Can physical therapies help individuals with a Colles’ or wrist fracture?
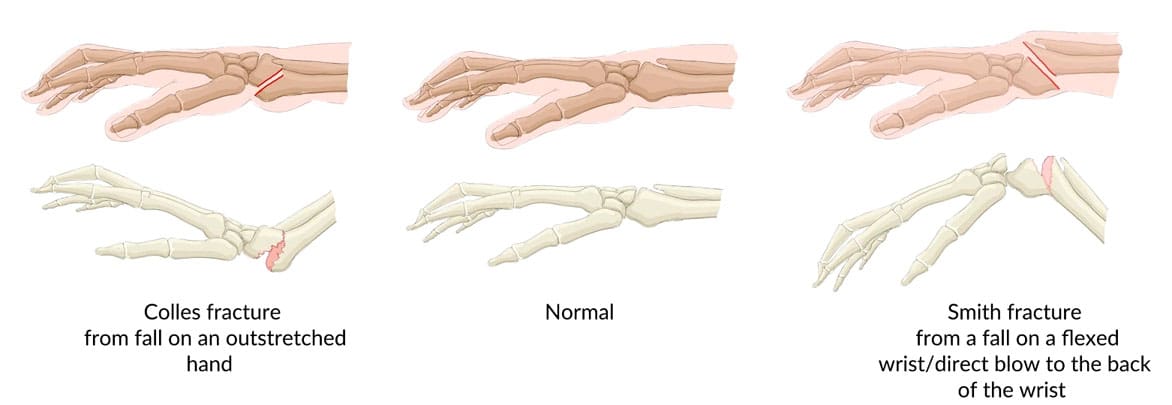
Table of Contents
Colles’ Fracture
A broken wrist or Colles fracture can be a painful and stressful experience. Individuals may be unable to perform their jobs or engage in recreational activities. A Colles fracture is a break in the radius bone of the forearm that occurs near the wrist, usually about an inch from the end of the bone. It’s a common type of broken wrist often caused by falling on an outstretched hand. (American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons, 2022) As the individual lands on their hand, the end of the radius bone breaks off and gets pushed toward the inner wrist. If the wrist is flexed when falling on the hand, the radius may break and move toward the front of the wrist. This is called a Smith’s fracture. (Matsuura, Y. et al., 2017) A physical therapy team can help improve functional mobility to quickly and safely return to normal activity.
Symptoms
Individuals who have suffered trauma to their wrist or have fallen onto their hand or wrist may have a Colles fracture. Common signs and symptoms of a wrist or Colles fracture include: (American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons, 2022)
- Bruising
- Loss of mobility in the wrist.
- Swelling in the arm, wrist, or hand.
- Pain
- Visible deformity or a lump on the backside of the forearm near the wrist.
Initial Treatment
Individuals who have fallen and injured their wrist and hand and suspect a Colles fracture seek immediate medical attention. Call a healthcare provider or report to a local emergency clinic. Left untreated, it can result in complications and permanent loss of arm and hand function. (American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons, 2022)
An X-ray will show a wrist fracture.
Because of the pain and swelling, it is recommended that individuals put an ice pack on their wrists and hands until they can get to a healthcare provider or emergency room. The R.I.C.E. principle can help control swelling and lessen pain until a medical professional can provide treatment. The initial treatment is to reduce the fracture. This is where a healthcare provider situates the broken bone or bones back into the correct position to ensure proper healing. This is done manually if the fractured bone is not too far out. If the fracture is severe, a surgical procedure known as an open reduction internal fixation or ORIF may be required to reduce the fracture. (American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons, 2022)
Once the fracture has been reduced, it must be immobilized. This is done with a cast or a brace. Individuals may also be required to wear a sling. They may need to visit a physical therapist to learn how to wear the sling properly. It is essential to keep the bones immobilized for proper healing. Consult a healthcare provider for questions about cast, sling, or brace.
