Can individuals find therapeutic ways to reduce restless leg syndrome and improve their sleep quality in their beds?
Table of Contents
What Is Restless Leg Syndrome?
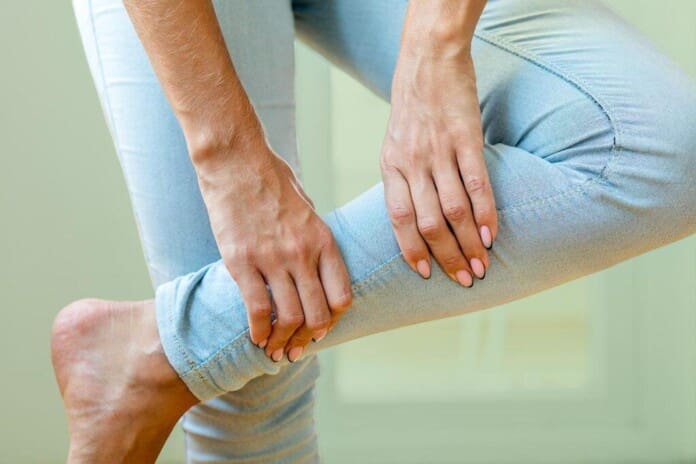
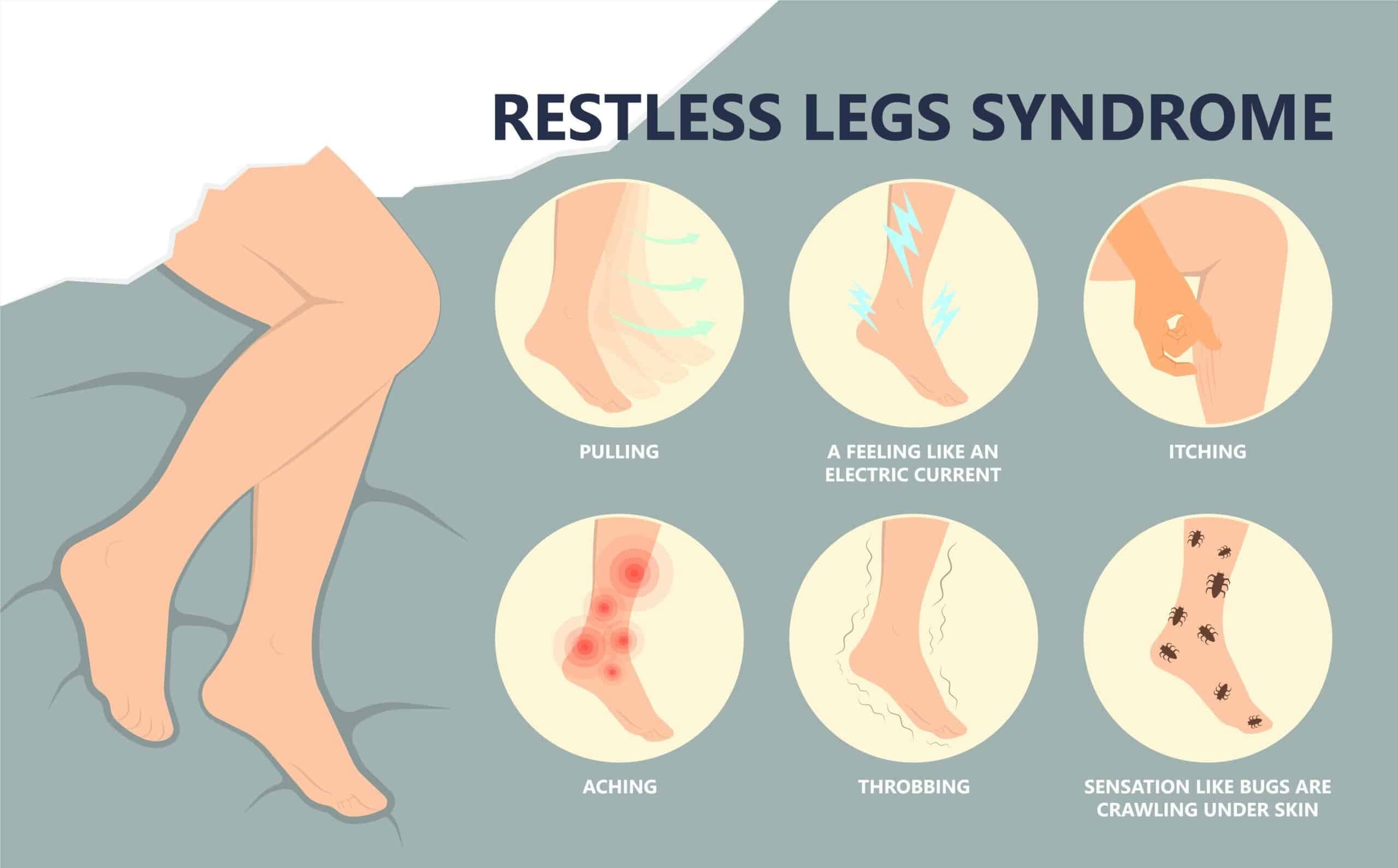
Do you feel general aches or leg pain, causing you to feel restless? Do you experience fatigue throughout the day, making it difficult to fall asleep? Or do you feel uncomfortable sensations in your legs, making falling and staying asleep difficult? Many people worldwide have experienced these issues known as restless leg syndrome. Also known as Willis-Ekbom disease, restless leg syndrome is often characterized by an uncomfortable urge to move legs when a person rests for the night and can be accompanied by unpleasant sensations that cause irresistible restlessness. (Gossard et al., 2021) Restless leg syndrome (RLS) can also be primary or secondary depending on the severity of the issue affecting the individual’s legs. Since the legs allow the individual to be mobile through walking, running, and jumping, the various muscles and tendons that make up the legs can succumb to RLS. As it is a chronic movement disorder, it is common to many individuals. It is associated with abnormal, non-painful sensations that are active when a person rests and relieved when they are in motion. (Mansur et al., 2025) We associate with certified medical providers who inform our patients of how restless leg syndrome affects their legs. While asking important questions to our associated medical providers, we advise patients to incorporate ways to reduce restless leg syndrome and restore their sleep quality. Dr. Alex Jimenez, D.C., envisions this information as an academic service. Disclaimer.
Causes
