Posture exercises: It is easy to get into the bad habit of poor/improper posture, especially at work where an individual gets into a groove and continues without thinking about their posture. Not until discomfort and pain begin to present do individuals start thinking about what is causing the issues. This usually includes:
- Back pain
- Shoulder pain
- Neck pain
- Tight/Compressed spine
They don’t realize that all these issues are brought on by prolonged sitting and practicing improper posture. Individuals that practice proper posture:
- Sleep better
- Move better
- Have reduced to no aches and pains
- Digestion improves
- Organ function improves
- Have better overall health
Being aware of proper posture is the first step in being able to maintain it. When you feel the spine starting to curve, shoulders hunching, or the back sway, stop and take a moment to reposition the body back into proper alignment.
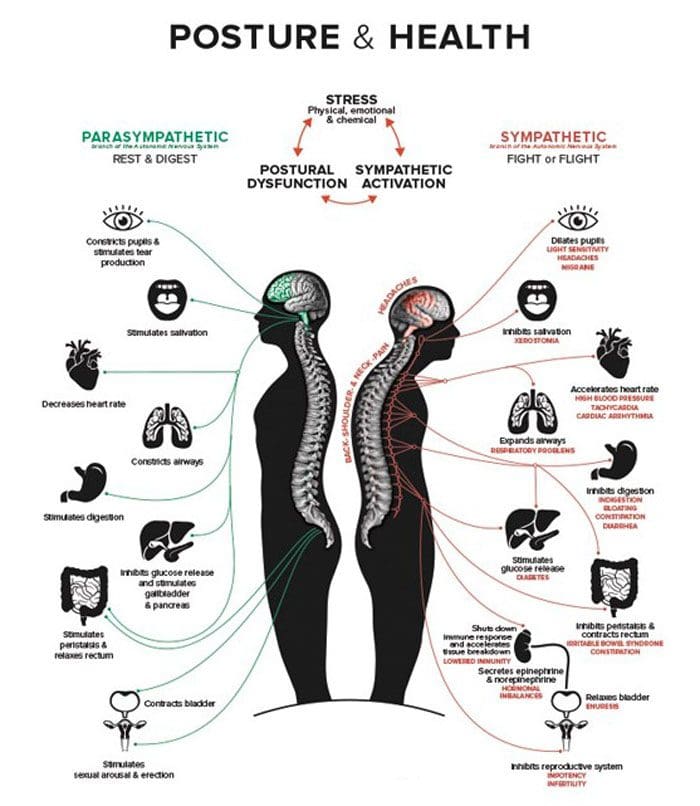
Table of Contents
Seated Posture
Proper posture means sitting, standing, or walking in a position with little to no strain on the body’s muscles and ligaments. Good seated position means:
- Sitting with the back straight and shoulders back.
- Having all of the natural curves of the spine in alignment.
- Keeping the knees bent at a right angle with the feet flat on the floor.
- The weight is distributed evenly to both hips.
- Keep the arms at 90 degrees to the torso, using the armrests or on a desk.
- When looking at a computer monitor, keep it at a position where you are looking straightforward.
- Use a chair with lower back support.
- Even when sitting with good posture, it’s important to avoid sitting in the same position for more than 30 minutes.
- Regularly stand up, walk around, and stretch out.
Posture Exercises
Posture exercises will help to strengthen the back, neck, and shoulders. They also help as a reminder for maintaining good posture throughout the day.
Shoulder Lift and Release
When sitting down for long periods, individuals tend to develop hunched shoulders. It is caused by an imbalance of muscles in the neck and upper back. Specific muscles in the neck, specifically the pectoralis major and minor, become shortened and tight. The other muscles in the upper back, the trapezius,latissimus dorsi, and rhomboids, weaken and stretch out. These muscles can be stimulated by stretching throughout the day.
- Sit in your chair with your feet flat on the floor and spine straight.
- Pull the shoulders up towards the ceiling.
- Hold them there for three to five seconds.
- Let the shoulders drop.
- It is recommended to repeat 5 to 6 times every hour.