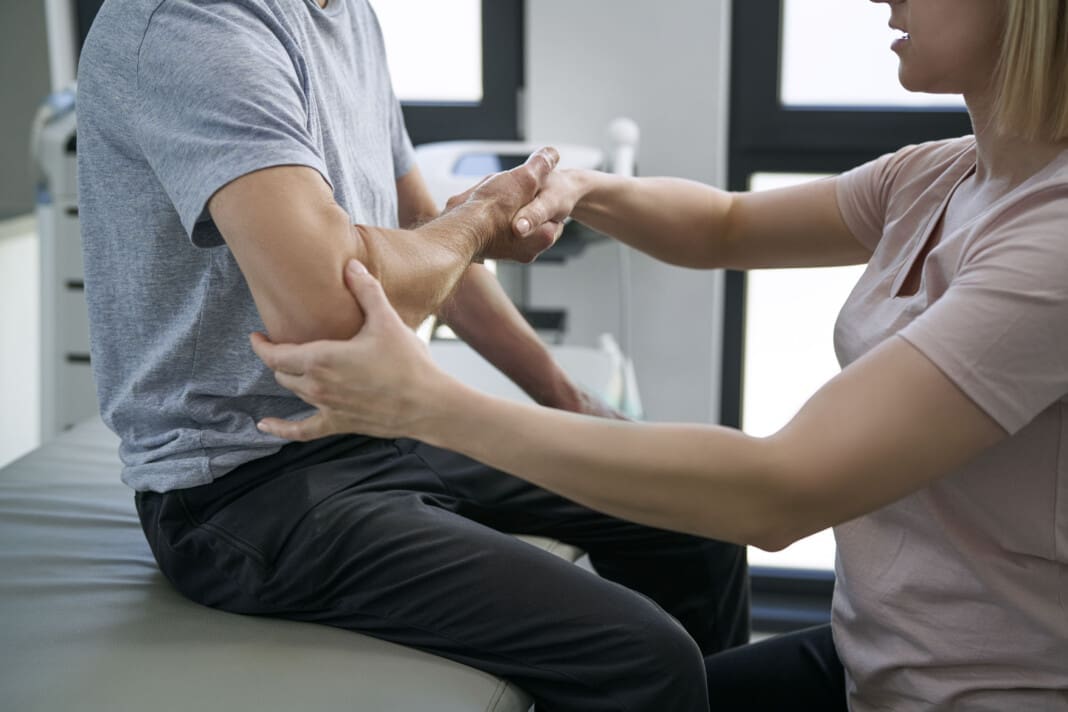
Physical Therapy
After four to six weeks of immobilization, a healthcare provider may remove the cast and refer a physical therapist or team. (American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons, 2022) A physical therapist may measure and evaluate pain, swelling, range of motion, and strengthening. The physical therapist may assess the surgical scar tissue and analyze the hand, wrist, and arm function of individuals who underwent an ORIF procedure to reduce the fracture. After the initial evaluation, a physical therapist will work with the patient to develop an appropriate plan of care to help improve the impairments and functional limitations. The therapist may prescribe a specific exercise program as well.
Pain and Swelling
- Individuals may experience pain and swelling around their wrists and hands.
- A physical therapist can provide individuals with various treatments and modalities to help decrease swelling and pain.
Range of Motion
- After a Colles’ fracture, individuals may lose hand, wrist, and elbow mobility.
- The shoulder may also be tight, especially after wearing a sling.
- Range of motion exercises for the hand, wrist, and elbow can be prescribed.
Strength
- Loss of strength is common after a Colles’ fracture.
- Exercises focusing on hand, wrist, and elbow strength may be prescribed.
- At-home exercises and stretches will get the best results from physical therapy.
Scar Tissue
- Individuals who have had an ORIF procedure will likely have scar tissue that has developed around the surgical site.
- A physical therapist may perform scar tissue massage and mobilization to help improve mobility and can train patients how to self-massage.
Injury Medical Chiropractic and Functional Medicine Clinic
After a few weeks of physical therapy, individuals should notice their mobility and strength improve while pain and swelling decrease. Individuals will find it easier to use their arms and hands to perform functional activities. While the fracture should be fully healed six to eight weeks after injury, individuals may still be limited for potentially 12 to 16 weeks. At Injury Medical Chiropractic and Functional Medicine Clinic, we focus on what works for every patient to restore function. If other treatment is needed, individuals will be referred to a clinic or physician best suited to their injury, condition, or ailment.
Personal Injury Rehabilitation
References
American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons. (2022). Distal radius fractures (broken wrist). https://orthoinfo.aaos.org/en/diseases–conditions/distal-radius-fractures-broken-wrist/
Matsuura, Y., Rokkaku, T., Kuniyoshi, K., Takahashi, K., Suzuki, T., Kanazuka, A., Akasaka, T., Hirosawa, N., Iwase, M., Yamazaki, A., Orita, S., & Ohtori, S. (2017). Smith’s fracture generally occurs after falling on the palm of the hand. Journal of orthopaedic research : official publication of the Orthopaedic Research Society, 35(11), 2435–2441. https://doi.org/10.1002/jor.23556
Professional Scope of Practice *
The information herein on "Colles' Fracture: Diagnosis and Treatment Options" is not intended to replace a one-on-one relationship with a qualified health care professional or licensed physician and is not medical advice. We encourage you to make healthcare decisions based on your research and partnership with a qualified healthcare professional.
