Herniated Disc
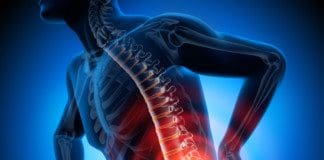
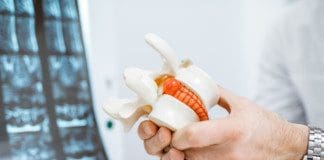
Herniated Disc: refers to a problem with one of the rubbery cushions (discs) between the individual bones (vertebrae) that stack up to make your spine.
A spinal disc has a soft center encased within a tougher exterior. Sometimes called a slipped disc or a ruptured disc, a herniated disc occurs when some of the soft centers push out through a tear in the tougher exterior.
A herniated disc can irritate the surrounding nerves which can cause pain, numbness or weakness. If a herniated disc irritates the sciatic nerve, it can ultimately cause sciatica or sciatic nerve pain. On the other hand, many people experience no symptoms from a herniated disk. Most people who have a herniated disc will not need surgery to correct the problem.
Symptoms
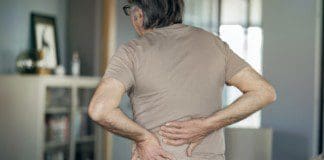
Most herniated disks occur in the lower back (lumbar spine), although they can also occur in the neck (cervical spine). Most common symptoms of a herniated disk:
Upper or lower extremity pain: A herniated disk in the lower back, typically an individual will feel the most intense pain in the buttocks, thigh, and calf, also referred to as sciatica or sciatic nerve pain. It may also involve part of the foot. If the herniated disc is in the neck, the pain will typically be most intense in the shoulder and arm. This pain may shoot into the arm or leg when coughing, sneezing or moving spine into certain positions.
Numbness or tingling: A herniated disk can feel like numbness or tingling in the body part served by the affected nerves.
Weakness: Muscles served by the affected nerves tend to weaken. This may cause stumbling or impair the ability to lift or hold items.
Someone can have a herniated disc without knowing. Herniated disks sometimes show up on spinal images of people who have no symptoms of a disc problem.