Polymyositis is a disease that causes the body’s muscles to become irritated and inflamed. It can affect the muscles all over the body. The muscles gradually begin to break down and weaken, making everyday movements difficult. This disease falls into a category known as inflammatory myopathies.
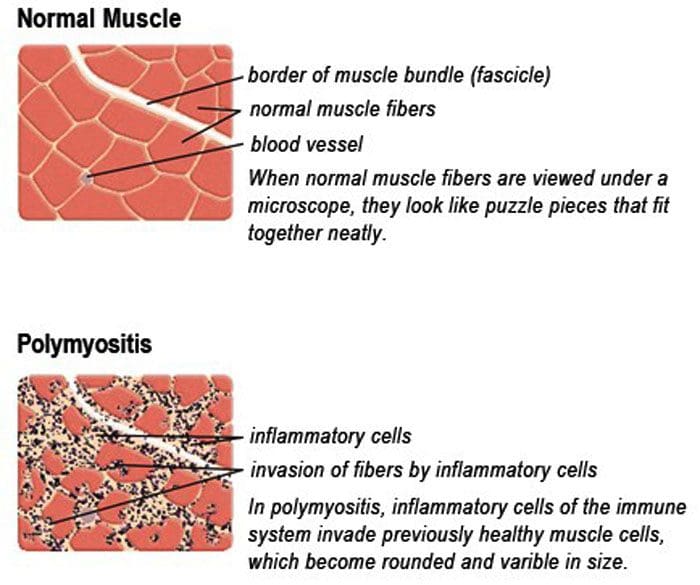
Table of Contents
Polymyositis Unknown Causation
The causes of polymyositis are currently unknown. However, experts believe it could be associated with or triggered by a virus or an autoimmune reaction. An autoimmune response is when the body attacks itself along with the body’s tissues. It’s seen in individuals ages 31 to 60 and is rarely seen in individuals younger than 18. In some instances, medication can lead to an allergic reaction/response that causes muscle irritation and damage. But in most cases, healthcare experts are not able to find the exact cause.
Symptoms
The condition can affect the muscles all over the body. Physical activities like walking, getting up from a chair, or lifting objects can become difficult to perform. It can also affect the muscles that allow for eating and breathing. The muscles at the center of the body tend to be affected the most. Common symptoms include:
- Muscle pain.
- Muscle stiffness.
- Muscle weakness, specifically in the abdomen, shoulders, upper arms, and hips.
- Joint pain and stiffness.
- Breathing problems.
- Problems swallowing.
- Abnormal weight loss can become an issue if there are problems with swallowing.
- Irregular heart rhythms if the heart muscle/myocardium becomes inflamed.
- Individuals may notice they have trouble climbing stairs or lifting their arms.
- The inflammation can worsen, causing pain and weakness that affects the wrists, lower arms, and ankles.
Diagnosis
Diagnosis begins with the individual’s medical history, family medical history if necessary, and a physical examination. The examination includes seeing and feeling the strength of the muscles. Tests will be required that include:
Blood Tests
- Blood tests allow the doctor to see if there are signs of muscle inflammation.
- They also show if there are abnormal proteins that form in autoimmune diseases.
Electromyogram EMG
- This test can be used to find abnormal electrical activity in the affected muscles.
MRI
- Magnets and computer graphic imagery are used to help the doctor inspect for inflammation in the body.
Muscle Biopsy
- A small piece of muscle tissue is removed to be analyzed with a microscope.
Treatment
Treatment depends on how severe the condition is, individual symptoms, age, and overall health. Currently, there is no cure for polymyositis, but symptoms can be managed. Individuals are recommended to utilize more than one type of treatment because the treatment plan may also need to be changed as treatment progresses. Treatments include:
Anti-inflammatory Medication
Steroid medication can help manage the disease and reduce symptoms, and corticosteroids can help ease inflammation in the body. The symptoms improve within 4 to 6 weeks, and a healthcare provider can lower the dosage after the symptoms decrease to reduce and ease any side effects.