Blog Information & Scope Discussions
Welcome to El Paso's Premier Wellness and Injury Care Clinic & Wellness Blog, where Dr. Alex Jimenez, DC, FNP-C, a Multi-State board-certified Family Practice Nurse Practitioner (FNP-BC) and Chiropractor (DC), presents insights on how our multidisciplinary team is dedicated to holistic healing and personalized care. Our practice aligns with evidence-based treatment protocols inspired by integrative medicine principles, similar to those found on this site and our family practice-based chiromed.com site, focusing on restoring health naturally for patients of all ages.
Our areas of multidisciplinary practice include Wellness & Nutrition, Chronic Pain, Personal Injury, Auto Accident Care, Work Injuries, Back Injury, Low Back Pain, Neck Pain, Migraine Headaches, Sports Injuries, Severe Sciatica, Scoliosis, Complex Herniated Discs, Fibromyalgia, Chronic Pain, Complex Injuries, Stress Management, Functional Medicine Treatments, and in-scope care protocols.
Our information scope is multidisciplinary, focusing on musculoskeletal and physical medicine, wellness, contributing etiological viscerosomatic disturbances within clinical presentations, associated somato-visceral reflex clinical dynamics, subluxation complexes, sensitive health issues, and functional medicine articles, topics, and discussions.
We provide and present clinical collaboration with specialists from various disciplines. Each specialist is governed by their professional scope of practice and their jurisdiction of licensure. We use functional health & wellness protocols to treat and support care for musculoskeletal injuries or disorders.
Our videos, posts, topics, and insights address clinical matters and issues that are directly or indirectly related to our clinical scope of practice.
Our office has made a reasonable effort to provide supportive citations and has identified relevant research studies that support our posts. We provide copies of supporting research studies upon request to regulatory boards and the public.
We understand that we cover matters that require an additional explanation of how they may assist in a particular care plan or treatment protocol; therefore, to discuss the subject matter above further, please feel free to ask Dr. Alex Jimenez, DC, APRN, FNP-BC, or contact us at 915-850-0900.
We are here to help you and your family.
Blessings
Dr. Alex Jimenez DC, MSACP, APRN, FNP-BC*, CCST, IFMCP, CFMP, ATN
email: [email protected]
Multidisciplinary Licensing & Board Certifications:
Licensed as a Doctor of Chiropractic (DC) in Texas & New Mexico*
Texas DC License #: TX5807, Verified: TX5807
New Mexico DC License #: NM-DC2182, Verified: NM-DC2182
Multi-State Advanced Practice Registered Nurse (APRN*) in Texas & Multi-States
Multi-state Compact APRN License by Endorsement (42 States)
Texas APRN License #: 1191402, Verified: 1191402 *
Florida APRN License #: 11043890, Verified: APRN11043890 *
Colorado License #: C-APN.0105610-C-NP, Verified: C-APN.0105610-C-NP
New York License #: N25929, Verified N25929
License Verification Link: Nursys License Verifier
* Prescriptive Authority Authorized
ANCC FNP-BC: Board Certified Nurse Practitioner*
Compact Status: Multi-State License: Authorized to Practice in 40 States*
Graduate with Honors: ICHS: MSN-FNP (Family Nurse Practitioner Program)
Degree Granted. Master's in Family Practice MSN Diploma (Cum Laude)
Dr. Alex Jimenez, DC, APRN, FNP-BC*, CFMP, IFMCP, ATN, CCST
My Digital Business Card
Licenses and Board Certifications:
DC: Doctor of Chiropractic
APRNP: Advanced Practice Registered Nurse
FNP-BC: Family Practice Specialization (Multi-State Board Certified)
RN: Registered Nurse (Multi-State Compact License)
CFMP: Certified Functional Medicine Provider
MSN-FNP: Master of Science in Family Practice Medicine
MSACP: Master of Science in Advanced Clinical Practice
IFMCP: Institute of Functional Medicine
CCST: Certified Chiropractic Spinal Trauma
ATN: Advanced Translational Neutrogenomics
Memberships & Associations:
TCA: Texas Chiropractic Association: Member ID: 104311
AANP: American Association of Nurse Practitioners: Member ID: 2198960
ANA: American Nurse Association: Member ID: 06458222 (District TX01)
TNA: Texas Nurse Association: Member ID: 06458222
NPI: 1205907805
| Primary Taxonomy | Selected Taxonomy | State | License Number |
|---|---|---|---|
| No | 111N00000X - Chiropractor | NM | DC2182 |
| Yes | 111N00000X - Chiropractor | TX | DC5807 |
| Yes | 363LF0000X - Nurse Practitioner - Family | TX | 1191402 |
| Yes | 363LF0000X - Nurse Practitioner - Family | FL | 11043890 |
| Yes | 363LF0000X - Nurse Practitioner - Family | CO | C-APN.0105610-C-NP |
| Yes | 363LF0000X - Nurse Practitioner - Family | NY | N25929 |
Dr. Alex Jimenez, DC, APRN, FNP-BC*, CFMP, IFMCP, ATN, CCST
My Digital Business Card