Individuals getting into fitness may wonder whether they should join a gym or exercise at home. Is there an advantage to one versus the other?

Table of Contents
Gym or Home
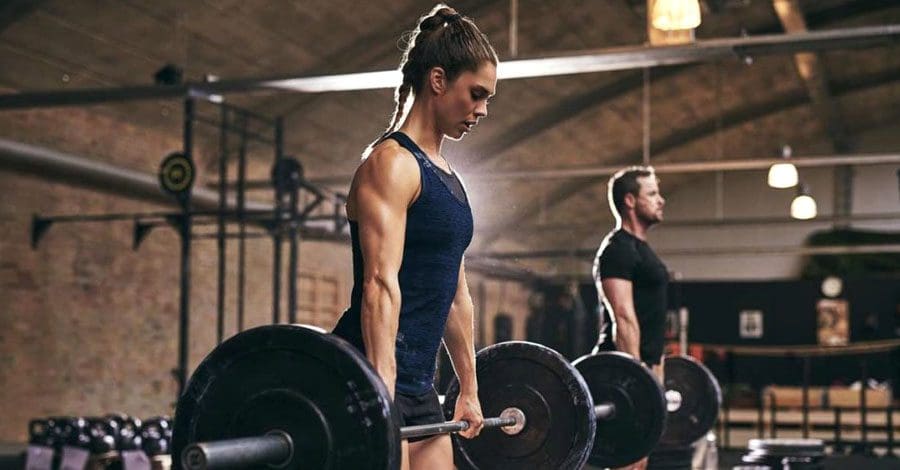
Exercising, whether at the gym or at home, depends on individual preference and budget. The first step is committing to a fitness health plan. Where to work out depends on the individual and their characteristics. For those who are self-motivated and will exercise no matter what, a home workout may be the best option. (Essery R. et al., 2017) Going to a gym may be a better choice for those who find too many distractions at home and other things to do besides the workout, like laundry, checking the phone, cleaning, etc. Working out at home is convenient; it takes driving out of the equation, changing into gym clothes, and going at the right time. However, the gym provides fewer distractions, community access, equipment like weights and cardiovascular machines, and group fitness classes. Each has pros and cons.

Pros and Cons – The Gym
Pros
- Gym features and resources
- Motivation
- Focus
- Classes
- Community
Cons
- Membership fees
- Inconvenience
- Too many people
Pros of a Gym
Features and Resources
- Exercise can be so much easier when there are plenty of options.
- There are various machines, such as treadmills, ellipticals, stair climbers, stationary bikes, and rowing machines.
- Weights and machines, free weights, cable machines, bands, and more.
Motivation
- Paying for a membership can be a motivating factor to regularly working out.
- There is a friendly, competitive vibe with the other members who can help motivate each other.
Focus
- Exercising at the gym can help maintain focus on fitness goals.
- No chores, kids, or distractions to break off from the workouts.
Classes
- Working out in a class can increase motivation and make working out fun.
- There are online classes for working out at home, but it’s not the same as going to the gym and being around people.
- Other features like a swimming pool, hot tub, tennis courts, etc may be available.
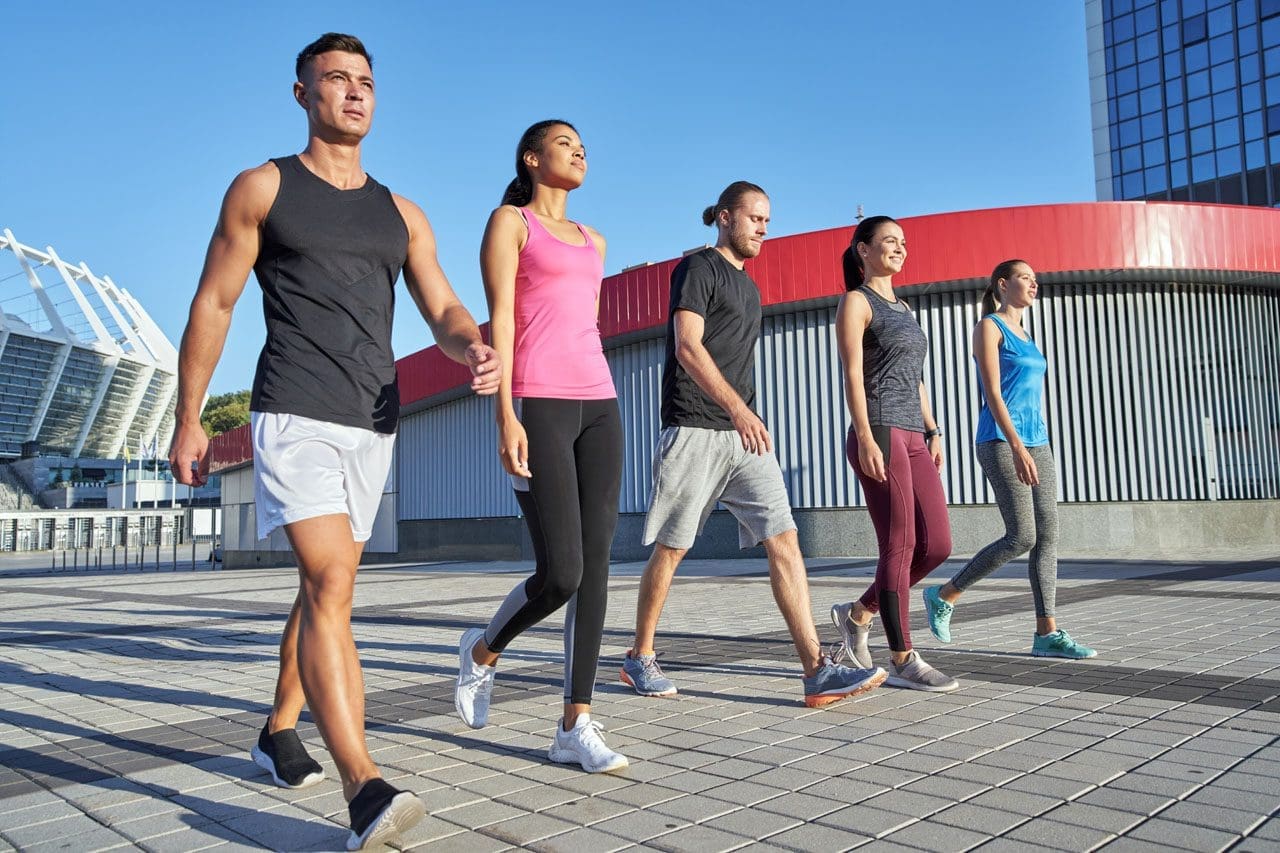
Community
- Working out with others can give a sense of community.
