Introduction
Dr. Alex Jimenez, D.C., presents how chronic stress can impact the body and how it is correlated with inflammation in this 2-part series. Part 1 examined how stress correlates with various symptoms affecting the body’s gene levels. Part 2 looks at how inflammation and chronic stress correlate with the various factors that can lead to physical development. We refer our patients to certified medical providers who provide available treatments for many individuals suffering from chronic stress associated with the cardiovascular, endocrine, and immune systems affecting the body and developing inflammation. We encourage each of our patients by mentioning them to associated medical providers based on their analysis appropriately. We understand that education is a delightful way when asking our providers questions at the patient’s request and understanding. Dr. Jimenez, D.C., only uses this information as an educational service. Disclaimer
How Stress Can Impact Us?
Dr. Alex Jimenez, D.C., presents: Stress can create many emotions that can hugely impact many of us. Whether it is anger, frustration, or sadness, stress can make anyone reach a breaking point and cause underlying conditions that can develop into cardiovascular issues. So those people with the highest level of anger, when you look at the cardiovascular literature, have the least probability of survival. Anger is a bad player. Anger causes arrhythmia. This study looked at, now that we have people with ICDs and defibrillators, we can monitor these things. And we see that anger can trigger ventricular arrhythmias in patients. And it’s easy now to follow, with some of our technology.
Anger has been linked to episodes of atrial fibrillation. When you think about it, it’s adrenaline outpouring into the body and causing coronary constriction. It’s increasing the heart rate. All of these things can lead to arrhythmia. And it doesn’t have to be AFib. It can be APCs and VPCs. Now, some very interesting research has come out about telomerase and telomeres. Telomeres are little caps on the chromosomes, and telomerase is the enzyme linked to telomere formation. And now, we can understand through the language of science, and we’re starting to use technology and use science in a way that we could never do before to understand the impact of stress on telomeres and telomerase enzymes.
The Factors That Lead Up To Chronic Stress
Dr. Alex Jimenez, D.C., presents: So one of the key people to study this is the Nobel Prize-winning, Dr. Elizabeth Blackburn. And what she said is that this is a conclusion, and we’ll come back to some of her other studies. She tells us that the telomeres of babies from women in utero had a lot of stress or were even shorter in young adulthood compared to mothers who did not have the same stressful situations. Maternal psychological stress during pregnancy may exert a programming effect on the developing telomere biology system that is already apparent at birth as reflected by the setting of newborn leukocyte telemetry length. So children can come in imprinted, and even if they do, this can be transformed.
What about racial discrimination these boxes here show high racial discrimination leading to low telomere length, which most of us have ever thought about. So, shorter telomere length leads to an increased risk of cancer and overall mortality. Cancer incidence rates are 22.5 per 1000 person-years in the shortest telomere group, verse 14.2 in the middle group, and 5.1 in the longest telomere group. Shorter telomeres can lead to instability of the chromosome and result in cancer formation. So, now we understand, through the language of science, the impact of stress on the telomerase enzyme and the telomere length. According to Dr. Elizabeth Blackburn, 58 premenopausal women were caregivers of their chronically ill children verse women who had healthy children. The women were asked how they perceive stress in their lives and whether it impacts their health by affecting their cellular aging.
That was the question of the study as they looked at telomere length and telomerase enzyme, and this is what they found. Now, the keyword here is perceived. We are not to judge each other’s stress. Stress is personal, and some of our responses may be genetic. For example, someone who has homozygous comps with a sluggish gene may have much more anxiety than someone who doesn’t have this genetic polymorphism. Someone who has an MAOA in an MAOB may have more anxiety than someone who doesn’t have that genetic polymorphism. So there is a genetic component to our response, but what she found was perceived psychological stress. And the number of years caring for chronically ill children was associated with shorter telomere length and less telomerase activity, providing the first indication that stress can impact telomere maintenance and longevity.
How To Transform Our Stress Response?
Dr. Alex Jimenez, D.C., presents: That’s powerful, and many healthcare providers are under some form of stress. And the question is, what can we do to transform our response? Framingham also looked at depression and identified clinical depression as a bigger risk for cardiovascular events and poor outcomes than smoking, diabetes, high LDL, and low HDL, which is crazy because we spend all of our time on these things. Yet, we don’t spend much time dealing with the emotional aspects of vascular disease. This is affected depression, inventory, a simple screening test for depression, looking at people with high levels of depression versus low levels of depression. And you can see that as you go from the low to the highest level, as you work your way through, the chance of survival becomes less.