What causes individuals to develop RLS can often be correlated with environmental factors. Additionally, since RLS can be primary or secondary, the overlapping risk profiles also play a factor. Environmental factors like stress and anxiety can cause the central nervous system to go haywire, causing the sensations to set off and become worse. When RLS is primary, the central nervous system can cause the legs to develop RLS by not getting enough dopamine, which is a neurotransmitter that regulates body movement. The RLS symptoms can worsen when there isn’t enough dopamine in the body. When RLS is secondary, it could be due to iron deficiency that the brain areas have low levels of iron being transported to the blood-brain barrier and not being imported to the neuronal cells. (Vlasie et al., 2022) This can cause numerous symptoms and affect the legs when a person is trying to get a good night’s rest.
Symptoms
Some of the symptoms associated with RLS can affect the circadian rhythm, which can cause the central nervous system to sensitize and hyperarousal, leading to sensory disturbances and frequent awakening periods. (Tang et al., 2023) Other symptoms include:
- Crawling/ Itching sensations
- Fatigue
- Mood changes
- Difficulty concentrating
- Sleep disruptions
Peripheral Neuropathy & Chiropractic Care-Video

Ways To Reduce Restless Leg Syndrome
When it comes to reducing restless leg syndrome, many people can find ways to minimize the comorbidities associated with RLS. Many people can sleep with the right mattress and pillows that can help provide them with a restful night. Others may try exercising or meditation to reduce the everyday stress that is affecting them. These small changes can help many people develop healthy sleeping habits that improve sleep quality and incorporate a proper sleeping routine. (Taximaimaiti et al., 2021)
Vitamins & Supplements
Incorporating iron supplements to reduce the effects of restless leg syndrome by replenishing the neurons and cells in the central nervous system. (Elstrott et al., 2020) Combined with magnesium, this can help lower the intensity of the RLS symptoms and even improve sleep quality. (Jadidi et al., 2022) Ask the doctor which iron supplement the body is low on before buying.