Shoulder rolls
Another exercise for avoiding rounded/hunched shoulders.
- Sit in your chair with your feet flat on the floor and spine straight.
- Take a breath in.
- Lift the shoulders towards the ears.
- Move the shoulders back.
- Squeeze the shoulder blades together.
- On the exhale, finish the rotation by dropping the shoulders back to a neutral position.
- Repeat 5 to 6 times every hour.
- The exercise can be done in the opposite direction.
Neck rolls
Forward head posture, aka text neck, can develop. Neck rolls are recommended throughout the day.
- Lean your head towards the right shoulder.
- Relax the neck and let your head roll towards your chest.
- Continue rolling your head towards the left and up and around back to the starting position.
- Perform at least 3-4 neck rolls every few hours.
- Repeat the exercise and change direction.
Trapezius stretch
The trapezius is a major muscle group in the upper-middle section of the back and the neck. The trapezius is responsible for moving the shoulder blades and extending the neck. Stretching these muscles regularly will help maintain good posture.
- Sit in your chair with the spine straight and feet flat on the ground.
- Place the right hand over the top of your head.
- Gently pull your head towards the right shoulder.
- Perform one to three times for each side.
- Hold the pose for 30 to 60 seconds.
Arm rotations
This exercise can help maintain back and shoulder alignment. This can be performed sitting or standing.
- Stretch out the arms to the sides with palms facing downward.
- While keeping the spine straight, move the arms in small circles.
- Perform ten repetitions rotating the arms forward, then backward.
- Perform 3-4 sets.
Doing these posture exercises at your workstation regularly will help improve and maintain proper posture and minimize the risk of back, neck, and shoulder pain.
Body Composition
Fitness for Long-Term Health
Muscle building isn’t only for bodybuilders and athletes. Everyone can benefit from building their Lean Body Mass for long-term health. It is crucial to monitor Lean Body Mass changes by having body composition measured. Body composition analysis divides the body’s weight into various components.
- Fat Mass
- Lean Body Mass
- Basal Metabolic Rate
- This will give a clearer picture of overall fitness and health.
Building Lean Body Mass is an investment in the body’s future. The more LBM that is built, the more is in reserve when the body needs it. But before adding protein shakes and resistance workouts to the daily regimen, there needs to be a plan. The first step to building healthy lean body mass is to measure how much there is with a body composition analysis.
References
Biswas A, Oh PI, Faulkner GE, et al. Sedentary Time and Its Association With Risk for Disease Incidence, Mortality, and Hospitalization in Adults. Ann Intern Med. 2015;162:123-132. doi:10.7326/M14-1651. Accessed January 7, 2017.
Ergonomics for Prolonged Sitting. UCLA Spine Center Web site. http://spinecenter.ucla.edu/ergonomics-prolonged-sitting. Accessed January 7, 2017.
Florido R, Michos E. Sitting Disease: Moving Your Way to a Healthier Heart. U.S. News & World Report. http://health.usnews.com/health-news/patient-advice/articles/2015/09/14/sitting-disease-moving-your-way-to-a-healthier-heart. Published September 14, 2015. Accessed January 7, 2017.
Fortner, Miles O et al. “Treating ‘slouchy’ (hyperkyphosis) posture with chiropractic biophysics®: a case report utilizing a multimodal mirror image® rehabilitation program.” Journal of physical therapy science vol. 29,8 (2017): 1475-1480. doi:10.1589/jpts.29.1475
Levine JA. What are the risks of sitting too much? Mayo Clinic Web site. http://www.mayoclinic.org/healthy-lifestyle/adult-health/expert-answers/sitting/faq-20058005. Published September 4, 2015. Accessed January 7, 2017.
O’Connor B. Sitting Disease: The New Health Epidemic. The Chopra Center Web site. http://www.chopra.com/articles/sitting-disease-the-new-health-epidemic. Accessed January 7, 2017.
Wolfe, Robert R. “The underappreciated role of muscle in health and disease.” The American journal of clinical nutrition vol. 84,3 (2006): 475-82. doi:10.1093/ajcn/84.3.475