And many of us have our theories as to why this occurs. And is it because if we are depressed, we don’t say, “Oh, I’m going to eat some brussels sprouts, and I’m going to take those B vitamins, and I’m going to go out and exercise, and I’m going to do some meditation.” So post-MI independent risk factor for an event is depression. Our mindset regarding depression makes us incapable of functioning normally and can make our bodies develop issues that affect our vital organs, muscles, and joints. So, depression is a big player, as 75% of post-MI deaths are related to depression, right? So looking at patients, now, you have to ask the question: Is it the depression causing the problem, or is it the cytokine sickness that’s already led to the heart disease causing the depression? We have to factor all of this in.
And yet another study looked at over 4,000 people with no coronary disease at baseline. For every increase of five points on the depression scale, that increased risk by 15%. And those with the highest depression scores had a 40% higher coronary artery disease rate and a 60% higher death rate. So mostly everyone thinks it’s a cytokine sickness that leads to MI, vascular disease, and depression. And then, of course, when you have an event, and you come out with a whole host of issues around it, we know that people who are depressed have a twofold increase in mortality, a fivefold increase in death after a heart attack, and poor outcomes with surgery. It’s like this, what came first, the chicken or the egg?
How Depression Is Linked With Chronic Stress?
Dr. Alex Jimenez, D.C., presents: Every surgeon knows this. They don’t want to do surgery on depressed people. They know the outcome is not good, and of course, they are less likely to follow through on all of our great functional medicine recommendations. So what are some of the mechanisms of autonomic dysfunction have been evaluated heart rate variability and low levels of omega-3s, which have a profound effect on the brain, and low levels of vitamin D. There are those inflammatory cytokines we talked about not getting restorative sleep, and many of our heart patients do have apnea. And remember, don’t just think it’s the heavyset heart patients with thick short necks; it can be quite deceiving. And it’s really important to look at the structure of the face and, of course, social connection, which is the secret sauce. So is autonomic dysfunction a mechanism? One study looked at heart rate variability in people with a recent MI, and they looked at over 300 people with depression and those without depression. They found that four heart rate variability indices will lower in people with depression.
Gut Inflammation & Chronic Stress
Dr. Alex Jimenez, D.C., presents: So here are two groups of people having a heart attack and heart rate variability, rising to the top as a possible etiology. One of the many things that can also affect chronic stress in the body is how the gut microbiome plays its part in oxidative stress. The gut is everything, and many heart patients laugh because they would ask their cardiologists, “Why do you care about my gut microbiome? Why would this affect my heart?” Well, all that gut inflammation is causing cytokine sickness. And what a lot of us have forgotten since medical school is that many of our neurotransmitters come from the gut. So chronic inflammation and exposure to inflammatory cytokines appear to lead to alterations in dopamine function and the basal ganglia, reflected by depression, fatigue, and psychomotor slowing. So we can’t emphasize the role of inflammation and depression enough if we take a look at acute coronary syndrome and depression, which was associated with higher markers for inflammation, more elevated CRP, lower HS, lower heart rate variability, and something that never gets checked in the hospital, which is nutrition deficiencies.
And in this case, they looked at omega-3s and vitamin D levels, so at a minimum, an omega-3 check and a vitamin D level are warranted in all of our patients. And certainly, if you can get a full diagnosis for stress-induced inflammation. Another condition you must look at when it comes to stress-induced inflammation is osteoporosis in the joints. Many people with osteoporosis will have muscle loss, immune dysfunction, fat around the midline, and high blood sugar are associated with aging, and it can come from elevated cortisol levels in the body.
High cortisol heart disease risks are two times higher in people taking high doses of steroids. Small amounts of steroids don’t have the same risk, so it is not as big a deal. Of course, we try to get our patients off of steroids. But the point here is that cortisol is a stress hormone and is a stress hormone that raises blood pressure and puts weight on the midline, makes us diabetic, causes insulin resistance, and the list is endless. So, cortisol’s a big player, and when it comes to functional medicine, we have to look at the various tests that pertain to elevated levels of cortisol like food sensitivity, a 3-day stool valve, a nutra-valve, and an adrenal stress index test to look at what is going on with the patients. When there is a heightened sympathetic nervous system and high cortisol, we discussed everything from coagulopathy to decreased heart rate variability, central obesity, diabetes, and hypertension.