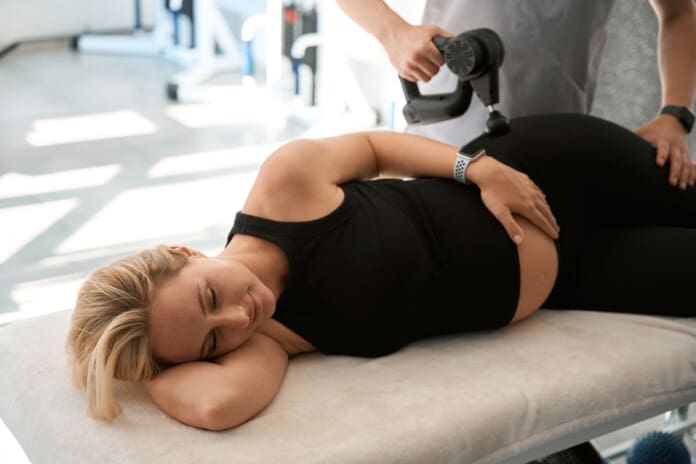
Massage
Incorporating massages as part of a routine to reduce restless leg syndrome can benefit the body. Massage therapists can work on the muscles in the lower extremities to manipulate the soft tissues while strengthening the immune system. Massages like reflexology, Swedish, and deep tissue can help reduce stress and anxiety, relieve leg fatigue, improve blood circulation, and reduce sleep disturbances. (Ghanbari et al., 2022)
Conclusion
Incorporating these various techniques and remedies to reduce restless leg syndrome can improve the body and increase sleep quality. Making small changes to these everyday stressors can reduce the chances of restless leg syndrome returning.
References
Elstrott, B., Khan, L., Olson, S., Raghunathan, V., DeLoughery, T., & Shatzel, J. J. (2020). The role of iron repletion in adult iron deficiency anemia and other diseases. Eur J Haematol, 104(3), 153-161. https://doi.org/10.1111/ejh.13345
Ghanbari, A., Shahrbabaki, P. M., Dehghan, M., Mardanparvar, H., Abadi, E. K. D., Emami, A., & Sarikhani-Khorrami, E. (2022). Comparison of the Effect of Reflexology and Swedish Massage on Restless Legs Syndrome and Sleep Quality in Patients Undergoing Hemodialysis: a Randomized Clinical Trial. Int J Ther Massage Bodywork, 15(2), 1-13. https://doi.org/10.3822/ijtmb.v15i2.705
Gossard, T. R., Trotti, L. M., Videnovic, A., & St Louis, E. K. (2021). Restless Legs Syndrome: Contemporary Diagnosis and Treatment. Neurotherapeutics, 18(1), 140-155. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13311-021-01019-4
Jadidi, A., Rezaei Ashtiani, A., Khanmohamadi Hezaveh, A., & Aghaepour, S. M. (2022). Therapeutic effects of magnesium and vitamin B6 in alleviating the symptoms of restless legs syndrome: a randomized controlled clinical trial. BMC Complement Med Ther, 23(1), 1. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12906-022-03814-8
Mansur, A., Castillo, P. R., Rocha Cabrero, F., & Bokhari, S. R. A. (2025). Restless Legs Syndrome. In StatPearls. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/28613628
Tang, M., Sun, Q., Zhang, Y., Li, H., Wang, D., Wang, Y., & Wang, Z. (2023). Circadian rhythm in restless legs syndrome. Front Neurol, 14, 1105463. https://doi.org/10.3389/fneur.2023.1105463
Taximaimaiti, R., Luo, X., & Wang, X. P. (2021). Pharmacological and Non-pharmacological Treatments of Sleep Disorders in Parkinson’s Disease. Curr Neuropharmacol, 19(12), 2233-2249. https://doi.org/10.2174/1570159X19666210517115706
Vlasie, A., Trifu, S. C., Lupuleac, C., Kohn, B., & Cristea, M. B. (2022). Restless legs syndrome: An overview of pathophysiology, comorbidities and therapeutic approaches (Review). Exp Ther Med, 23(2), 185. https://doi.org/10.3892/etm.2021.11108