Immunosuppressive Medication
- These medications block or slow down the body’s immune system responses.
- Talk with a doctor about the risks, benefits, and side effects of all medications.
Chiropractic and Physical therapy
- Chiropractic treatment and physical therapy can help:
- Aligning the spine to provide optimal nerve energy and blood circulation.
- Therapeutic massage to stimulate and keep the muscles loose.
- Specific exercises to help stretch and strengthen the muscles.
- These can help keep the muscles from shrinking.
Heat therapy and Rest
- Heat therapy and allowing the body to rest thoroughly can help decrease pain symptoms.
Special Braces
- Body, hip, and leg braces can help support the muscles and help with mobility.
Complications
Polymyositis left untreated can lead to severe complications. The muscles become weaker, increasing the risk of falling and limiting daily activities.
- If the chest muscles are affected, there could be problems with breathing that can lead to respiratory failure.
- If the digestive tract is affected, malnutrition and unintentional weight loss can result.
- Polymyositis poorly managed well can cause severe disability.
Body Composition
Nutrition and Muscle Growth
Protein
- Protein is the foundation for gaining muscle.
- This essential component is for all of the body’s daily functions.
- It is essential to balance protein increase with overall diet.
Complex Carbs
- Carbs are the body’s fuel source.
- Carbs should be a daily element of nutritional intake because they are the primary component.
- Acquiring energy
- Preventing muscle weakness and degradation
Consuming Carbs
- Understanding how accurate results only happen when both sides work together.
- Healthy consumption of protein and carbohydrates can help muscle growth and sustain optimal health for all body types.
References
Corrado, Bruno et al. “Supervised Physical Therapy and Polymyositis/Dermatomyositis-A Systematic Review of the Literature.” Neurology international vol. 12,3 77-88. 24 Nov. 2020, doi:10.3390/neurolint12030015
Findlay, Andrew R et al. “An overview of polymyositis and dermatomyositis.” Muscle & nerve vol. 51,5 (2015): 638-56. doi:10.1002/mus.24566
Sasaki, Hirokazu, and Hitoshi Kohsaka. “Current diagnosis and treatment of polymyositis and dermatomyositis.” Modern rheumatology vol. 28,6 (2018): 913-921. doi:10.1080/14397595.2018.1467257
Van Thillo, Anna et al. “Physical therapy in adult inflammatory myopathy patients: a systematic review.” Clinical rheumatology vol. 38,8 (2019): 2039-2051. doi:10.1007/s10067-019-04571-9
Professional Scope of Practice *
The information herein on "Polymyositis: Inflammatory Myopathy" is not intended to replace a one-on-one relationship with a qualified health care professional or licensed physician and is not medical advice. We encourage you to make healthcare decisions based on your research and partnership with a qualified healthcare professional.
Blog Information & Scope Discussions
Welcome to El Paso's Premier Wellness and Injury Care Clinic & Wellness Blog, where Dr. Alex Jimenez, DC, FNP-C, a Multi-State board-certified Family Practice Nurse Practitioner (FNP-BC) and Chiropractor (DC), presents insights on how our multidisciplinary team is dedicated to holistic healing and personalized care. Our practice aligns with evidence-based treatment protocols inspired by integrative medicine principles, similar to those found on this site and our family practice-based chiromed.com site, focusing on restoring health naturally for patients of all ages.
Our areas of multidisciplinary practice include Wellness & Nutrition, Chronic Pain, Personal Injury, Auto Accident Care, Work Injuries, Back Injury, Low Back Pain, Neck Pain, Migraine Headaches, Sports Injuries, Severe Sciatica, Scoliosis, Complex Herniated Discs, Fibromyalgia, Chronic Pain, Complex Injuries, Stress Management, Functional Medicine Treatments, and in-scope care protocols.
