with Honors: ICHS: MSN-FNP (Family Nurse Practitioner Program)
Degree Granted. Master's in Family Practice MSN Diploma (Cum Laude)
Dr. Alex Jimenez, DC, APRN, FNP-BC*, CFMP, IFMCP, ATN, CCST
My Digital Business Card
Licenses and Board Certifications:
DC: Doctor of Chiropractic
APRNP: Advanced Practice Registered Nurse
FNP-BC: Family Practice Specialization (Multi-State Board Certified)
RN: Registered Nurse (Multi-State Compact License)
CFMP: Certified Functional Medicine Provider
MSN-FNP: Master of Science in Family Practice Medicine
MSACP: Master of Science in Advanced Clinical Practice
IFMCP: Institute of Functional Medicine
CCST: Certified Chiropractic Spinal Trauma
ATN: Advanced Translational Neutrogenomics
Memberships & Associations:
TCA: Texas Chiropractic Association: Member ID: 104311
AANP: American Association of Nurse Practitioners: Member ID: 2198960
ANA: American Nurse Association: Member ID: 06458222 (District TX01)
TNA: Texas Nurse Association: Member ID: 06458222
NPI: 1205907805
| Primary Taxonomy | Selected Taxonomy | State | License Number |
|---|---|---|---|
| No | 111N00000X - Chiropractor | NM | DC2182 |
| Yes | 111N00000X - Chiropractor | TX | DC5807 |
| Yes | 363LF0000X - Nurse Practitioner - Family | TX | 1191402 |
| Yes | 363LF0000X - Nurse Practitioner - Family | FL | 11043890 |
| Yes | 363LF0000X - Nurse Practitioner - Family | CO | C-APN.0105610-C-NP |
| Yes | 363LF0000X - Nurse Practitioner - Family | NY | N25929 |
Dr. Alex Jimenez, DC, APRN, FNP-BC*, CFMP, IFMCP, ATN, CCST
My Digital Business Card