- People draw energy from others, pushing us to work harder.
Cons of a Gym
Gym membership drawbacks.
Cost
- Membership fees can cause stress.
- Some high-end gyms charge more than $100 monthly, while smaller gyms may charge only $10.
Inconvenience
- Going to the gym includes packing a bag, driving there, parking, and waiting for the machines, weights, etc.
- Total time will be longer because of the drive time.
Too Many People
- At times, the gym can be packed with people.
- Sometimes, individuals talk too loudly on their phones, leave sweat on the machines, and do not put weights away.
- These could be the days or nights to work out at the house.
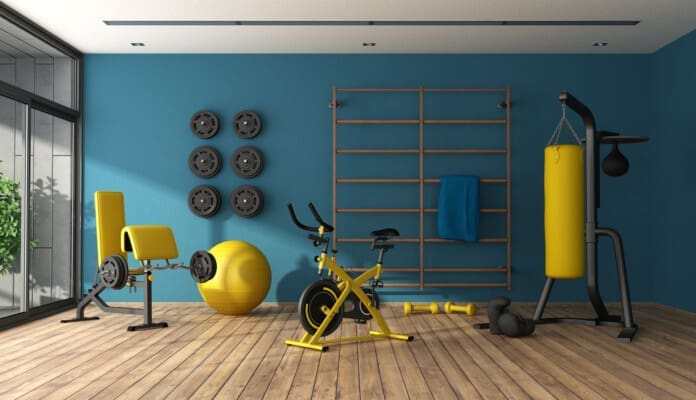
At Home Workouts
Pros
- Cost
- Convenience
- Mix workouts
Cons
- Space
- Excuses
- Boredom
Pros at Home
For some, home workouts could be the better option, and the benefits include:
Cost
- There’s no membership fee.
- Individuals can do bodyweight workouts that require no equipment.
- Develop a house gym with inexpensive resistance bands, a few weights, and an exercise ball.
Convenience
- Individuals do not have to get their gym bag, drive, and arrange for child care.
- Individuals can work out in pajamas or underwear.
- Individuals can also work out whenever they like if they need to split their workouts or work out at a specific time.
Mix Workouts
- Although gyms also mix things up, individuals can do it at home at their convenience.
- Combining weights and cardio and finishing up with yoga.
- Individuals can go outside, watch exercise videos, stream live classes, use fitness mirrors, play exercise games, or download workout apps.
- There is also versatile home gym equipment.
Cons at Home
These can cause individuals to lose home workout motivation.
Space
- Although not much space is needed to work out, wanting to use a treadmill or other large equipment might not be practical, which could lead to boredom.
Excuses
- There can be endless excuses to skip a workout.
- Individuals who are not self-motivated might avoid workouts with chores or other important home tasks.
Boredom
- At a gym, there is energy potential that motivates individuals to move.
- If there is not enough exercise variety at home, boredom can set in.
Injury Medical Chiropractic and Functional Medicine Clinic
Injury Medical Chiropractic and Functional Medicine Clinic treats patients’ injuries and chronic pain syndromes. We focus on improving ability through flexibility, mobility, and agility programs tailored to the individual. We use in-person and virtual health coaching and comprehensive care plans to ensure every patient’s personalized care and wellness outcomes. Our providers use an integrated approach to create customized care plans that include Functional Medicine, Acupuncture, Electro-Acupuncture, and Sports Medicine principles. Our goal is to relieve pain naturally by restoring health and function to the body. Suppose he feels the individual needs other treatment. In that case, they will be referred to a clinic or physician best suited for them. Dr. Jimenez has teamed up with the top surgeons, clinical specialists, medical researchers, and premier rehabilitation providers to provide our community with the best clinical treatments.
The Right Way To Implement an Exercise Prescription
References
Essery, R., Geraghty, A. W., Kirby, S., & Yardley, L. (2017). Predictors of adherence to home-based physical therapies: a systematic review. Disability and rehabilitation, 39(6), 519–534. https://doi.org/10.3109/09638288.2016.1153160