–
We are excited you are taking positive steps to learn about health challenges affecting you and your family. There is the power in making educated decisions about your health by gaining high-level science-based truth and knowledge. We work to uncover the root causes of health issues. Our unique health approach uses functional wellness principles to identify and treat health issues’ potential underlying causes.
Our care plans are base on Functional Medicine as a systems approach based on biology that focuses on identifying and addressing the root cause of disease. We focus on the paradigm that symptom or differential diagnosis may be one of many contributing factors to an individual’s illness.
This approach shifts from the traditional disease-centered focus of most medical practices to a more holistic person-centered approach.
Our discussions team includes Integrative Doctors, Functional Medicine Experts, Nutritionists, Health Coaches, Chiropractors, Physical Medicine Doctors, Therapists, and Exercise Performance Specialists.
We provide clinical insights, treatment options, and methods to achieve clinically sound, specific measured goals.*
Functional & Integrative Health Live Events *
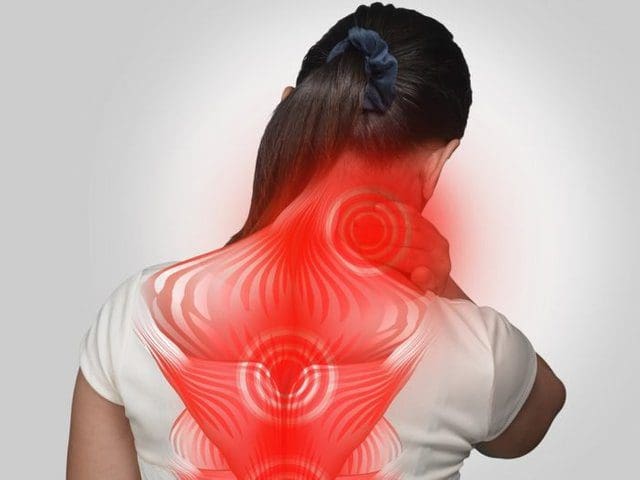
✅ Stress Hormones & Health
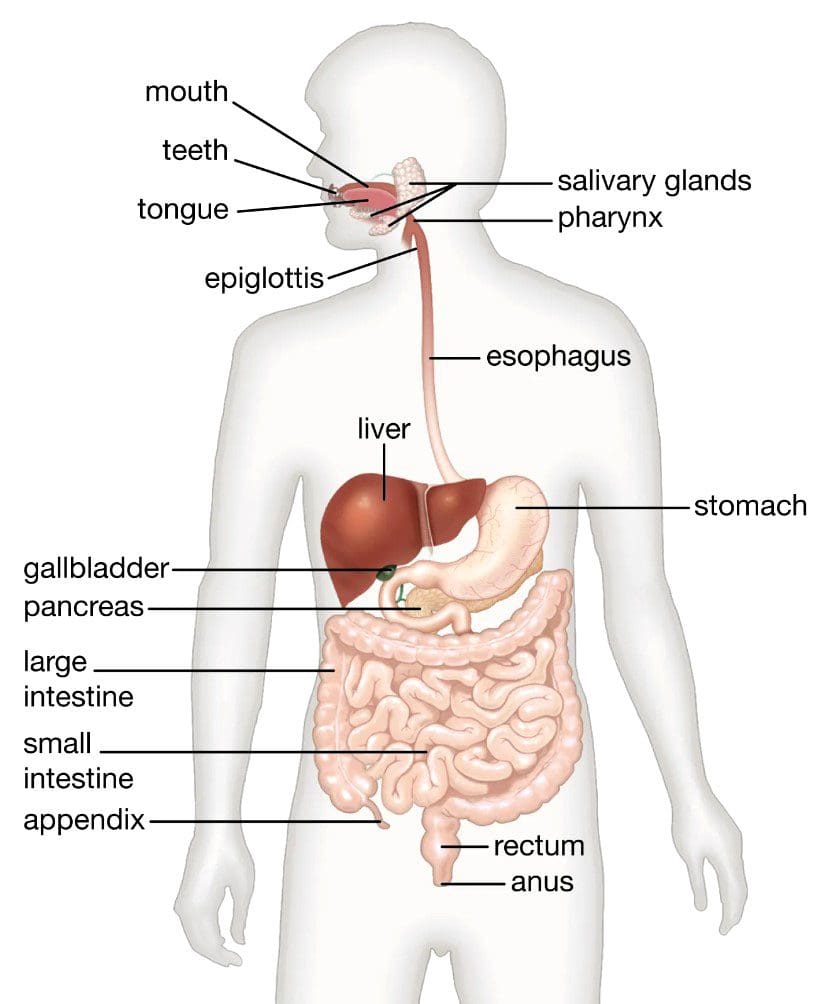
✅ Gut Health, Inflammation & Auto-Immunity*
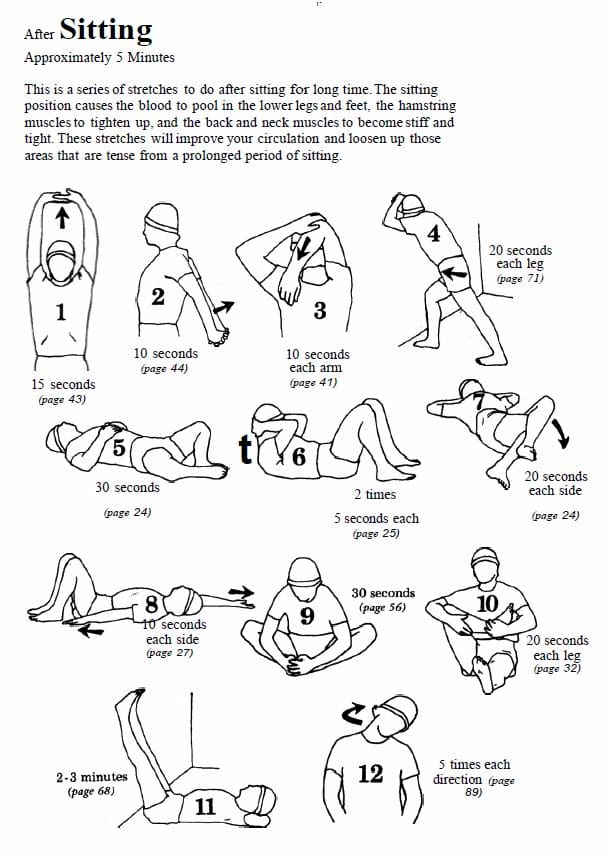
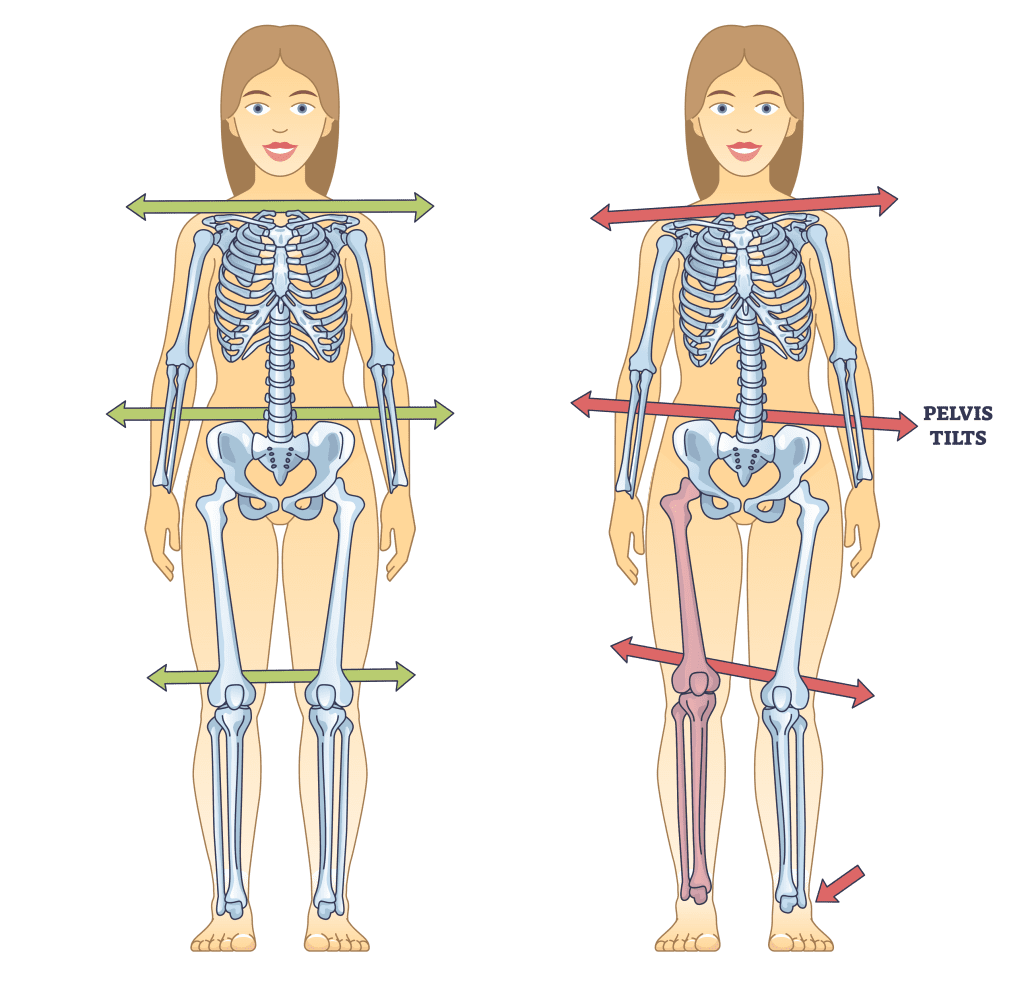
✅ Musculoskeletal Rehabilitation
✅ Fibromyalgia & Inflammation
✅ Diabetes & Autoimmunity*
✅ Weight Loss
✅ Body Composition Analysis
✅ Thyroid Dysfunction*
✅ Autoimmune Disorder*
✅ Heart Disease & Inflammation*
✅ Agility & Mobility
✅ Injury Recovery Programs
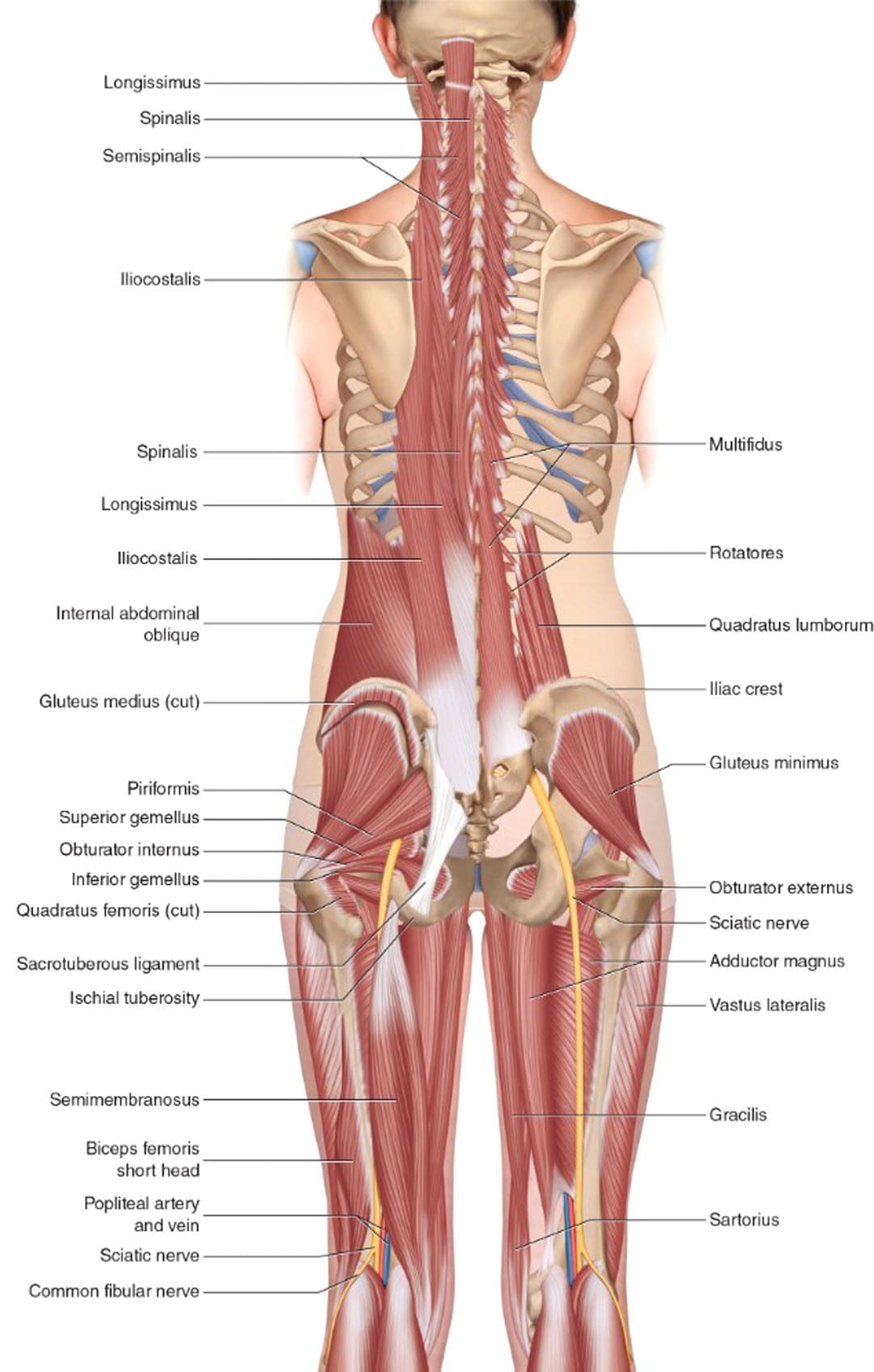
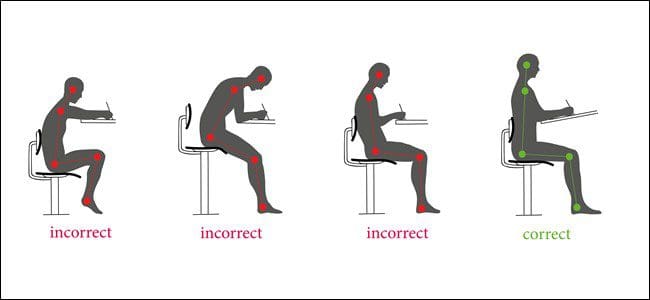
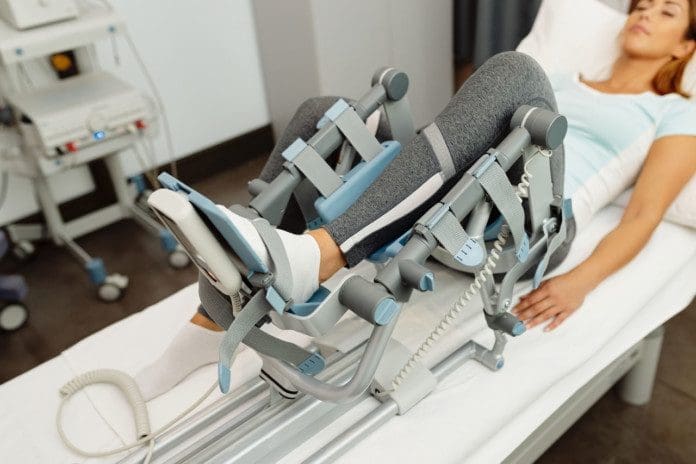
✅ Complex Lower Back Pain Recovery Plans
✅ Severe Sciatica Syndromes
✅ Other Complex Health Challenges
✅ Neutraceutical Recommendations
✅ Advanced Translational Nutrigenomics*
✅ Nutrigenomics, Proteomics, Metabalomics
✅ Care Plans (Advanced Clinical Practice)
We present, bridge, and connect these various health programs, functional medicine protocols, fitness methods, injury recovery programs, and offer complete wellness packages.
To that end, we shed light and offer treatment options and bring a deep understanding of the real underlying causes of those suffering from acute and interconnected chronic degenerative disorders.