Our information scope is multidisciplinary, focusing on musculoskeletal and physical medicine, wellness, contributing etiological viscerosomatic disturbances within clinical presentations, associated somato-visceral reflex clinical dynamics, subluxation complexes, sensitive health issues, and functional medicine articles, topics, and discussions.
We provide and present clinical collaboration with specialists from various disciplines. Each specialist is governed by their professional scope of practice and their jurisdiction of licensure. We use functional health & wellness protocols to treat and support care for musculoskeletal injuries or disorders.
Our videos, posts, topics, and insights address clinical matters and issues that are directly or indirectly related to our clinical scope of practice.
Our office has made a reasonable effort to provide supportive citations and has identified relevant research studies that support our posts. We provide copies of supporting research studies upon request to regulatory boards and the public.
We understand that we cover matters that require an additional explanation of how they may assist in a particular care plan or treatment protocol; therefore, to discuss the subject matter above further, please feel free to ask Dr. Alex Jimenez, DC, APRN, FNP-BC, or contact us at 915-850-0900.
We are here to help you and your family.
Blessings
Dr. Alex Jimenez DC, MSACP, APRN, FNP-BC*, CCST, IFMCP, CFMP, ATN
email: [email protected]
Multidisciplinary Licensing & Board Certifications:
Licensed as a Doctor of Chiropractic (DC) in Texas & New Mexico*
Texas DC License #: TX5807, Verified: TX5807
New Mexico DC License #: NM-DC2182, Verified: NM-DC2182
Multi-State Advanced Practice Registered Nurse (APRN*) in Texas & Multi-States
Multi-state Compact APRN License by Endorsement (42 States)
Texas APRN License #: 1191402, Verified: 1191402 *
Florida APRN License #: 11043890, Verified: APRN11043890 *
Colorado License #: C-APN.0105610-C-NP, Verified: C-APN.0105610-C-NP
New York License #: N25929, Verified N25929
License Verification Link: Nursys License Verifier
* Prescriptive Authority Authorized
ANCC FNP-BC: Board Certified Nurse Practitioner*
Compact Status: Multi-State License: Authorized to Practice in 40 States*
Graduate with Honors: ICHS: MSN-FNP (Family Nurse Practitioner Program)
Degree Granted. Master's in Family Practice MSN Diploma (Cum Laude)
Dr. Alex Jimenez, DC, APRN, FNP-BC*, CFMP, IFMCP, ATN, CCST
My Digital Business Card
Licenses and Board Certifications:
DC: Doctor of Chiropractic
APRNP: Advanced Practice Registered Nurse
FNP-BC: Family Practice Specialization (Multi-State Board Certified)
RN: Registered Nurse (Multi-State Compact License)
CFMP: Certified Functional Medicine Provider
MSN-FNP: Master of Science in Family Practice Medicine
MSACP: Master of Science in Advanced Clinical Practice
IFMCP: Institute of Functional Medicine
CCST: Certified Chiropractic Spinal Trauma
ATN: Advanced Translational Neutrogenomics
Memberships & Associations:
TCA: Texas Chiropractic Association: Member ID: 104311
AANP: American Association of Nurse Practitioners: Member ID: 2198960
ANA: American Nurse Association: Member ID: 06458222 (District TX01)
TNA: Texas Nurse Association: Member ID: 06458222
NPI: 1205907805
| Primary Taxonomy | Selected Taxonomy | State | License Number |
|---|---|---|---|
| No | 111N00000X - Chiropractor | NM | DC2182 |
| Yes | 111N00000X - Chiropractor | TX | DC5807 |
| Yes | 363LF0000X - Nurse Practitioner - Family | TX | 1191402 |
| Yes | 363LF0000X - Nurse Practitioner - Family | FL | 11043890 |
| Yes | 363LF0000X - Nurse Practitioner - Family | CO | C-APN.0105610-C-NP |
| Yes | 363LF0000X - Nurse Practitioner - Family | NY | N25929 |
Dr. Alex Jimenez, DC, APRN, FNP-BC*, CFMP, IFMCP, ATN, CCST
My Digital Business Card