Parental Relationships & Chronic Stress
Dr. Alex Jimenez, D.C., presents: And turning on the renin-angiotensin system it’s all linked to stress. Let’s look at this study that looked at 126 Harvard Medical students, and they were followed for 35 years, a long research. And they said, what’s the incidence of significant illness, heart disease, cancer, hypertension? And they asked these students very simple questions, what was your relationship with your mom and your dad? Was it very close? Was it warm and friendly? Was it tolerant? Was it strained and cold? This is what they found. They found that if the students identified their relationship with their parents as strained 100% incidence of significant health risk. Thirty-five years later, if they said it was warm and close, the results cut that percentage in half. And it would help if you thought about what it is and what can explain this, and you’ll see how adverse childhood experiences make us sick in a few minutes and how we learn our coping skills from our parents.
Conclusion
Dr. Alex Jimenez, D.C., presents: Our spiritual tradition comes from our parents often. Our parents are the ones who frequently teach us how to get angry or how to resolve conflict. So our parents have had a profound effect on us. And when you think about that, our connection is also not very surprising. This is a 35-year follow-up study.
Chronic stress can lead to multiple issues that can correlate to illness and dysfunction in the muscles and joints. It can affect the gut system and lead to inflammation if it is not taken care of immediately. So when it comes to the impact of stress affecting our daily lives, it can be numerous factors, from chronic conditions to family history. Eating nutritious foods high in antioxidants, exercising, practicing mindfulness, and going to daily treatments can lower the effects of chronic stress and reduce the associated symptoms that overlap and cause pain to the body. We can continue with our health and wellness journey pain-free by utilizing various ways to lower chronic stress in our bodies.
Disclaimer














 Stretching Objective
Stretching Objective



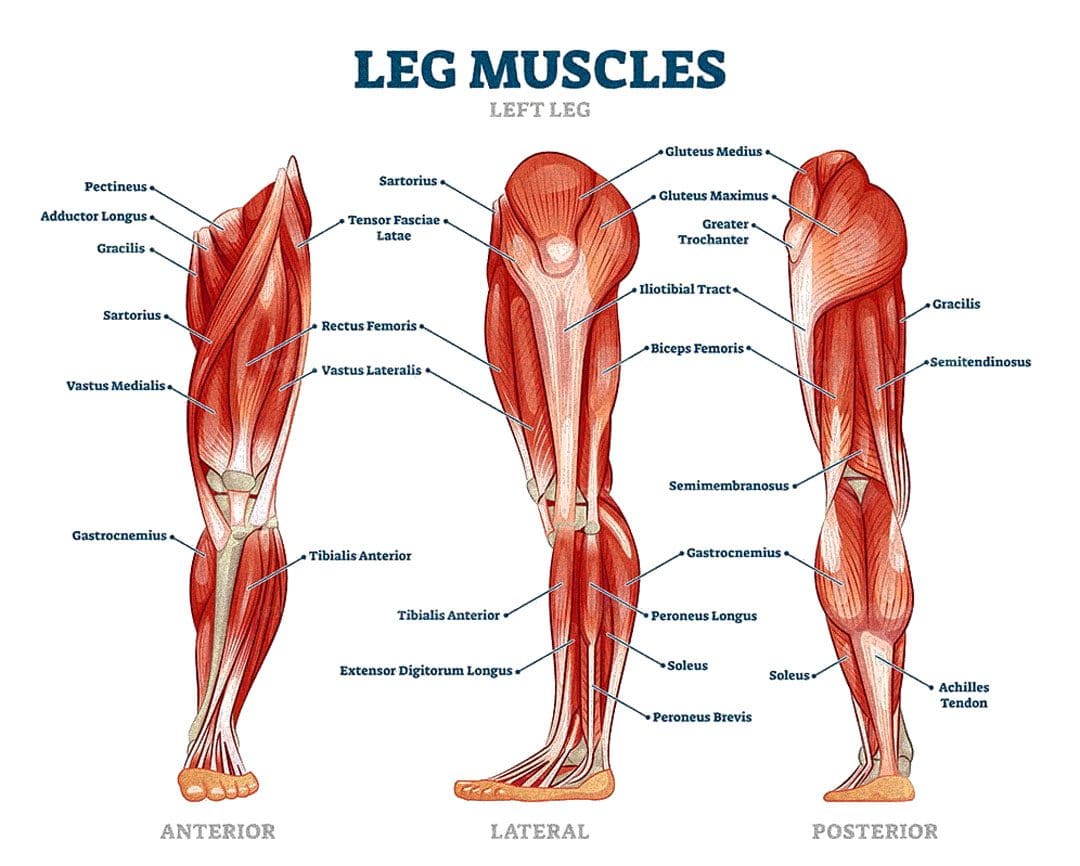 Leg Adjustments
Leg Adjustments