Ultimately, we empower you to achieve and maintain your personalized, healthy way of living by understanding the root causes of disorders.
It is all about.
LIVING, LOVING & MATTERING
Join us in improving your health.
Blessings,
Dr. Alex Jimenez DC, MSACP, CCST, IFMCP*, CIFM*, CTG*
email: [email protected] phone:
phone: 915-850-0900
Licensed in Texas & New Mexico*
Notice: Our information scope is limited to musculoskeletal, physical medicines, wellness, sensitive health issues, functional medicine articles, topics, and discussions. We provide and present talks and clinical collaboration with specialists from a wide array of disciplines. Each specialist in our events is governed by their professional scope of practice and their jurisdiction of licensure.
The information in these events is not intended to replace a one-on-one relationship with a qualified health care professional and is not intended as medical advice.
Our presentations are designed to share knowledge and information from Dr. Jimenez’s research, experience, and collaborative functional medicine community. We encourage you to make your own health care decisions based on your research and partnership with a qualified health care professional.
We use and discuss functional health & wellness protocols to treat and support the musculoskeletal system’s care for injuries or disorders. Our events, webinars, posts, topics, subjects, and insights cover clinical matters, issues, and issues that relate and support, directly or indirectly, our clinical scope of practice.*
Subscribe: http://bit.ly/drjyt
Facebook Clinical Page: https://www.facebook.com/dralexjimenez/
Facebook Injuries Page: https://www.facebook.com/elpasochiropractor/
Facebook Neuropathy Page: https://www.facebook.com/ElPasoNeuropathyCenter/
Yelp: El Paso Rehabilitation Center: http://goo.gl/pwY2n2
Yelp: El Paso Clinical Center: Treatment: https://goo.gl/r2QPuZ
Clinical Testimonies: https://www.dralexjimenez.com/category/testimonies/
Information:
Clinical Site: https://www.dralexjimenez.com
Injury Site: https://personalinjurydoctorgroup.com
Sports Injury Site: https://chiropracticscientist.com
Back Injury Site: https://www.elpasobackclinic.com
Functional Medicine: https://wellnessdoctorrx.com
Twitter: https://twitter.com/dralexjimenez
Twitter: https://twitter.com/crossfitdoctor
DISCLAIMER: https://dralexjimenez.com/legal-disclaimer/